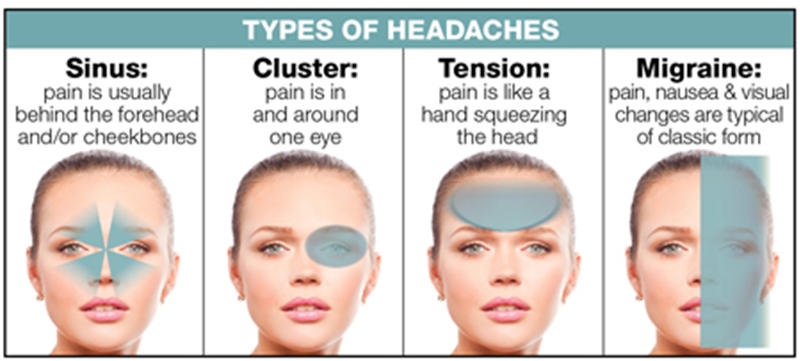
Topic best foods to eat with a headache: Discover the best foods to eat with a headache, offering natural relief and effective headache management through simple dietary changes. Unlock the power of nutrition for a healthier, headache-free life.
Table of Content
- What are the best foods to eat with a headache?
- Foods That May Help Relieve Headaches
- Understanding Caffeine"s Role in Headache Relief
- The Impact of Hydration on Headache Management
- Foods to Avoid: Triggers of Headaches and Migraines
- Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Migraine Prevention
- Benefits of Magnesium-rich Foods in Headache Relief
- Antioxidant-rich Berries for Sinus Pressure Relief
- YOUTUBE: Foods that Cause Headaches
- How Processed Meats Affect Headaches
- The Link Between Aged Cheeses and Migraines
- Understanding MSG and Its Impact on Migraines
- Artificial Sweeteners and Their Role in Triggering Migraines
- Citrus Fruits and Their Association with Migraines
What are the best foods to eat with a headache?
When experiencing a headache, there are several foods that can help alleviate the pain:
- Leafy greens: Spinach, Swiss chard, and other leafy greens are rich in magnesium, which can decrease or prevent migraines.
- Fresh fruits: Opt for brightly colored fruits that are high in antioxidants, such as berries, oranges, and kiwis.
- Low sodium foods: Consuming foods with low sodium levels can help reduce headache symptoms.
- Magnesium-rich foods: Besides leafy greens, other sources of magnesium include nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Foods like salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are rich in omega-3s, which may help alleviate headaches.
- Keto-friendly foods: For those following a ketogenic diet, foods like avocados, olive oil, and coconut oil can be beneficial.
- Caffeine: While excessive caffeine intake can trigger headaches, consuming small amounts or a cup of coffee may provide relief for some individuals.
It\'s important to note that individual results may vary, and it\'s recommended to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
READ MORE:
Foods That May Help Relieve Headaches
Discover a variety of foods that can naturally aid in headache relief. From hydrating options to nutrient-rich choices, these foods offer potential benefits for those suffering from headaches.
- Fortified Whole Grain Cereal: Rich in riboflavin (vitamin B2), which is known to help keep migraines at bay.
- Hot Peppers: Spicy foods like hot peppers can help decrease sinus pressure and pain, especially in headaches caused by congestion.
- Pumpkin Seeds: A great source of magnesium, which helps in relaxing blood vessels and preventing head pain.
- Oatmeal & Brown Rice: These complex carbohydrates can maintain steady blood sugar levels, thus preventing headaches.
- Chocolate: Particularly dark chocolate, contains caffeine and magnesium, both known to aid in easing caffeine withdrawal headaches.
- Berries: High in antioxidants, berries like blueberries and strawberries can help relieve sinus pressure.
- Mushrooms: Known to improve gut health, which can be beneficial in preventing migraines.
- Water: Staying hydrated is crucial. Aim for 6-8 glasses per day and include electrolytes for better hydration.
- Coffee: In small amounts, it can help with headaches due to its vasodilating properties.
- Salad with Protein: Balanced meals with protein and vegetables help in maintaining blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of headaches.

Understanding Caffeine"s Role in Headache Relief
Caffeine"s relationship with headaches is complex and multifaceted. It can both alleviate and trigger headaches, depending on individual sensitivity and consumption habits. Here we explore how caffeine affects headaches and ways to use it effectively for relief.
- Caffeine as a Headache Reliever: In moderate amounts, caffeine has pain-relieving properties. It helps by narrowing the blood vessels surrounding the brain. When these vessels dilate, they can cause headaches.
- Caffeine in Medication: Caffeine is a common ingredient in many over-the-counter headache medications. It enhances the effectiveness of pain relievers like acetaminophen and aspirin.
- Caffeine Withdrawal Headaches: Regular consumption of caffeine can lead to dependence. Abrupt cessation can cause withdrawal symptoms, including severe headaches.
- Balancing Caffeine Intake: It"s important to balance caffeine consumption. Avoiding excessive or too little caffeine can help manage headache frequency and intensity.
- Caffeine Sources: Coffee, tea, chocolate, and some soft drinks contain caffeine. The key is consuming these in moderation and observing how your body responds.
- Individual Sensitivity: Sensitivity to caffeine varies. Some may find relief from a small amount of coffee, while others might experience headaches even with minimal caffeine intake.
- Alternatives to Caffeine: For those sensitive to caffeine, considering alternatives like decaffeinated drinks or herbal teas can be beneficial.
- Caffeine and Hydration: While consuming caffeine, maintaining hydration is crucial as caffeine has diuretic properties, which can contribute to dehydration-related headaches.
The Impact of Hydration on Headache Management
Staying adequately hydrated is crucial in managing headaches. Dehydration can trigger headaches, making hydration an essential part of headache prevention and relief. Here we explore how proper hydration impacts headache management.
- Importance of Water: Drinking enough water is fundamental. Dehydration is a known headache trigger, so maintaining hydration can reduce or prevent headaches.
- Electrolyte Balance: Alongside water, maintaining a balance of electrolytes is important. Electrolyte imbalances can contribute to headaches. Consider drinks or foods that replenish electrolytes.
- Hydration with Meals: Consuming water-rich foods like cucumbers or watermelon can contribute to overall hydration.
- Monitoring Hydration Levels: Pay attention to signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth, fatigue, or dark urine, which can be precursors to headaches.
- Avoiding Dehydration Headaches: Regular intake of fluids throughout the day is essential. Carrying a water bottle can be a helpful reminder to stay hydrated.
- Role of Diet in Hydration: A balanced diet including fruits and vegetables, which have high water content, can aid in maintaining hydration.
- Caffeine and Hydration: Be mindful of caffeine intake as it can cause dehydration. Moderating coffee and tea consumption is advised for those prone to dehydration headaches.

Foods to Avoid: Triggers of Headaches and Migraines
Identifying and avoiding food triggers is crucial for managing headaches and migraines. While individual sensitivities vary, certain foods are commonly recognized as potential triggers. Here"s a guide to foods you might consider avoiding.
- Caffeine: Excessive caffeine can lead to headaches, and abrupt cessation might cause withdrawal headaches. Moderation is key.
- Tyramine-Rich Foods: Foods high in tyramine, like aged cheeses and certain meats, can trigger migraines in some individuals.
- Processed Meats: These often contain preservatives like nitrates, which can trigger headaches.
- Alcohol: Especially red wine and beer, which are known to be common triggers for migraines.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Aspartame and other artificial sweeteners can be potential headache triggers.
- Monosodium Glutamate (MSG): A flavor enhancer found in many processed foods, MSG can trigger headaches in sensitive individuals.
- Chocolate: For some, chocolate can trigger migraines, likely due to its caffeine and other compounds.
- Citrus Fruits: These might trigger migraines in certain individuals, possibly due to specific compounds they contain.
- Extremely Hot or Cold Foods: Consuming foods at extreme temperatures may trigger headaches in some people.
Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Migraine Prevention
Omega-3 fatty acids are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can play a significant role in preventing and managing migraines. This section explores the benefits of omega-3s for those susceptible to migraines.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Omega-3 fatty acids help reduce inflammation, a contributing factor in migraine development.
- Sources of Omega-3s: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources. Plant-based options include flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Omega-3s and Vascular Health: These fatty acids support vascular health, potentially reducing the frequency and severity of migraines.
- Recommended Intake: Incorporating omega-3 rich foods into your diet regularly can be beneficial. Supplements are also available, but food sources are preferred.
- Omega-3s in Balanced Diets: A balanced diet including omega-3s can contribute to overall health, which is crucial for migraine prevention.
- Research on Omega-3s and Migraines: Studies suggest that increased omega-3 intake may reduce migraine occurrences, but more research is needed to fully understand this relationship.
- Combining Omega-3s with Other Nutrients: Pairing omega-3s with other migraine-preventive nutrients, such as magnesium and riboflavin, can be more effective.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Migraine-Prevention-Diet_Danie-Drankwalter_Final-897f52ce800c43988733830362e92859.jpg)
Benefits of Magnesium-rich Foods in Headache Relief
Magnesium, a vital mineral, plays a key role in headache relief, particularly for migraines. This section explores how incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet can help manage and prevent headaches.
- Magnesium"s Role: Magnesium helps in relaxing blood vessels, which can prevent the constriction that often leads to headaches.
- Sources of Magnesium: Foods rich in magnesium include dark chocolate, pumpkin seeds, almonds, and leafy greens like spinach.
- Recommended Intake: Incorporating these foods into your daily diet can help meet your magnesium needs and reduce headache occurrences.
- Magnesium for Muscle Relaxation: This mineral also aids in muscle relaxation, potentially reducing tension-related headaches.
- Magnesium and Brain Function: Essential for many biochemical reactions, magnesium supports overall brain health, which is crucial in managing headaches.
- Combating Magnesium Deficiency: A deficiency in magnesium can contribute to headaches, making it important to maintain adequate levels.
Antioxidant-rich Berries for Sinus Pressure Relief
Berries, known for their high antioxidant content, can be particularly effective in relieving sinus pressure, a common cause of headaches. This section delves into how including berries in your diet can aid in alleviating sinus-related headaches.
- Types of Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, blackberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and sinus pressure.
- Organic Options: Opting for organic berries can be beneficial as they tend to have less exposure to pesticides.
- How Berries Help: The antioxidants in berries can alleviate sinus pressure over time, thus reducing the occurrence of headaches.
- Incorporating Berries in Diet: Berries can be added to cereals, yogurts, or enjoyed as a healthy snack to reap their benefits.
- Combination with Other Foods: Pairing berries with other anti-inflammatory foods can enhance their effectiveness in relieving headaches.

Foods that Cause Headaches
Are you tired of dealing with constant headaches? Discover effective strategies and natural remedies to alleviate your pain and regain control of your life. Click here to watch the video and say goodbye to headaches for good!
How Processed Meats Affect Headaches
Processed meats can potentially contribute to the occurrence of headaches and migraines due to certain ingredients they contain. This section discusses how and why processed meats might trigger headaches.
- Preservatives in Processed Meats: Many processed meats contain preservatives like nitrates and nitrites, which can dilate blood vessels and potentially trigger headaches.
- Tyramine Content: Processed meats often have high levels of tyramine, a natural by-product of protein breakdown that can affect headache susceptibility.
- Individual Sensitivity: Sensitivity to the compounds in processed meats varies from person to person, affecting how likely they are to cause headaches.
- Alternatives to Processed Meats: Considering less processed meat options or plant-based proteins may help reduce headache occurrences.
- Monitoring Intake: Being mindful of the quantity and frequency of processed meat consumption can be beneficial in managing headache frequency.
- Migraine Triggers: For individuals prone to migraines, limiting intake of processed meats may help in reducing the frequency of migraine attacks.
Top 6 Foods for Headache Relief - Best Foods for Migraine Relief
Seeking relief from aches and discomfort? Explore this incredible video that shares simple yet powerful techniques to find relief and restore harmony in your body. Don\'t miss out on the opportunity to experience a life free from unnecessary suffering. Watch now!
The Link Between Aged Cheeses and Migraines
Aged cheeses are known to be potential triggers for migraines in some individuals. This section explores why certain cheeses might induce headaches and what to consider for migraine prevention.
- Tyramine Content: Aged cheeses contain tyramine, a natural by-product of protein breakdown, which is known to trigger migraines in some people.
- Examples of Aged Cheeses: Common aged cheeses include blue cheese, cheddar, gorgonzola, and parmesan.
- Individual Sensitivity: Sensitivity to tyramine varies; some may experience migraines after consuming aged cheeses, while others may not.
- Alternative Cheese Options: Considering cheeses with lower tyramine content, such as cottage cheese or cream cheese, might be beneficial.
- Migraine Management: For those prone to migraines, monitoring and possibly reducing the intake of aged cheeses can help manage symptoms.
- Keeping a Food Diary: Tracking your diet and headache patterns can help determine if aged cheeses are a trigger for your migraines.

Understanding MSG and Its Impact on Migraines
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG), a common food additive, has been linked to migraine headaches in some individuals. This section explores the connection between MSG and migraines, and how to manage this trigger.
- MSG as a Trigger: MSG can cause rapid expansion of blood vessels, which is a contributing factor in migraine headaches.
- Sources of MSG: Often found in processed foods, fast food, canned vegetables, soups, and processed meats.
- Identifying MSG in Foods: MSG can be labeled under various names, making it important to read food labels carefully.
- Individual Sensitivity: Sensitivity to MSG varies among individuals. Those who are sensitive may experience migraines after consumption.
- Managing MSG Intake: Reducing or eliminating foods containing MSG can help manage migraine symptoms in sensitive individuals.
- Natural Alternatives: Using natural flavor enhancers like herbs and spices can be a good alternative to MSG.
Artificial Sweeteners and Their Role in Triggering Migraines
Artificial sweeteners, particularly aspartame, have been linked to migraines in some individuals. This section examines the potential impact of artificial sweeteners on migraine sufferers and provides guidance on managing this trigger.
- Aspartame and Headaches: Aspartame, found in many diet sodas and sugar-free products, can cause headaches and migraines in sensitive individuals.
- Chemical Sensitivity: Some people may have a sensitivity to the chemicals in artificial sweeteners, leading to migraine attacks.
- Identifying Triggers: Keeping a food diary can help identify if artificial sweeteners are a trigger for your migraines.
- Alternatives to Artificial Sweeteners: Natural sweeteners like stevia or honey can be used as alternatives, but individual responses can vary.
- Reading Labels: Being vigilant about reading food labels can help avoid unintended consumption of artificial sweeteners.
- Consulting Healthcare Providers: If you suspect artificial sweeteners are triggering your migraines, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.

READ MORE:
Citrus Fruits and Their Association with Migraines
Citrus fruits, while healthy, can be potential triggers for migraines in some individuals. This section delves into the relationship between citrus fruits and migraine occurrence, helping to understand how these fruits might affect migraine sufferers.
- Citrus Fruits as Migraine Triggers: For some, citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits may induce migraines due to specific compounds they contain.
- Chemical Composition: Certain chemicals in citrus fruits, possibly related to their strong aromas and flavors, might trigger migraines in sensitive individuals.
- Individual Variability: Not everyone experiences migraines from citrus fruits. Sensitivity varies greatly among individuals.
- Monitoring Reactions: Keeping a food diary can help in identifying whether citrus fruits are a migraine trigger for you.
- Alternative Fruit Options: If citrus fruits trigger migraines, consider other fruits like apples or berries that are less likely to cause headaches.
Exploring the right foods can significantly ease headache discomfort. Remember, individual responses vary, so listen to your body and choose foods that support your wellbeing, paving the way for a healthier, headache-free lifestyle.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/spicy-foods-that-help-fight-congestion-3877348_final-75083860f0a1490fbbd8dd50c2e68f68.png)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Getting-Rid-of-a-Migraine_Illustrator_Ellen-Lindner_Final-a245985cbf4645a7874d573991fb6cbb.jpg)