Topic period headache won't go away: Struggling with a period headache that won"t go away? Discover effective strategies for relief and prevention in this comprehensive guide, designed to help you navigate through the pain with ease and confidence.
Table of Content
- How to get rid of a period headache that won\'t go away?
- What Causes Period Headaches and How Hormones Play a Role
- Identifying Your Headache: Is It a Menstrual Migraine?
- Effective Home Remedies for Managing Period Headaches
- When to See a Doctor: Signs Your Headache Needs Medical Attention
- Preventative Strategies and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Medications and Treatments: From Over-the-Counter to Prescription Options
- YOUTUBE: How to Deal with Menstrual Migraines
- Understanding Hormonal Contraceptives" Role in Headache Management
- Navigating Headaches During Menopause and Perimenopause
- Exploring Hormone Replacement Therapy and Its Effects on Headaches
- Keeping a Headache Diary: A Tool for Identifying Patterns and Triggers
How to get rid of a period headache that won\'t go away?
Dealing with a period headache that won\'t go away can be frustrating, but there are steps you can take to find relief. Here is a step-by-step approach to help you manage and alleviate the pain:
- Identify triggers: Keep a headache diary to track when your period headaches occur and any potential triggers such as certain foods, stress, lack of sleep, or hormonal changes. This can help you identify patterns and make necessary lifestyle changes.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Engage in stress-reducing activities like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. These relaxation techniques can help alleviate tension in your body and relieve headache symptoms.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can worsen headache symptoms. Make sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during your period.
- Consider over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen sodium can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation associated with period headaches. Follow the instructions on the packaging and consult a healthcare professional if needed.
- Apply heat or cold therapy: Using a heating pad or a cold compress can provide relief by relaxing tense muscles or numbing the area. Experiment to see which option works best for you.
- Try natural remedies: Some individuals find relief from period headaches through alternative remedies. These may include acupuncture, herbal supplements, or essential oils. It\'s important to consult a healthcare professional before trying any new treatments.
- Ensure proper sleep: Aim for a regular sleep schedule and create a sleep-friendly environment that promotes deep restful sleep. Sufficient sleep can help reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches.
- Consider hormonal birth control: If period headaches persist and significantly impact your quality of life, consult with a healthcare professional about hormonal birth control options. Certain contraceptives may regulate hormone levels and reduce the occurrence of period-related headaches.
Remember, it\'s essential to consult with a healthcare professional if your period headaches are severe, interfere with your daily activities, or if you experience other concerning symptoms. They can provide a more tailored approach and offer guidance specific to your case.
READ MORE:
What Causes Period Headaches and How Hormones Play a Role
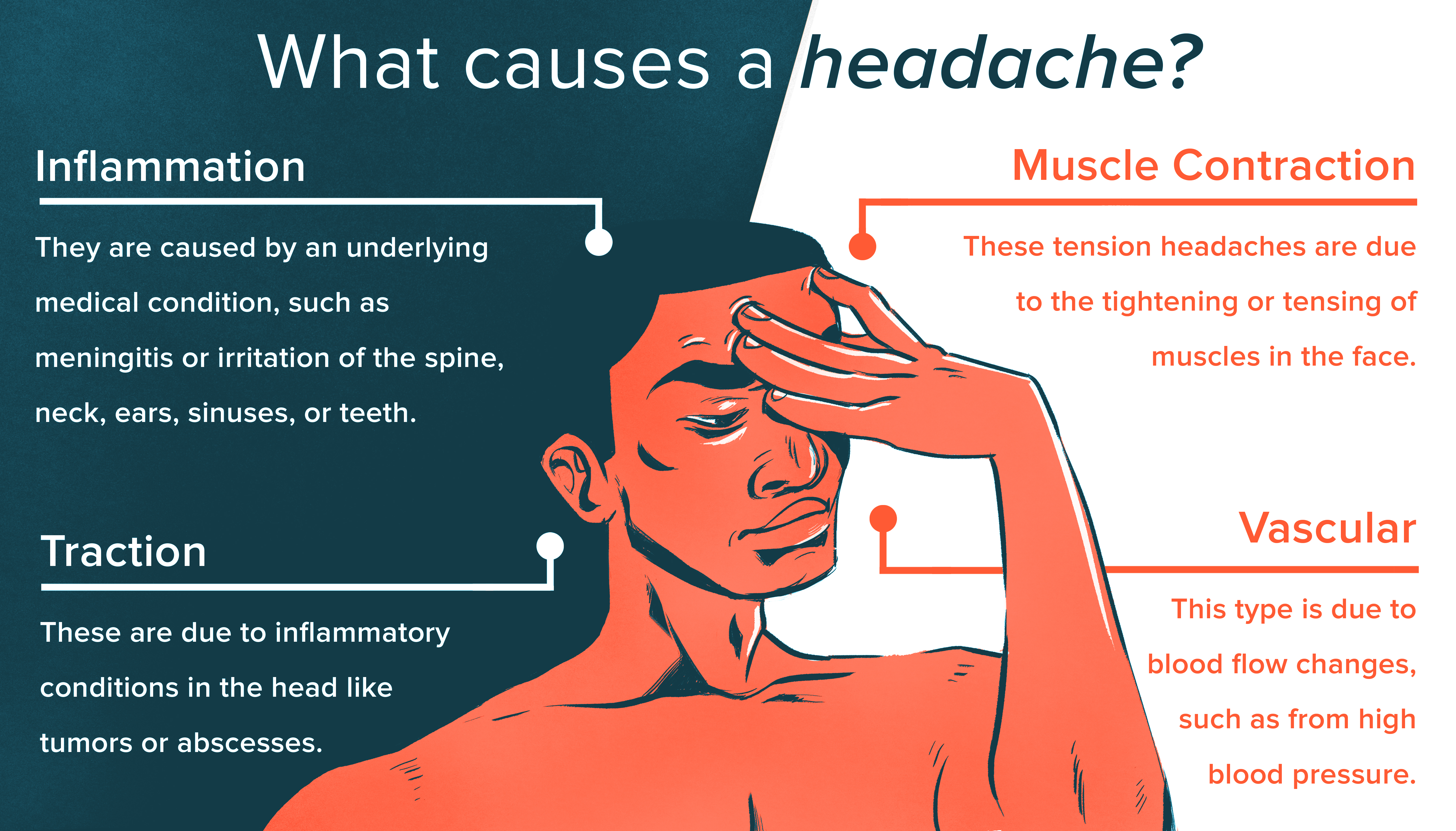
Period headaches, often experienced before, during, or after a menstrual cycle, are primarily influenced by hormonal fluctuations in the body. The rapid change in estrogen levels is a significant trigger, affecting how brain chemicals that are responsible for headache response behave. Here"s a closer look at the interplay between hormones and period headaches:
- Estrogen Drop: Just before menstruation, levels of estrogen drop sharply, leading to headaches for many women. This decrease can affect various bodily functions, including the regulation of pain sensation.
- Prostaglandins Role: During menstruation, the body produces prostaglandins, chemicals that cause inflammation and pain, contributing to the severity of headaches.
- Menstrual Migraines: For some, this hormonal shift can trigger menstrual migraines, a more severe form of headache that can last for several days. These migraines are often without aura and can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
Besides hormonal changes, other factors may contribute to period headaches, such as stress, dehydration, lack of sleep, and dietary triggers. Understanding these factors can help in managing and potentially reducing the frequency and severity of headaches associated with your period.

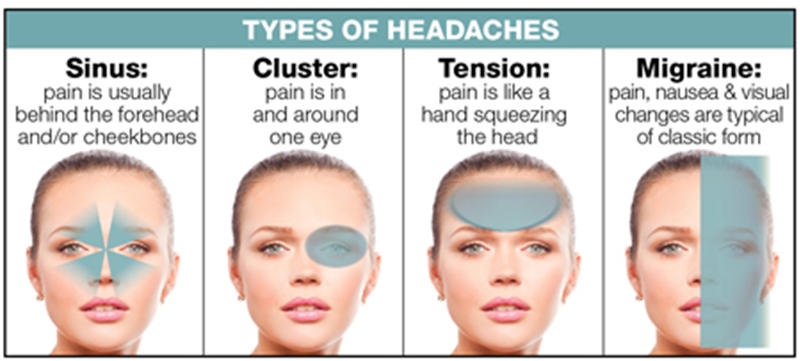
Identifying Your Headache: Is It a Menstrual Migraine?
Understanding whether your headache is a menstrual migraine is crucial for finding the right treatment and relief strategies. Menstrual migraines are specifically linked to the menstrual cycle and present unique symptoms that distinguish them from other headaches. Here’s how you can identify a menstrual migraine:
- Timing: Menstrual migraines typically occur in the days leading up to your period or during menstruation, a result of the drop in estrogen levels.
- Symptoms: These migraines often come without an aura and include symptoms such as intense throbbing pain on one side of the head, nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound.
- Duration: They can last longer than other migraines, sometimes extending over several days, and may be more resistant to typical migraine treatments.
- Severity: The pain is usually moderate to severe and can significantly impact daily activities.
To accurately diagnose menstrual migraines, keeping a headache diary can be incredibly helpful. Note the timing, symptoms, and duration of your headaches, as well as any potential triggers you"ve encountered. This information is vital for your healthcare provider to make an accurate diagnosis and recommend the best treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Effective Home Remedies for Managing Period Headaches
When a period headache strikes, turning to home remedies can offer significant relief without the need for medication. These natural strategies can help manage the discomfort and pain associated with period headaches. Here are some effective home remedies:
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can trigger headaches. Drinking plenty of water can help prevent or alleviate headache pain.
- Magnesium-rich Foods: Consuming foods high in magnesium, such as almonds, spinach, and bananas, can help reduce the frequency of headaches.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can reduce the severity and frequency of headaches by improving overall health and reducing stress.
- Essential Oils: Applying lavender or peppermint essential oil to the temples can provide soothing relief from headache pain.
- Yoga and Meditation: Stress is a common trigger for headaches. Yoga and meditation can help reduce stress levels, which may in turn reduce the frequency of headaches.
- Adequate Sleep: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule can help prevent headaches. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Warm Compress or Bath: Applying a warm compress to the neck and shoulders or taking a warm bath can help relax muscles and reduce headache pain.
These remedies can be easily incorporated into your daily routine to help manage period headaches. However, if your headaches are severe or persistent, it"s important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/iron-deficiency-anemia-and-migraines-4111553_final-470634aa9faf4a2585d7a9571ac1dfa8.jpg)
When to See a Doctor: Signs Your Headache Needs Medical Attention
While many period-related headaches can be managed with home remedies and over-the-counter medications, there are instances when a headache warrants medical attention. Recognizing the signs that differentiate a routine headache from one that may require a doctor"s evaluation is essential for your health and well-being. Here are the key indicators that suggest your headache needs professional assessment:
- Persistent or Severe Pain: If your headache doesn"t improve with standard treatments like hydration, rest, and over-the-counter pain relievers, or if the pain is severe and debilitating, it"s time to consult a healthcare provider.
- Changes in Headache Patterns: A sudden change in the frequency, severity, or characteristics of your headaches is a red flag. This includes headaches that feel different, are more intense, or occur more often than your typical period headaches.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Headaches that come with new or unusual symptoms such as vision changes, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of consciousness, or difficulty speaking should prompt an immediate medical consultation.
- Impact on Daily Life: If your headache is impacting your ability to carry out daily activities, attend work or school, or if it"s significantly affecting your quality of life, seeking medical advice is advisable.
- Neurological Symptoms: Symptoms such as confusion, seizures, numbness, or weakness in any part of the body alongside a headache are serious and require prompt medical attention.
- Headache after Head Injury: A headache that develops after a head injury, even a minor one, can be a sign of a concussion or other serious condition and should be evaluated by a professional immediately.
- Worsening Despite Medication: If your headache worsens or doesn"t respond to the medications you usually take for period-related headaches, this could indicate an underlying issue that needs medical evaluation.
Listening to your body and understanding these warning signs can help you determine when to seek professional help. Early intervention by a healthcare provider can prevent complications, provide relief, and ensure proper management of your headaches.
Preventative Strategies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Managing period headaches involves more than just treating symptoms as they arise. By incorporating preventative strategies and making certain lifestyle adjustments, you can reduce the frequency, severity, and duration of headaches associated with your menstrual cycle. Consider these proactive measures to help prevent period headaches:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can help reduce the intensity and frequency of headaches. Exercise promotes overall well-being and stress reduction, which are beneficial for headache management.
- Stress Management: Stress is a common trigger for headaches. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels and reduce the likelihood of stress-induced headaches.
- Adequate Hydration: Dehydration can trigger headaches. Maintaining a consistent intake of water throughout the day can prevent dehydration-related headaches.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and may help prevent headaches. Avoiding foods and drinks that are known to trigger headaches, such as those high in caffeine, sugar, and processed ingredients, is also advisable.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Poor sleep or changes in sleep patterns can trigger headaches. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night and try to go to bed and wake up at the same times every day, even on weekends.
- Limited Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol can lead to headaches. Moderating your intake of these substances can help prevent headaches.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can trigger headaches and worsen headache symptoms. Quitting smoking is an important step in preventing headaches.
- Magnesium Supplements: Some studies suggest that magnesium deficiency may be linked to headaches. Taking a magnesium supplement, after consulting with your healthcare provider, may help reduce the frequency of headaches.
Implementing these strategies may not only help in preventing period headaches but also contribute to an overall healthier lifestyle. It"s important to remember that changes may take time to show effects, and what works for one person may not work for another. Therefore, it may be helpful to try different approaches to see what best helps you manage and prevent your period headaches.
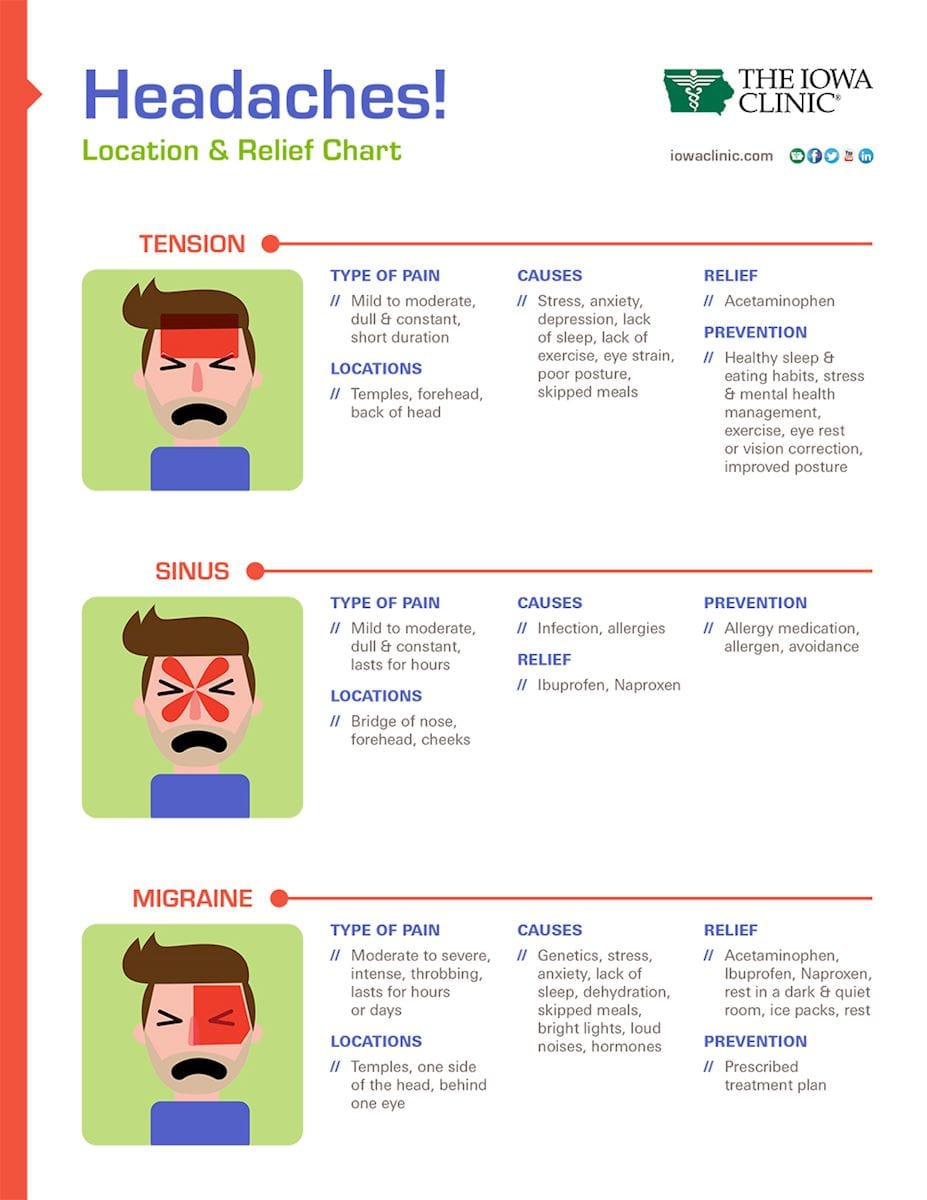
Medications and Treatments: From Over-the-Counter to Prescription Options
When it comes to managing period headaches, a variety of medications and treatments are available, ranging from over-the-counter (OTC) options to prescription medications. Understanding the various choices can help you find the most effective relief for your symptoms. Here"s an overview of common medications and treatments for period headaches:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: OTC medications such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve), and acetaminophen (Tylenol) can be effective for relieving mild to moderate headache pain. These should be used as directed on the package or by a healthcare provider.
- Triptans: For more severe menstrual migraines, prescription triptans can be effective. Triptans work by narrowing blood vessels and blocking pain pathways in the brain. Examples include sumatriptan (Imitrex) and rizatriptan (Maxalt). They are specifically designed for migraine relief and should be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Anti-Nausea Medications: For those who experience nausea or vomiting with their headaches, anti-nausea medications can be prescribed alongside pain relief medication to help manage these symptoms.
- Preventive Medications: If you experience frequent, severe headaches, your doctor might recommend preventive medications. These can include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antidepressants, or anticonvulsants, which are taken regularly to reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
- Non-Medication Therapies: Alongside or instead of medication, treatments such as biofeedback, acupuncture, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help manage headache pain and frequency. These therapies aim to reduce stress and improve pain management skills.
- Hormonal Treatments: Since hormonal fluctuations often trigger period headaches, hormonal contraceptives or hormone therapy might be recommended to help stabilize hormone levels and reduce headache occurrences.
- Magnesium Supplements: As mentioned earlier, magnesium supplements may help prevent migraines in some individuals, especially if they have a magnesium deficiency. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
It"s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication or treatment for period headaches. They can help determine the most appropriate options based on your individual health profile and headache characteristics. Remember, managing period headaches often requires a combination of treatments tailored to your specific needs.
How to Deal with Menstrual Migraines
Experience relief from menstrual migraines with this informative video! Learn about the potential triggers and effective strategies to manage and prevent these debilitating headaches. Don\'t let menstrual migraines hold you back - find empowerment and freedom by watching this video now!
Migraine: A Neurological Condition That\'s Not Just in Your Head
Discover valuable insights and solutions for living with a neurological condition in this engaging video. Uncover the latest research, treatment options, and practical tips to enhance your quality of life. Gain a better understanding of your condition and find hope for a brighter future by watching this video today!
Understanding Hormonal Contraceptives" Role in Headache Management
Hormonal fluctuations are a common trigger for headaches and migraines, particularly those associated with the menstrual cycle. Hormonal contraceptives, which work by regulating or altering hormone levels, can play a significant role in managing and sometimes preventing these headaches. Understanding how these contraceptives impact headache patterns can help you make informed decisions about your headache management strategy.
- Estrogen and Progesterone: Most hormonal contraceptives contain either a combination of estrogen and progesterone or progesterone alone. These hormones can stabilize the hormonal fluctuations that trigger headaches in some women.
- Combination Birth Control Pills: For some, combination birth control pills can reduce the frequency and severity of hormone-related headaches by providing a steady level of hormones throughout the cycle. However, it"s important to note that in a small number of women, these pills may actually increase headache frequency or intensity.
- Progesterone-Only Pills: Progesterone-only contraceptives, including the mini-pill, implants, and IUDs, can be a better option for those who experience headaches worsened by estrogen or who cannot take estrogen for medical reasons.
- Continuous Dosing: Using hormonal contraceptives in a way that skips the placebo days and prevents menstruation (continuous dosing) can be effective for those whose headaches are primarily associated with their period. This approach minimizes the hormonal fluctuations that can lead to menstrual migraines.
- Menstrual Migraine Management: For women who experience menstrual migraines, a short course of NSAIDs or a triptan medication starting a few days before their period and continuing through the menstrual period can be combined with hormonal contraceptives for additional relief.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: It"s crucial to monitor how hormonal contraceptives affect your headaches. What works for one person may not work for another, and adjustments may be necessary. Working closely with a healthcare provider can help you find the most effective approach.
Choosing the right type of hormonal contraceptive for headache management requires a personalized approach. Factors to consider include your headache pattern, intensity, medical history, and how you respond to different hormonal formulations. Consulting with a healthcare provider who understands both headache management and reproductive health is essential for optimizing your treatment plan.

Navigating Headaches During Menopause and Perimenopause
The transition into menopause, known as perimenopause, brings about hormonal fluctuations that can significantly impact headache patterns for many women. Understanding how menopause and perimenopause affect headaches and exploring strategies to manage them can help mitigate their impact on your life. Here are some insights and tips for navigating headaches during these transitional phases:
- Hormonal Changes: The fluctuating levels of estrogen and progesterone during perimenopause can trigger headaches in some women. These may change in frequency, intensity, or nature during this time.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage headaches. This includes regular physical activity, a balanced diet, adequate hydration, stress management techniques, and consistent sleep patterns.
- Medication Review: It"s a good time to review your current medications with your healthcare provider. Some medications you were taking before may not be as effective or necessary, and others may now be more beneficial.
- Hormone Therapy: For some women, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can help stabilize hormone levels and reduce headache frequency and severity. However, HRT is not suitable for everyone and should be discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider.
- Non-Hormonal Therapies: Non-hormonal medications, such as blood pressure medications, antidepressants, or anti-seizure drugs, may be recommended to help prevent headaches during this time.
- Alternative Treatments: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and mindfulness-based stress reduction are examples of alternative treatments that some women find helpful for managing headaches during perimenopause and menopause.
- Keeping a Headache Diary: Tracking your headaches along with your menstrual cycle, diet, stress levels, and sleep patterns can help identify triggers and patterns, making it easier to manage headaches effectively.
Headaches during menopause and perimenopause can be challenging, but with the right strategies and support, they can be managed effectively. It"s important to communicate openly with your healthcare provider about your symptoms and any changes you notice. Together, you can develop a comprehensive approach to manage headaches and improve your quality of life during this transition.
Exploring Hormone Replacement Therapy and Its Effects on Headaches
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is commonly used to alleviate symptoms of menopause and perimenopause, including hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness. Its impact on headaches, however, can vary from person to person, depending on the type of HRT, dosage, and individual response. Understanding the relationship between HRT and headaches can help in making informed decisions about managing menopausal symptoms effectively. Here"s what you need to know:
- Estrogen"s Role: Fluctuations in estrogen levels are a known trigger for headaches in some women. HRT aims to stabilize these levels, which can potentially reduce the frequency and severity of headaches triggered by hormonal fluctuations.
- Types of HRT: The effect of HRT on headaches can differ based on whether the therapy is estrogen-only or a combination of estrogen and progesterone. Some women may experience relief from headaches with one type of HRT and not another.
- Method of Administration: The way HRT is administered (oral, transdermal, or vaginal) can also influence its impact on headaches. Transdermal patches, for example, provide a steady release of hormones and may be less likely to trigger headaches compared to oral forms, which cause more fluctuation in hormone levels.
- Starting Dose and Adjustment: The starting dose of HRT is typically low and can be adjusted based on your body"s response. Finding the right balance is crucial, as too high a dose may worsen headaches, while the right dose can provide relief.
- Individual Variability: Response to HRT is highly individual. Some women report improvement in headache symptoms, while others may experience an increase in headache frequency or intensity.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential when using HRT, especially if you have a history of headaches. This allows for timely adjustments to the treatment plan based on your symptoms and side effects.
- Alternative Therapies: For women who cannot use HRT or for whom HRT worsens headaches, other non-hormonal treatments and lifestyle adjustments can be explored to manage menopausal symptoms and headaches.
Deciding whether to use HRT and understanding its potential effects on headaches requires a personalized approach. It"s important to discuss all your symptoms, medical history, and concerns with your healthcare provider. Together, you can weigh the benefits and risks of HRT and choose the best strategy for managing menopause-related symptoms and improving your quality of life.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/why-do-i-have-a-headache-after-childbirth-1719586-5c046eeb46e0fb0001c253cf.png)
READ MORE:
Keeping a Headache Diary: A Tool for Identifying Patterns and Triggers
One of the most effective strategies for managing period-related headaches is to keep a detailed headache diary. This diary can help you and your healthcare provider understand the patterns and triggers of your headaches, leading to more personalized and effective treatment plans. Here"s how to create and use a headache diary effectively:
- Daily Tracking: Record your headaches each day, noting when they start, how long they last, and their severity on a scale of 1 to 10. Include details about the type of pain (throbbing, stabbing, pressure, etc.) and location.
- Symptom Description: Write down any accompanying symptoms such as nausea, light sensitivity, or aura (visual disturbances), as these can help differentiate between types of headaches, such as tension headaches versus migraines.
- Menstrual Cycle: Note the dates of your menstrual cycle. This can help identify if your headaches are hormonally related and if they follow a pattern in relation to your cycle.
- Diet and Hydration: Keep track of what you eat and drink, as certain foods and beverages can be headache triggers. Note the time of consumption and any headaches that occur afterward.
- Exercise and Activity: Document your physical activity, as both lack of exercise and intense exercise can trigger headaches in some individuals.
- Stress Levels: Record your daily stress levels and any significant events that might impact your stress. Stress is a common trigger for headaches, and identifying this can help in developing stress management strategies.
- Sleep Patterns: Monitor your sleep quality and duration. Poor sleep or changes in sleep patterns can trigger headaches.
- Medication and Relief Measures: Note any medications taken, including over-the-counter or prescription drugs, as well as any other relief measures like applying cold packs, resting in a dark room, or using relaxation techniques. This can help identify what works best for you.
After several months of tracking, review your headache diary with your healthcare provider. Together, you can identify any patterns or triggers that emerge. This information is invaluable in developing a comprehensive approach to manage and potentially reduce the frequency and severity of your headaches. A headache diary not only aids in understanding your headaches better but also empowers you to take an active role in your treatment plan.
Understanding and managing period headaches is crucial for well-being. With the right knowledge, strategies, and treatments, you can navigate these challenges effectively. Empower yourself by exploring these insights and take a step towards a healthier, headache-free life.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Natural-Remedies-for-Managing-Headaches_Paige-McLaughlin_Final-461a780622884c479edf3dc01234692c.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Getting-Rid-of-a-Migraine_Illustrator_Ellen-Lindner_Final-a245985cbf4645a7874d573991fb6cbb.jpg)
