Topic tension headache: Discover effective strategies to manage tension headaches, offering a deep dive into causes, symptoms, and relief methods for those seeking lasting solace from this common ailment.
Table of Content
- What are the causes of tension headaches?
- Understanding Tension Headaches
- Common Causes and Triggers
- Symptoms of Tension Headaches
- Role of Stress in Tension Headaches
- Diagnosis of Tension Headaches
- Treatment Options
- YOUTUBE: Say Goodbye to Tension Headaches in Just 5 Minutes!
- Role of Physiotherapy in Management
- Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
- When to See a Doctor
- Conclusion
What are the causes of tension headaches?
Tension headaches are a common type of headache that is characterized by pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. The exact cause of tension headaches is not known, but several factors are believed to contribute to their development:
- Stress: Stress is considered a primary trigger for tension headaches. When you experience stress, your muscles tend to tense up, including those in the neck and scalp, which can lead to the development of a tension headache.
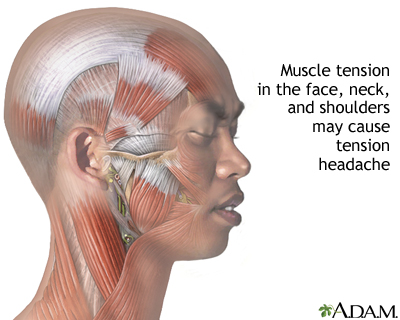
- Muscle tension: Tension headaches are often associated with muscle contractions in the head and neck region. Prolonged muscle tension, whether it\'s due to stress, poor posture, or repetitive activities, can contribute to the development of these headaches.
- Anxiety and depression: Mental health conditions like anxiety and depression are often associated with tension headaches. The relationship between these conditions and tension headaches is complex and may involve a combination of muscle tension, neurotransmitter imbalances, and altered pain perception.
- Poor posture: Spending long hours in a sedentary position with poor posture, such as slouching or hunching over a desk, can strain the muscles in your neck and scalp, leading to tension headaches.
- Eyestrain: Extended periods of focusing on digital screens, reading, or any visually demanding activities can cause eyestrain, which may contribute to the development of tension headaches.
- Sleep disturbances: Poor sleep quality, lack of sleep, or disrupted sleep patterns can make you more susceptible to tension headaches. It is important to establish regular sleep habits and create a comfortable sleep environment to reduce the risk of headaches.
- Skipping meals: Low blood sugar levels caused by skipping meals or not eating regularly can trigger tension headaches. It is advisable to maintain a balanced diet and eat at regular intervals to avoid such headaches.
Although the exact cause of tension headaches is not fully understood, these factors are commonly associated with their occurrence. Managing stress, practicing good posture, getting regular exercise, and taking breaks from prolonged sedentary activities can help reduce the frequency and intensity of tension headaches.
Understanding Tension Headaches
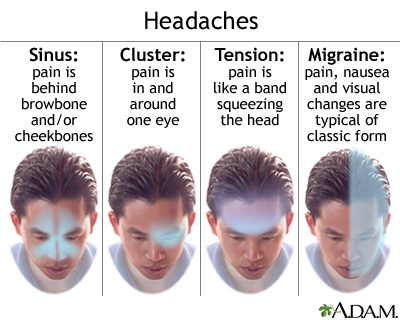
Tension headaches, the most common type of headache among adults, are characterized by a dull, aching head pain. The sensation of tightness or pressure across the forehead or on the sides and back of the head is typical. Unlike migraines, tension headaches do not cause nausea or vomiting, and they rarely halt daily activities despite their discomfort.
- Causes: Often linked to stress, muscle strain, or anxiety.
- Symptoms: Dull, aching pain, tightness, or pressure around the forehead, scalp, or neck.
- Duration: Can last from 30 minutes to several days.
- Frequency: May occur occasionally or frequently, even daily in chronic cases.
Understanding the triggers and symptoms of tension headaches is crucial for effective management and treatment. While they are generally not indicative of a serious underlying condition, chronic headaches can significantly impact quality of life, making identification and appropriate management strategies essential for those affected.
Common Causes and Triggers
Tension headaches arise from various factors that contribute to the tightening of muscles in the head and neck. Understanding these triggers can help in managing and preventing the onset of headaches.
- Stress: The most common trigger, stress can tighten muscles and lead to a headache.
- Poor Posture: Sitting or standing in an awkward position for long periods can strain head and neck muscles.
- Eyestrain: Prolonged screen time without breaks can contribute to tension headaches.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can lead to headaches.
- Lack of Sleep: Poor sleep patterns or not getting enough sleep can trigger headaches.
- Caffeine: Both excessive consumption and withdrawal from caffeine can cause headaches.
- Hunger: Skipping meals or fasting can lead to low blood sugar levels and headaches.
By identifying and addressing these triggers, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce the frequency and severity of tension headaches. Implementing lifestyle changes, such as regular breaks from screen time, maintaining hydration, and managing stress through relaxation techniques, can be effective in preventing tension headaches.
Symptoms of Tension Headaches
Tension headaches, known for their distinctive characteristics, can affect individuals differently. Recognizing these symptoms is key to managing and treating tension headaches effectively.
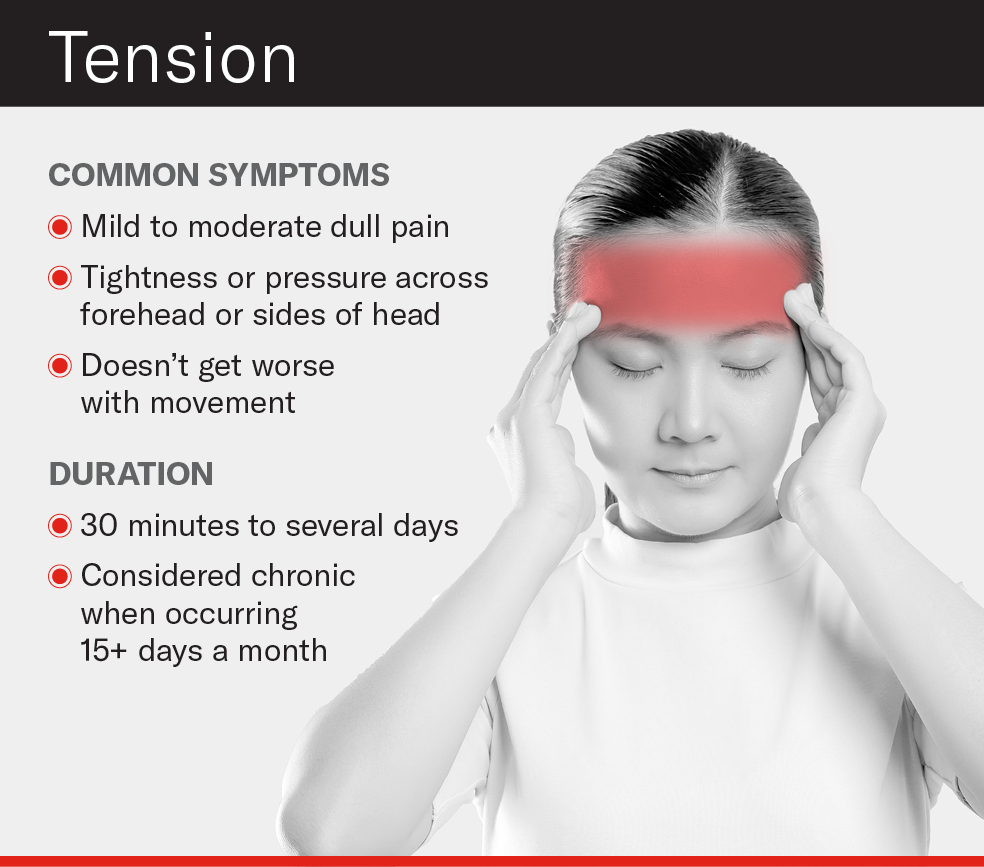
- Head Pain: A constant, dull ache that affects both sides of the head, often described as a tight band around the forehead.
- Scalp Sensitivity: Tenderness when touching the scalp, neck, and shoulder muscles.
- Pressure: Sensation of tightness or pressure across the forehead or on the sides and back of the head.
- Muscle Ache: Pain in the neck and shoulder muscles, which may be related to stress or poor posture.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Some people report trouble focusing or feeling mentally "foggy" during a tension headache.
- Light and Sound Sensitivity: While less common than with migraines, some individuals may experience sensitivity to light and sound.
Although tension headaches are generally not severe enough to prevent daily activities, they can significantly impact an individual"s quality of life. Understanding these symptoms is the first step toward effective treatment and relief.
Role of Stress in Tension Headaches
Stress is a significant factor in the development and exacerbation of tension headaches, influencing both their frequency and severity. Understanding how stress impacts tension headaches is crucial for effective management and prevention.
- Physiological Response: Stress triggers a physiological response in the body, leading to muscle tension in the head, neck, and shoulders, which can precipitate a headache.
- Emotional Stress: Emotional challenges, anxiety, and depression are closely linked to tension headaches, often resulting in a cyclical pattern of stress and pain.
- Physical Stress: Physical factors, such as fatigue, poor posture, and eyestrain, often related to high stress levels, can also contribute to tension headaches.
- Stress Management Techniques: Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga, can significantly reduce the occurrence of tension headaches.
By recognizing the role of stress in tension headaches, individuals can adopt stress reduction strategies to mitigate their impact. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and healthy eating habits, along with mindfulness practices, are effective in managing stress and reducing the frequency of tension headaches.
Diagnosis of Tension Headaches
The diagnosis of tension headaches primarily involves a thorough medical history and physical examination to rule out other causes of headaches. No specific tests exist for tension headaches, making the diagnosis largely based on patient-reported symptoms and exclusion of other headache disorders.
- Medical History: A detailed discussion of the headache patterns, symptoms, duration, and triggers is essential for diagnosing tension headaches.
- Physical Examination: A physical exam focusing on the head, neck, shoulders, and nervous system can help identify signs of muscle tension or other physical causes of headaches.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: Doctors may perform tests to rule out other causes of headaches, such as migraines, cluster headaches, or underlying medical conditions.
- Criteria for Diagnosis: According to the International Headache Society, tension headaches are diagnosed based on specific criteria, including headache frequency, duration, and absence of certain characteristics typical of other headaches.
While tension headaches are generally not indicative of a serious underlying condition, a healthcare provider may recommend further testing if the headache pattern changes, or if symptoms suggest a more serious condition. Effective diagnosis is crucial for appropriate management and treatment planning.

Treatment Options
Treatment for tension headaches varies depending on the frequency and intensity of the headaches. For episodic tension headaches, common over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers are often recommended, including:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol®)
- Aspirin
- Ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®)
- Naproxen sodium (Aleve®)
For those experiencing chronic tension headaches, more specific treatments may be prescribed, such as:
- Antiseizure medications like gabapentin (Neurontin®) or topiramate (Topamax®, Topiragen®)
- Antidepressants, for example, amitriptyline, which can help relieve pain
- Other antidepressants, including venlafaxine (Effexor XR) and mirtazapine (Remeron), may also be effective in preventing tension-type headaches.
- Anti-seizure medicines and muscle relaxants, though more studies are needed to understand their efficacy in preventing tension-type headaches.
Alternative therapies and lifestyle modifications can also play a crucial role in managing tension headaches:
- Acupuncture, massage, deep breathing, biofeedback, and behavior therapies can be useful for coping with tension-type headaches.
- Stress management, regular exercise, and sufficient rest are essential preventive measures.
It"s important to limit the use of pain relief medication to avoid rebound headaches, which can occur from overuse. Health professionals recommend not using pain relief medication more than 10 days per month.
Consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual symptoms and medical history.
Say Goodbye to Tension Headaches in Just 5 Minutes!
Goodbye to all your tensions and worries! This incredible video will show you effective techniques to relieve headaches in just 5 minutes. Say goodbye to pain and hello to instant relaxation!
Role of Physiotherapy in Management
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing tension-type headaches (TTH), offering a non-pharmacological treatment option that can reduce the intensity and frequency of headaches. It focuses on addressing the musculoskeletal elements of TTH, particularly the muscles and soft tissues of the neck, shoulders, and head.
- Manual therapy techniques, such as myofascial release, cervical traction, and trigger point therapy, are effective in alleviating the musculoskeletal components of TTH, targeting the cervical and thoracic regions.
- Exercises designed to strengthen and stretch the neck, shoulder, and head muscles can help in reducing the tension and improving posture, which in turn can decrease the frequency of headaches.
- Physiotherapy treatments may also include massage, which helps in relaxing tight muscles and improving blood flow, and heat therapy to relieve muscle tension.
- Education on proper posture and ergonomics is an essential part of physiotherapy to prevent the recurrence of TTH by minimizing strain on the muscles and joints.
- Acupuncture and dry needling, as part of a physiotherapy program, have shown effectiveness in reducing headache symptoms by targeting specific points associated with pain relief.
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach in physiotherapy for TTH, a tailored treatment plan that includes a combination of these techniques can provide significant relief for patients. Continuous evaluation and adjustment of the treatment plan are essential for long-term management and reduction of TTH.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing tension headaches. Key strategies include:
- Eating nutritious foods on a regular schedule and staying hydrated.
- Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to release pain-blocking chemicals in the body.
- Ensuring adequate sleep by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Limiting caffeine intake to avoid headaches and irritability associated with excessive consumption.
- Managing stress through simplification of daily activities, taking breaks, deep breathing, and positive thinking.
- Quitting smoking to improve blood flow to the brain and reduce headache triggers.
Additionally, maintaining proper posture, using good lifting techniques, and engaging in low-impact sports can minimize physical strains that lead to headaches. Dental check-ups for jaw tension, updating eyewear to prevent eye strain, and stress management techniques such as deep breathing, visualization, and progressive relaxation are beneficial. Regular sleep patterns and meal schedules are important to avoid stress that may trigger headaches.
Exercises specifically designed to relax the neck muscles, along with low-impact aerobic activities, stretching, tai chi, and yoga, can improve overall health and stress management, further aiding in the prevention of tension headaches.
Keeping a headache diary can help identify triggers and patterns, allowing for more targeted lifestyle adjustments to prevent headaches.
When to See a Doctor
It"s essential to know when to consult a healthcare professional for tension headaches. While tension-type headaches are common and often manageable with home remedies and over-the-counter medication, certain situations require medical attention:
- If you find yourself needing medication for your headaches more than twice a week.
- When tension-type headaches disrupt your daily life or change in pattern.
- If you experience headaches that feel different from your usual tension-type headaches.
Seek immediate medical help if you encounter any of the following:
- A sudden, very severe headache.
- A headache accompanied by a fever, stiff neck, mental confusion, seizures, double vision, weakness, numbness, or trouble speaking.
- A headache following a head injury, especially if it worsens over time.
These symptoms could indicate a more serious condition, such as a brain tumor or an aneurysm, and require urgent care.
Regular check-ups and discussing any changes in your headache patterns with a healthcare provider can help manage your condition effectively and prevent potential complications. Always consult a professional if you"re unsure about your symptoms or if your headaches become more frequent or severe.
Conclusion
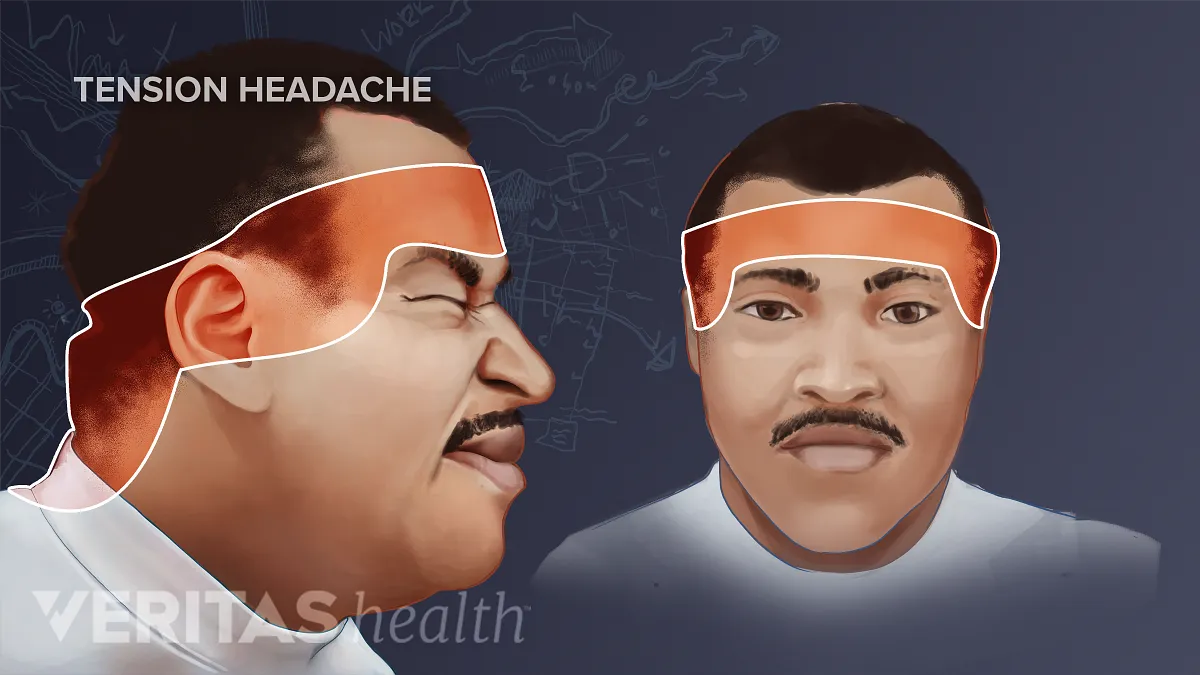
Tension headaches, characterized by mild to moderate pain that feels like a tight band around the head, are the most common type of headache. These headaches, often resulting from stress and muscle tension, can affect both sides of the head and typically do not cause nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light.
The precise cause of tension headaches is still under investigation, but factors such as genetics, environment, and muscle contractions in the head and neck area are believed to play significant roles. Although they can be challenging to distinguish from migraines, tension headaches usually lack the visual disturbances and nausea associated with migraine attacks. Stress is the most commonly reported trigger, and lifestyle changes aimed at stress reduction, such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and relaxation techniques, can be effective preventative measures.
Treatment varies, ranging from over-the-counter pain relievers for episodic headaches to prescriptions for chronic conditions, alongside alternative therapies like biofeedback, meditation, and cognitive behavioral therapy. It"s crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you experience tension headaches frequently or if there"s a significant change in their pattern. In some cases, headaches may signal a serious condition, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Ultimately, understanding your triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate medical advice are key to managing tension headaches and improving your quality of life.
Discover how to manage tension headaches effectively with our comprehensive guide. Learn about causes, symptoms, and tailored treatments to relieve pain and enhance your quality of life. Embrace a headache-free future today.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-PaigeMcLaughlin-WhatisaClusterHeadache-Standard-87c962b6a28d4b1ab0359ed3ae5b696f.jpg)