Topic what to do with high blood pressure headache: Discover effective strategies for managing high blood pressure headaches, blending medical advice with holistic approaches to provide relief and improve your overall health.
Table of Content
- Understanding High Blood Pressure Headaches
- Symptoms and Immediate Actions
- What is the relationship between high blood pressure and headaches?
- YOUTUBE: Hypertension Headache Causing High Blood Pressure: The Cause and Treatment Solution
- Medical Interventions and When to Seek Help
- Medications: Dos and Don"ts
- Non-Drug Approaches for Headache Relief
- Preventing High Blood Pressure Headaches
- Lifestyle Modifications to Lower Blood Pressure
- Conclusion: Integrating Management and Prevention
Understanding High Blood Pressure Headaches
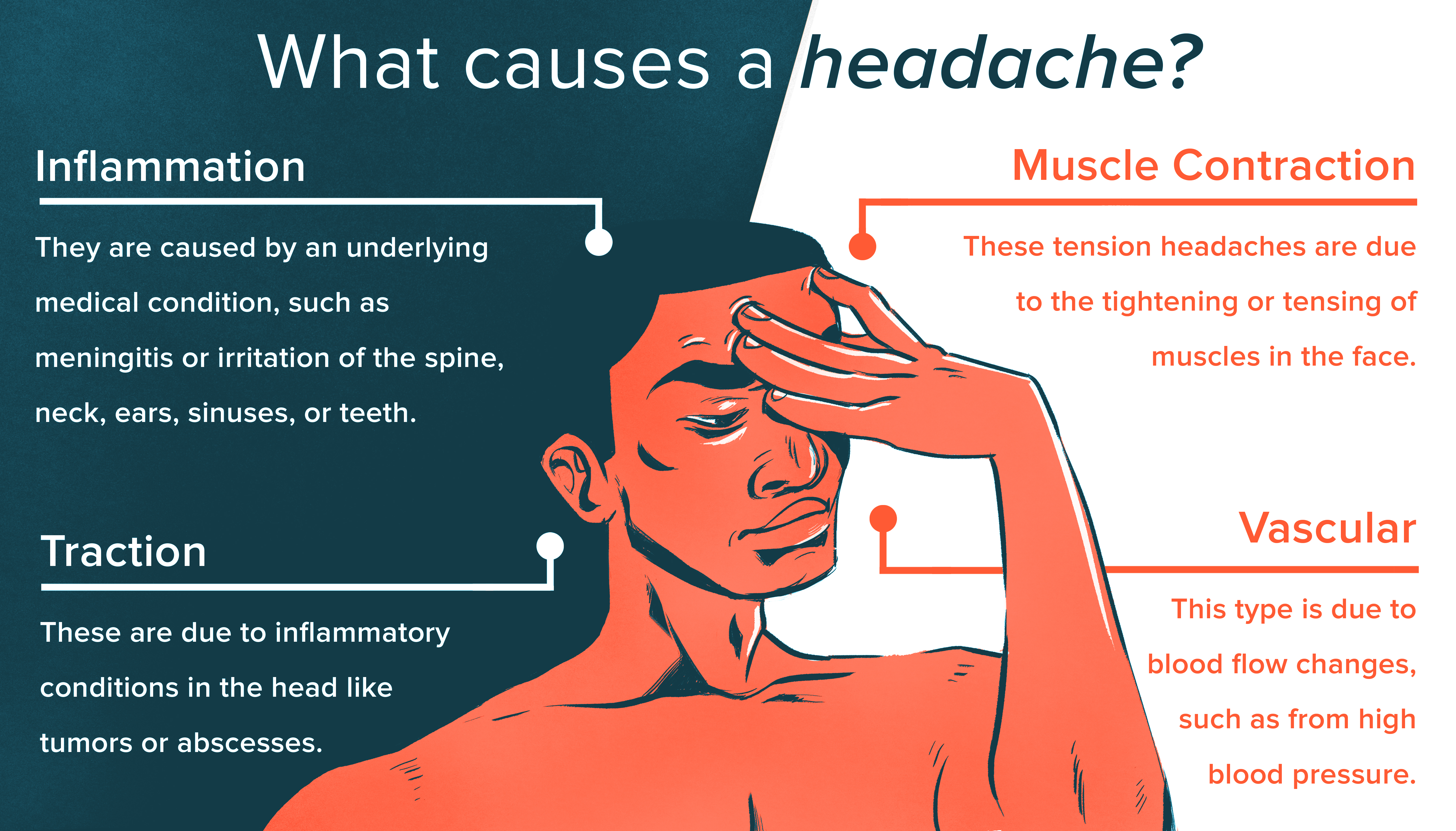
High blood pressure can lead to serious health emergencies, including headaches that may not distinguish themselves from regular headaches in terms of symptoms. These may be accompanied by chest pain, blurred vision, nausea, and shortness of breath.
Symptoms and Complications
- Severe pain and a pulsing sensation in the head
- Nosebleeds, blood spots in the eyes, flushed face
- Vision problems, anxiety, back pain
- Complications can include stroke, heart attack, and kidney failure
Immediate Actions for High Blood Pressure Headaches
- Measure your blood pressure
- If over 180/120 mm Hg, take prescribed medication and seek emergency care
- Avoid traditional pain relievers as they may be ineffective
Prevention and Management
Regular blood pressure monitoring, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help prevent high blood pressure headaches. Medications may be necessary for those with a history of high blood pressure.
Medications and Migraines
For those with migraines, certain medications, including triptans and NSAIDs, should be used with caution. Blood pressure medications may play a role in both causing and preventing headaches.
Non-Drug Approaches
- Biofeedback
- Low-salt diet
- Weight management
If you experience a headache with high blood pressure of 180/120 mm Hg or higher, retest in five minutes. If it remains high, seek immediate medical assistance, especially if accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain or numbness.

READ MORE:
Symptoms and Immediate Actions
When dealing with high blood pressure headaches, recognizing the symptoms early and taking immediate action can significantly mitigate health risks. Below are the common symptoms associated with high blood pressure headaches and the recommended immediate steps to take.
- Sudden, severe headache not typical of your usual headache patterns
- Blurred vision or visual disturbances
- Chest pain or difficulty breathing
- Nausea or vomiting
- Confusion or neurological symptoms
Immediate actions to take if you or someone else is experiencing these symptoms:
- Measure the blood pressure to confirm if it"s significantly elevated (e.g., 180/120 mm Hg or higher).
- If high blood pressure is confirmed, take any prescribed blood pressure medication if available.
- Call emergency services or go to the nearest emergency room immediately, especially if blood pressure remains high or symptoms worsen.
It"s crucial not to ignore these symptoms, as they may indicate a hypertensive crisis, a life-threatening condition requiring urgent medical attention. Taking swift and appropriate action can prevent serious complications, including stroke and heart attack.
What is the relationship between high blood pressure and headaches?
The relationship between high blood pressure and headaches is a complex one, as research findings may vary. Here is a general overview of this relationship:
- High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a condition in which the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high.
- While high blood pressure itself may not directly cause headaches in most cases, some individuals may experience headaches as a symptom of severely elevated blood pressure levels.
- The presence of headaches in individuals with high blood pressure can sometimes be an indication of other underlying health issues or complications.
- It is essential to monitor and manage high blood pressure effectively to reduce the risk of developing severe complications that may contribute to headaches or other symptoms.
It\'s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan if you are experiencing headaches or other concerning symptoms related to high blood pressure.
Hypertension Headache Causing High Blood Pressure: The Cause and Treatment Solution
Discover the latest advancements in hypertension treatment in this informative video. Learn about effective strategies, lifestyle changes, and medication options to help you manage your blood pressure and improve your overall health. Take control of your wellness journey today!
Case: Headache, Balance Problems, High Blood Pressure, and Low Heart Rate
Struggling to find the right balance to alleviate your headaches? Watch this video for useful tips and techniques to manage and prevent headaches. Learn how to strike a perfect balance in your daily routine for a headache-free life.
Medical Interventions and When to Seek Help
Understanding when to seek medical help and the available interventions for high blood pressure headaches is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. Here are the steps and scenarios that warrant immediate medical attention.
- If blood pressure readings are consistently 180/120 mm Hg or higher, it"s essential to seek emergency medical care immediately.
- Signs of a hypertensive crisis, in addition to a severe headache, may include severe anxiety, nosebleeds, and severe shortness of breath.
- If experiencing a high blood pressure headache accompanied by symptoms such as chest pain, confusion, seizures, or blurred vision, emergency services should be contacted right away.
Medical interventions may include:
- Immediate administration of blood pressure medications to gradually lower blood pressure without dropping it too quickly, which could be dangerous.
- Continuous monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate to ensure stability.
- Assessment for any potential organ damage caused by the elevated blood pressure.
Preventive measures and regular monitoring by a healthcare provider can help manage high blood pressure and reduce the risk of developing severe headaches. Always follow your healthcare provider"s advice on medication, lifestyle changes, and regular blood pressure monitoring.
Medications: Dos and Don"ts
Managing high blood pressure headaches often involves medication. Knowing which medications are safe and effective, as well as those to avoid, is crucial for your health. Here are some general guidelines on the dos and don"ts of medications for high blood pressure headaches.
- Do: Use prescribed blood pressure medications to manage your hypertension. Commonly prescribed types include ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers.
- Do: Consult your healthcare provider before taking any over-the-counter pain relievers. Aspirin or acetaminophen may be recommended as they are generally considered safe for people with high blood pressure.
- Do: Keep a log of your medication intake, including any over-the-counter medications or supplements, to share with your healthcare provider.
- Don"t: Take NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like ibuprofen or naproxen without consulting your doctor, as these can raise blood pressure and interfere with blood pressure medications.
- Don"t: Ignore potential side effects of medications, such as dizziness or changes in kidney function, and report them to your healthcare provider.
- Don"t: Start or stop any medication without the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It"s essential to follow a healthcare provider"s advice regarding medication for high blood pressure and headaches. Adjustments to your treatment plan should be made under medical supervision to ensure your safety and well-being.
Non-Drug Approaches for Headache Relief
While medication plays a crucial role in managing high blood pressure and associated headaches, non-drug approaches can also significantly contribute to relief and overall well-being. Here are several effective strategies:
- Stress Management: Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress, which is often a trigger for both high blood pressure and headaches.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular, moderate exercise like walking, swimming, or cycling can improve cardiovascular health and reduce the frequency of headaches.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting salt, processed foods, and saturated fat can help manage blood pressure and reduce headache occurrence.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring you get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night can help prevent headaches and improve overall health.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is important for overall health and can help prevent headaches.
- Biofeedback and Relaxation Techniques: These can teach you how to control certain physical responses related to stress and may help reduce headache frequency.
Combining these non-drug approaches with any medical treatments prescribed by your healthcare provider can offer a comprehensive strategy for managing high blood pressure headaches. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your lifestyle, especially if you have underlying health conditions.

Preventing High Blood Pressure Headaches
Preventing high blood pressure headaches involves managing your blood pressure through healthy lifestyle choices and, if necessary, medication. Here are key strategies to help minimize the risk of developing these headaches:
- Monitor Your Blood Pressure Regularly: Keeping track of your blood pressure can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can increase your risk of high blood pressure and related headaches. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and low in sodium, can help control blood pressure.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Consuming these in moderation can help prevent spikes in blood pressure and reduce headache risk.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can elevate blood pressure and harm your overall cardiovascular health.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy blood pressure and reduces stress, a common trigger for headaches.
- Manage Stress: Stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga, can help lower blood pressure and reduce the likelihood of headaches.
Implementing these strategies can not only help prevent high blood pressure headaches but also contribute to overall cardiovascular health and well-being. Consult with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that"s right for you.
Lifestyle Modifications to Lower Blood Pressure
Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is essential for preventing high blood pressure headaches and other cardiovascular diseases. Here are effective lifestyle modifications that can help in lowering blood pressure:
- Healthy Eating Habits: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. Reduce your intake of saturated fats and cholesterol to improve heart health and lower blood pressure.
- Salt Reduction: Limiting salt (sodium) in your diet can have a significant effect on lowering your blood pressure. Aim for no more than 2,300 milligrams a day, with an ideal limit of less than 1,500 milligrams for most adults.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes a week, or about 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Weight loss is one of the most effective lifestyle changes for controlling blood pressure. Losing even a small amount of weight if you"re overweight or obese can help reduce your blood pressure.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Drinking alcohol in moderation, if at all, can help lower your blood pressure. This means up to one drink a day for women and two drinks a day for men.
- Avoid Tobacco Use: Smoking and tobacco use increase your blood pressure and put you at higher risk for heart attack and stroke. Quitting can improve your overall health and lower your blood pressure.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help lower blood pressure.
Implementing these lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce blood pressure levels and improve your overall cardiovascular health, decreasing the risk of high blood pressure headaches. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hypertension-symptoms-5afedc4da9d4f90036e90344.png)
READ MORE:
Conclusion: Integrating Management and Prevention
Successfully managing high blood pressure and preventing associated headaches requires a comprehensive approach that integrates medical treatments with lifestyle modifications. Key strategies include:
- Maintaining regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Implementing lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Using prescribed medications appropriately and being mindful of over-the-counter medications that may affect blood pressure.
- Staying informed about the signs and symptoms that indicate the need for immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
By embracing a proactive approach to health, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of high blood pressure headaches and improve their overall well-being. Collaboration with healthcare professionals is crucial to tailor a plan that fits individual health needs and lifestyle preferences, ensuring the best outcomes in managing and preventing high blood pressure headaches.
Embrace a healthier lifestyle and informed choices to manage high blood pressure headaches effectively. Discover your path to wellness and enjoy a life free from the discomfort of hypertension-induced headaches.