Topic how to make a headache go away instantly: Discover instant headache relief strategies that can ease your pain quickly. From natural remedies to effective medical treatments, learn how to make a headache go away instantly and get back to your day with minimal disruption.
Table of Content
- How can I make a headache go away instantly?
- Immediate Relief Methods
- Understanding Different Headache Types
- Hydration and Diet Adjustments
- Exercise for Prevention and Relief
- YOUTUBE: 5 Fast Ways to Fix Your Headache | Dr. Mandell
- Limiting Caffeine Intake
- Meditation and Relaxation Techniques
- Over-The-Counter Medications
- Prescription Treatments for Severe Cases
- Natural Remedies and Supplements
- Neurostimulation Devices
How can I make a headache go away instantly?
While it may not be possible to make a headache go away instantly, there are some steps you can take to alleviate the pain and reduce its duration. Here are some methods you can try:
- Find a calm environment: Move to a quiet, dimly lit room where you can relax.
- Apply temperature therapy: Use a cold pack or a hot compress on the affected area. Experiment with both to see which works better for you.
- Try relaxation techniques: Practice deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation to help relax your body and mind.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can contribute to headaches, so drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Manage stress: Identify and address any sources of stress in your life. Engage in activities that help you relax and unwind.
- Consider over-the-counter pain relievers: Non-prescription medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve mild to moderate headaches. Follow the recommended dosage.
- Avoid triggers: If you notice certain triggers, such as specific foods, bright lights, or loud noises, try to avoid them as much as possible.
- Get enough sleep: Maintain a regular sleep schedule and ensure you are getting adequate rest each night.
- Practice good posture: Poor posture can contribute to tension headaches. Be mindful of your posture and make adjustments when needed.
It\'s important to note that if you frequently experience severe headaches or migraines, it\'s recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
READ MORE:
Immediate Relief Methods
Experiencing a headache can be debilitating, but there are immediate steps you can take to alleviate the pain. These methods are designed to offer quick relief and can be done at home or on the go.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water, as dehydration can be a common cause of headaches.
- Apply Cold or Warm Compress: For tension headaches, a warm compress on the back of the neck can help. For migraines, a cold pack on the forehead might provide relief.
- Dim the Lights: Bright or flickering light, even from your computer screen, can exacerbate headaches. Dimming the lights can help reduce the pain.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga can reduce stress and alleviate headache symptoms.
- Limited Caffeine: A small amount of caffeine may help relieve headache pain, but be cautious as too much can lead to rebound headaches.
- Over-the-Counter Medication: Nonprescription pain relievers like ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen can offer quick relief, but they should be used sparingly.
- Get Fresh Air and Exercise: Light exercise and fresh air can improve blood circulation and reduce the severity of headache symptoms.
- Avoid Strong Smells: Strong odors from perfumes, cleaning products, or smoke can trigger headaches in some people. Moving to a well-ventilated area may help.
These methods can provide immediate relief, but if your headache persists or becomes more frequent, consulting a healthcare professional is advised.
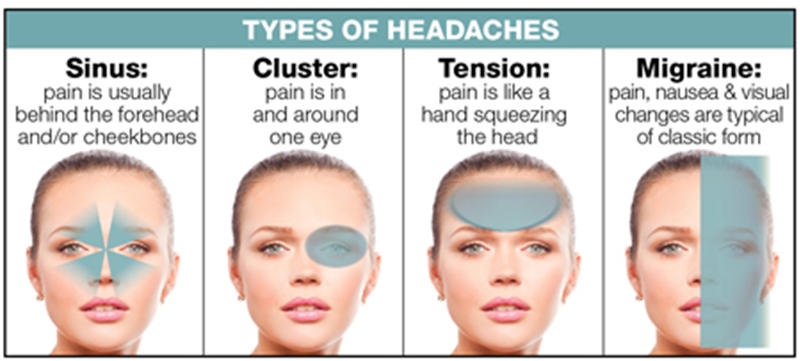
Understanding Different Headache Types
Knowing the type of headache you"re experiencing is crucial for finding the most effective treatment. Headaches can range from mild to severe and can be a symptom of various underlying conditions.
- Tension Headaches: The most common type, characterized by a constant pressure or ache around the head, especially at the temples or back of the head and neck.
- Migraines: Intense and often pulsating pain, typically affecting one side of the head, accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and sometimes visual disturbances.
- Cluster Headaches: Severe, piercing pain around one eye or temple, occurring in groups or "clusters" over weeks or months, followed by periods of remission.
- Sinus Headaches: Caused by sinus infection or inflammation, featuring pressure and pain around the cheeks, forehead, and eyes, often accompanied by fever.
- Rebound Headaches: Result from overuse of headache medication, leading to a cycle of pain and medication use that perpetuates the headache.
Each type of headache may have different triggers, symptoms, and treatments. Identifying the specific characteristics of your headache is a key step towards finding relief.
Hydration and Diet Adjustments
Managing headaches often involves simple but effective dietary and hydration adjustments. Dehydration, for instance, can cause headaches as the brain contracts due to fluid loss. Drinking water and fluids can alleviate this type of headache as the brain returns to its normal size.
Hydration Tips
- Drink water in small sips to avoid overwhelming the stomach. Ice cubes or electrolyte drinks can be alternatives, especially if nausea is present.
- Rest in a cool, shaded area if you"re outdoors and feeling dehydrated.
- Use over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for immediate relief, but avoid those with caffeine as they can worsen dehydration.
- Apply a cold compress or a wet washcloth to the forehead for additional relief.
Preventing dehydration headaches involves regular fluid intake, especially during physical activity or in hot weather.
Dietary Considerations
Diet also plays a significant role in managing and preventing headaches. Certain foods can help alleviate headache symptoms or prevent them from occurring.
- Dark chocolate, containing caffeine, can ease caffeine withdrawal headaches and is also a good source of magnesium.
- Berries, such as blueberries and strawberries, are high in antioxidants and may help relieve sinus pressure.
- Mushrooms may improve gut health, which can be linked to migraine prevention.
- Limiting caffeine intake by opting for "half caff" or decaffeinated coffee can reduce withdrawal headaches.
Note that individual dietary needs and responses can vary, so it"s important to observe how your body reacts to different foods and hydration levels.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Getting-Rid-of-a-Migraine_Illustrator_Ellen-Lindner_Final-a245985cbf4645a7874d573991fb6cbb.jpg)
Exercise for Prevention and Relief
Regular exercise is not only beneficial for overall health, but it"s also an effective way to reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches. Engaging in physical activity helps in managing stress, reducing tension that can trigger headaches, and releasing endorphins which act as natural pain blockers.
Recommended Exercise Routine
- Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, at least five days a week.
- Start with a gentle warm-up to avoid sudden, intense exertion which can sometimes lead to headaches.
- Maintain a consistent exercise schedule to maximize benefits.
Regular aerobic exercises not only help in tension relief but also contribute to maintaining a healthy body weight, which is important as obesity can be a factor in migraines.
Additional Tips
- Stay hydrated before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration-related headaches.
- Keep a headache diary to track the effectiveness of your exercise routine in headache management.
- Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have a history of migraines or other health concerns.
Remember, while exercise is a powerful tool in headache management, it should be part of a holistic approach that includes proper diet, adequate sleep, and stress management.
5 Fast Ways to Fix Your Headache | Dr. Mandell
Looking for instant relief from that nagging headache? Check out this video that offers effective tips and techniques to help you say goodbye to headaches and hello to a pain-free day!
Tension Headache Gone in Just 5 Minutes
Tired of constantly battling tension headaches? This video is your ultimate guide to finding long-lasting relief. Discover easy-to-follow exercises and relaxation techniques that will help you dissolve tension and finally find relief from this debilitating condition. Don\'t miss out!
Limiting Caffeine Intake
Limiting caffeine intake can be a crucial strategy for managing and preventing headaches. While moderate caffeine consumption can offer benefits like increased alertness, excessive intake can lead to increased headache frequency, especially in individuals sensitive to caffeine.
Understanding Caffeine Sources
- Be aware that caffeine is present in coffee, tea, soda, chocolate, and some medications. A mug of instant coffee, for instance, contains about 100 milligrams of caffeine.
- Caffeine can also be found in less obvious sources like energy drinks, pre-workout powders, and water flavor enhancers, often under different names such as guarana or taurine.
Strategies to Reduce Caffeine Intake
- Gradual Reduction: To avoid withdrawal symptoms, gradually reduce your caffeine intake. This can be done by mixing caffeinated and decaffeinated beverages, like half-caff coffee.
- Stay Hydrated: Increase your water intake. Dehydration can often mimic the symptoms of caffeine withdrawal and lead to headaches.
- Set a Time Limit: Avoid consuming caffeine after a certain time, such as 2 p.m., to prevent it from affecting your sleep.
- Monitor Your Body"s Response: Pay attention to how your body reacts to reduced caffeine intake and adjust accordingly.
Note that individuals who regularly consume high amounts of caffeine or are more sensitive to it may experience more pronounced withdrawal symptoms. It"s important to listen to your body and adjust your caffeine reduction plan as needed.

Meditation and Relaxation Techniques
Meditation and relaxation techniques can be highly effective for the relief and prevention of headaches. These practices not only promote physical relaxation but also mental calmness, helping to reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches.
Effective Meditation and Relaxation Strategies
- Mindfulness Meditation: Begin with 10-minute daily sessions, focusing on your breathing or a peaceful scenario. Consistency is key to success in mindfulness practices.
- Body Scan Technique: Focus your attention on different parts of your body, becoming aware of any sensations such as pain, tension, or relaxation. Combine this with deep breathing exercises.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This involves tensing and then relaxing each muscle group in your body, which helps to distinguish between feelings of tension and relaxation.
- Guided Imagery: Use visualization to imagine yourself in a peaceful and relaxing setting. Engage all your senses in this process for a more profound experience.
- Autogenic Relaxation: Use visual imagery and body awareness to reduce stress. Repeat calming words or phrases in your mind while focusing on slowing your breathing and heart rate.
- Regular Practice: Incorporate meditation into your daily routine, either through structured sessions or by finding moments throughout your day to practice mindfulness.
Remember that the effectiveness of these techniques can improve with regular practice. If you"re new to meditation, start with guided sessions and gradually explore different methods to find what works best for you.
Over-The-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are a common and effective way to treat headaches. The effectiveness of these medications can vary based on their form, such as liquid, orally disintegrating tablets, or chewable tablets, which generally work faster than extended-release pills. Additionally, the state of your stomach can influence absorption, with a fuller stomach slowing down the process.
When choosing an OTC pain reliever, it"s important to consult with a doctor or pharmacist to ensure the medication is safe and appropriate for your needs. Be mindful that frequent use of analgesics and caffeine-containing medications can lead to medication-overuse headaches, so it"s recommended to use them judiciously.
- Acetaminophen: Often taken for pain and fever relief.
- Ibuprofen: A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) useful for tension headaches and migraines.
- Aspirin: Effective for migraine relief, particularly when taken at the onset of symptoms.
- Naproxen: Another NSAID effective for tension headaches.
- Indomethacin: A prescription-strength NSAID, used for arthritis but also effective for headaches.
- Triptans: A category of drugs, including sumatriptan and others, used for migraine relief.
- CGRP receptor antagonists: New class of drugs for acute migraine treatment, like rimegepant and ubrogepant.
OTC medications can be effective for various headache types, including those related to sinus infections or migraines. It"s important to note that not everyone will respond to all medications, and it may be necessary to try different types to find the most effective treatment for your specific headache.

Prescription Treatments for Severe Cases
For severe or chronic headache cases, prescription treatments may be necessary. These treatments often target specific types of headaches, such as migraines or cluster headaches, and are prescribed by healthcare professionals. It"s important to follow the doctor"s instructions carefully when using these medications.
- Triptans: Used specifically for migraine relief. Examples include sumatriptan, rizatriptan, and others.
- Ergotamines: Effective for severe migraines. Common examples include ergotamine and dihydroergotamine (DHE).
- CGRP Receptor Antagonists: A newer class of drugs for preventing and treating migraines.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications like topiramate and valproic acid, used for migraine prevention.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants can be effective in preventing migraines and tension headaches.
- Botulinum Toxin Injections (Botox): Used for chronic migraine prevention.
- Opioids: Sometimes prescribed for severe cases but generally avoided due to addiction risks.
- Beta-Blockers: Commonly used for migraine prevention.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Also used for migraine prevention.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: A new category of injectable drugs for preventing migraines.
Prescription treatments can be highly effective but may also come with side effects. It is crucial to discuss potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider to ensure the best treatment plan for your specific condition.
Natural Remedies and Supplements
Natural remedies and supplements can be a gentle, yet effective way to manage headaches. They are often used to reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches, especially migraines. It"s important to remember that while natural, these remedies can still interact with other medications and conditions, so consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement is advised.
- Magnesium: Known for its role in nerve transmission and pain relief, magnesium can be particularly effective for migraine prevention.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Shown to help reduce the frequency of migraines in some people.
- Coenzyme Q10: A supplement that may help reduce the frequency of migraines.
- Butterbur: An herb that, in extract form, has been used historically for pain relief and migraine prevention.
- Feverfew: Another herb traditionally used for migraine prevention and treatment.
- Peppermint and Lavender Oil: Applying these essential oils topically may help soothe tension headaches.
- Ginger: Can be effective in reducing migraine severity and duration.
- Hydration: Drinking adequate water can prevent headaches caused by dehydration.
- Yoga and Relaxation Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, or biofeedback can help reduce stress and tension, which can trigger headaches.
- Acupuncture: Some people find relief from headaches, especially migraines, through this traditional Chinese medicine practice.
While these natural remedies can be helpful, it"s important to approach them as part of a comprehensive headache management plan, which might also include lifestyle changes and traditional medical treatments.
READ MORE:
Neurostimulation Devices
Neurostimulation devices represent a cutting-edge approach to headache treatment, especially for migraines and cluster headaches. These devices use various forms of mild electrical or magnetic stimulation to relieve pain. They are non-invasive, generally well-tolerated, and can be an option for those who prefer not to take medication or have found medications ineffective.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): A device that delivers small electrical currents to key areas, such as the temples or neck, to alleviate headache pain.
- Occipital Nerve Stimulation: Involves a small device implanted under the skin to deliver electrical pulses to the occipital nerves, often used for chronic migraine management.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulators: Handheld devices that deliver gentle electrical stimulation to the vagus nerve through the skin, used for both migraine and cluster headache treatment.
- Supraorbital Nerve Stimulation: A device worn on the forehead that targets nerves above the eyes, useful in treating migraines.
- Remote Electrical Neuromodulation (REN): A novel approach where a device stimulates peripheral nerves to induce a pain-inhibiting response in the brain"s pain centers.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if neurostimulation is appropriate for your headache type and severity. These devices are typically used in conjunction with other treatments as part of a comprehensive headache management plan.
Discover empowering strategies to alleviate headaches instantly with our comprehensive guide, blending natural remedies, modern medications, and innovative techniques for fast, effective relief tailored to your unique needs.