Topic kinds of headache: Discover the various kinds of headache, from tension-type to migraines, and learn effective strategies for prevention and relief in this comprehensive guide.
Table of Content
- Which types of headaches are commonly experienced by individuals?
- Overview of Headache Types
- Primary Headaches vs. Secondary Headaches
- Tension-Type Headaches
- Migraines
- Cluster Headaches
- Medication Overuse Headaches
- YOUTUBE: Types and Causes of Headache
- Secondary Headaches and Underlying Conditions
- Diagnosing Different Types of Headaches
- Treatment Options for Various Headaches
- Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Changes
- When to Seek Medical Help for Headaches
Which types of headaches are commonly experienced by individuals?
There are several types of headaches commonly experienced by individuals:
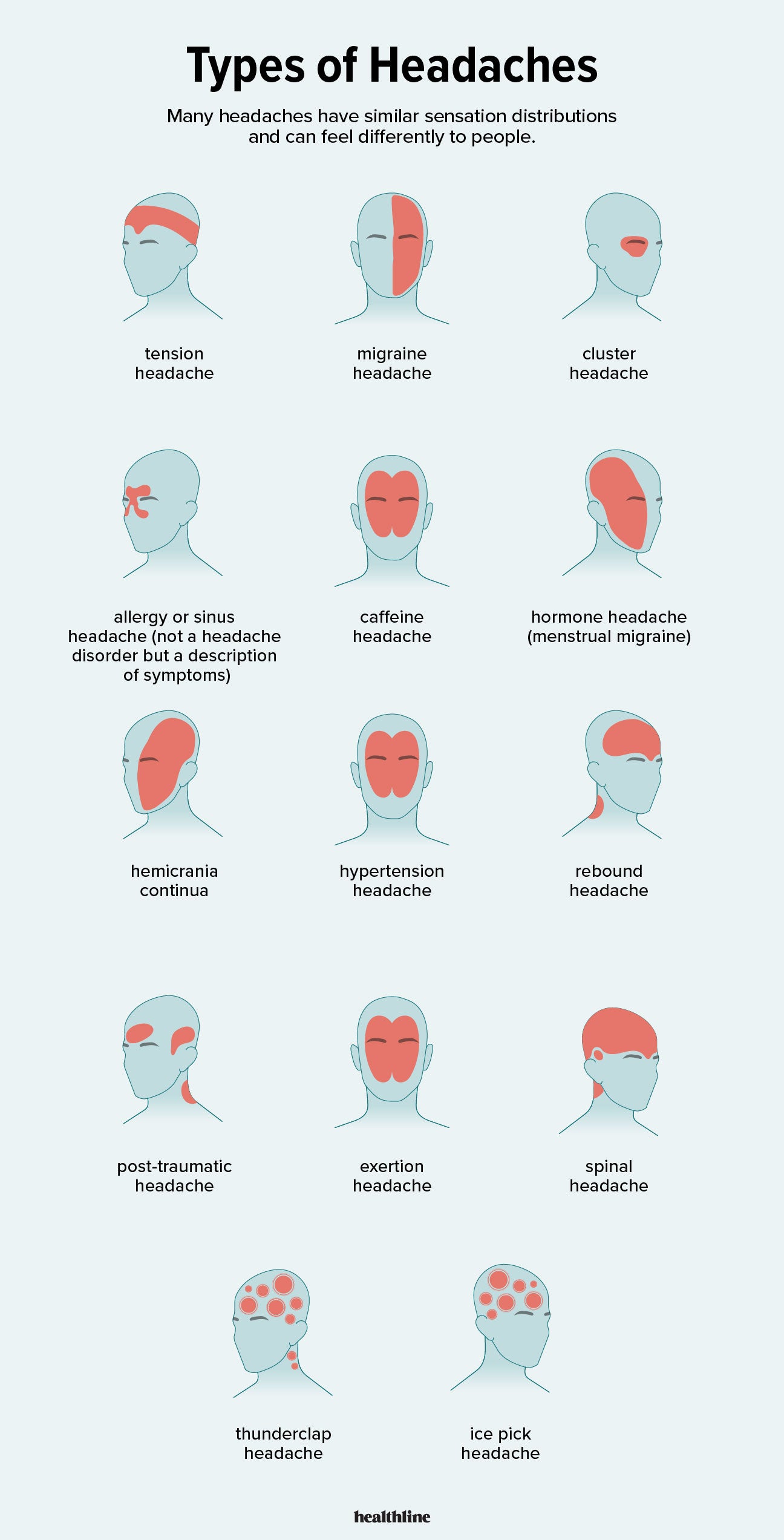
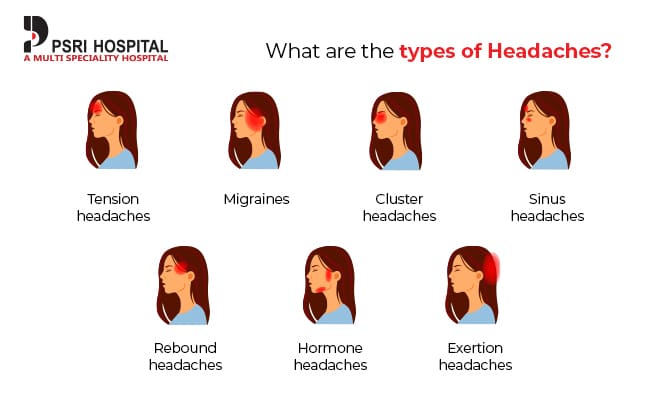
- Tension headache
- Migraine headache
- Cluster headache
- Hemicrania continua
- Ice pick headache
- Thunderclap headache
- Hypnic headache
- Sinus headache
READ MORE:
Overview of Headache Types
Headaches can significantly impact daily life, manifesting in various forms and intensities. Understanding the different types is key to effective management and treatment. Here, we explore the primary categories and characteristics of common headaches.
- Primary Headaches: These are not caused by underlying medical conditions and include tension-type headaches, migraines, and cluster headaches.
- Secondary Headaches: These result from other medical conditions, such as infection, injury, or blood vessel issues, affecting the head.
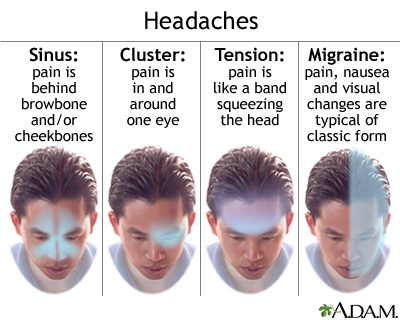
- Tension-Type Headaches: The most common form, characterized by a dull, aching sensation all over the head.
- Migraines: Known for causing severe, throbbing pain on one side of the head, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Cluster Headaches: Intensely painful headaches that occur in clusters or cycles, affecting one side of the head, often around the eye.
Identifying the specific type of headache you"re experiencing is the first step towards finding effective relief. Each type has distinct triggers, symptoms, and treatment approaches.

Primary Headaches vs. Secondary Headaches
Understanding the difference between primary and secondary headaches is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. Primary headaches are stand-alone illnesses caused directly by the overactivity of or problems with pain-sensitive structures in the head. Secondary headaches, on the other hand, are symptoms that happen when another condition stimulates the pain-sensitive nerves of the head.
- Primary Headaches: Include tension-type headaches, migraines, and cluster headaches. They are not symptoms of underlying illness but rather the result of a process in the brain.
- Secondary Headaches: These headaches are symptoms of another health disorder that can range from harmless to potentially life-threatening. Conditions like sinus infection, brain tumor, stroke, and others could lead to secondary headaches.
Key differences include their causes, the way they manifest, and the approaches to treatment. While primary headaches may be chronic and require management strategies, secondary headaches necessitate treating the underlying condition to alleviate the headache.
Tension-Type Headaches
Tension-type headaches are the most common type of primary headache, affecting a vast majority of people at some point in their lives. These headaches are characterized by a dull, aching pain that typically envelops the head, often described as a tight band around the forehead.
- Symptoms: Dull, aching head pain; sensation of tightness or pressure across the forehead or on the sides and back of the head; tenderness on scalp, neck, and shoulder muscles.
- Causes: While the exact cause is not known, tension-type headaches may be triggered by stress, poor posture, or muscle strain.
- Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, stress management, regular physical activity, adequate rest, and proper posture can help manage symptoms.
- Prevention: Identifying and avoiding headache triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and employing relaxation techniques can prevent the occurrence of tension-type headaches.
Although tension-type headaches are generally mild to moderate in intensity and do not significantly hinder daily activities, managing stress and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key to reducing their frequency and severity.
Migraines
Migraines are a type of primary headache known for their intensity and potential to significantly affect quality of life. These headaches are often characterized by a severe throbbing or pulsating pain, typically on one side of the head, and can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound.
- Symptoms: Severe throbbing or pulsating pain on one side of the head, sensitivity to light and sound, nausea, and sometimes visual disturbances known as aura.
- Triggers: Various factors can trigger migraines, including hormonal changes, certain foods and drinks, stress, and changes in sleep patterns.
- Treatment: Treatment options include over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers, anti-nausea medications, and preventive medications to reduce frequency and severity.
- Lifestyle and Home Remedies: Regular sleep, hydration, avoiding known triggers, stress management, and certain dietary supplements may help manage migraines.
- Preventive Strategies: In some cases, doctors may recommend preventive medications or lifestyle changes to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
Migraines require a targeted treatment approach, focusing on prevention, immediate relief, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and improve life quality.
Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are recognized as one of the most painful types of headache. They are called "cluster headaches" because they occur in cyclical patterns or clusters. These headaches are characterized by sudden, severe pain on one side of the head, often around the eye.
- Symptoms: Intense burning or piercing pain behind or around one eye, redness, swelling, and tearing of the eye on the affected side, nasal congestion, and restlessness.
- Causes: The exact cause of cluster headaches is unknown, but the pattern suggests a connection to the body"s biological clock (hypothalamus).
- Treatment: Treatment focuses on relieving pain and preventing future attacks. Options include oxygen therapy, triptans, and preventive medications.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoiding alcohol and smoking during cluster periods can help, as these have been identified as triggers for some individuals.
- Preventive Measures: Verapamil is commonly prescribed to prevent cluster headaches, along with other treatments aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of the attacks.
Due to their intense nature, cluster headaches can be challenging to manage, but with proper treatment and avoidance of triggers, individuals can significantly reduce their impact.

Medication Overuse Headaches
Medication overuse headaches (MOH), also known as rebound headaches, occur from the frequent use of headache medication. While it may seem counterintuitive, the very treatments intended to alleviate headaches can, over time, lead to more frequent or severe headaches if used too often.
- Symptoms: Daily or near-daily headaches, often waking the individual in the early morning; a persistent dull pain with episodes of severe pain; decreased effectiveness of headache medications.
- Causes: Regular, long-term use of medication to treat headache disorders, including over-the-counter and prescription drugs.
- Risk Factors: Risk increases with the frequent use of headache medications, especially when taken more than a few days a week.
- Treatment: The primary treatment involves reducing or stopping the overused medication, a process that should be supervised by a healthcare professional to manage withdrawal symptoms effectively.
- Prevention: Limit the use of headache medications, follow prescribed guidelines, and consult with a healthcare provider for a long-term management plan to prevent headaches without overusing medication.
Addressing MOH is crucial for breaking the cycle of overuse and returning to a pattern of less frequent headaches. A comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, alternative pain management strategies, and possibly preventive medication can help achieve this.
Types and Causes of Headache
Discover the surprising reasons behind your throbbing headaches and learn how to tame the pain once and for all in this informative video on headache causes. Don\'t let those pesky headaches ruin your day any longer!
Types of Headaches
Dive into the fascinating world of headaches as this video explores the different types and symptoms that can leave you feeling miserable. Gain valuable insights and strategies for managing each type of headache in this must-watch video.
Secondary Headaches and Underlying Conditions
Secondary headaches are those caused by an underlying medical condition. Unlike primary headaches, which are diseases in their own right, secondary headaches are symptoms of another issue affecting the body. Identifying and treating the root cause is crucial for relief.
- Common Causes: These can include sinus infection, head injury, stroke, brain tumors, medication overuse, and high blood pressure.
- Symptoms: Vary widely depending on the underlying condition, but may include a sudden onset of headache, a change in headache pattern, or headaches accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, neck stiffness, confusion, or vision changes.
- Diagnosis: Thorough medical evaluation including history taking, physical examination, and possibly imaging tests like MRI or CT scans to identify the underlying cause.
- Treatment: Focused on the underlying condition. Successfully treating the primary condition often alleviates the headache.
- Prevention: In some cases, managing the underlying condition or modifying risk factors can prevent secondary headaches.
Understanding the cause of secondary headaches is essential for effective treatment. Collaboration between healthcare providers and patients is key to identifying and addressing the underlying condition.

Diagnosing Different Types of Headaches
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective headache management. A comprehensive approach, combining patient history, physical examination, and sometimes diagnostic tests, helps differentiate between various types of headaches and identify any underlying conditions.
- Patient History: This includes the pattern of headaches, their frequency, duration, symptoms, and any known triggers. A detailed history helps narrow down the type of headache.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination, including checking for signs of infection, neurological deficits, or other physical clues that might indicate the cause of the headache.
- Diagnostic Tests: While not always necessary, tests such as MRI, CT scans, or blood tests may be required to rule out secondary causes of headaches.
- Specialist Referral: In certain cases, referral to a neurologist or other specialists might be necessary for further evaluation and treatment.
- Headache Diaries: Keeping a headache diary can be invaluable for diagnosing the type of headache. It can help identify patterns, triggers, and the effectiveness of treatments.
Diagnosing headaches accurately is a step-by-step process that may require patience and cooperation between the patient and healthcare provider. It is the foundation for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual"s needs.
Treatment Options for Various Headaches
The treatment of headaches varies significantly depending on the type of headache, its severity, and the individual"s specific needs. A combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and other therapies often provides the most effective relief.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, adequate sleep, hydration, stress management, and avoiding known triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, are commonly used for mild headaches. Prescription medications, including triptans for migraines and oxygen therapy for cluster headaches, are available for more severe cases.
- Preventive Treatments: For those with frequent or severe headaches, preventive medications can reduce the frequency, severity, and duration of headaches. These include beta-blockers, antidepressants, and anti-seizure medications.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and cognitive-behavioral therapy have been found to be effective for some people in managing headache pain and reducing recurrence.
- Neuromodulation Techniques: For treatment-resistant headaches, techniques such as nerve stimulation may offer relief.
Effective headache treatment is a personalized process that might require trying different methods to find what works best for the individual. Consultation with healthcare professionals is essential to devise a safe and effective treatment strategy.
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing headaches involves a combination of strategies tailored to individual needs and circumstances. Lifestyle changes, identifying and avoiding triggers, and sometimes medication can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: Common triggers include certain foods, stress, changes in sleep patterns, and environmental factors. Keeping a headache diary can help identify personal triggers.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce the frequency and severity of headaches by relieving stress and improving overall health.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and biofeedback can help manage stress levels and reduce the likelihood of stress-induced headaches.
- Adequate Sleep: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and ensuring sufficient sleep can help prevent headaches.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet and staying hydrated can reduce headache occurrences. Avoiding foods that trigger headaches is also crucial.
- Limited Caffeine and Alcohol: Reducing the intake of caffeine and alcohol can help prevent certain types of headaches.
- Medication Management: For those prone to frequent headaches, preventive medications prescribed by a healthcare provider can be effective.
Adopting a proactive approach to headache prevention can lead to a significant improvement in quality of life. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive prevention plan.
When to Seek Medical Help for Headaches
While most headaches are not indicative of a serious underlying condition, certain situations warrant prompt medical attention. Recognizing the signs that a headache may be symptomatic of a more serious issue is essential for timely and effective treatment.
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is severe, often described as a "thunderclap" headache, can be a sign of a serious condition such as an aneurysm.
- Changes in Pattern: Significant changes in the frequency, severity, or characteristics of your headaches should be evaluated.
- Accompanied by Other Symptoms: Headaches accompanied by fever, neck stiffness, confusion, seizures, double vision, weakness, or trouble speaking can indicate a serious condition requiring immediate attention.
- After a Head Injury: Headaches that develop after a head injury, especially if they worsen, may indicate a concussion or other injury.
- Impact on Daily Life: Headaches that regularly affect your ability to work, sleep, or participate in daily activities should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
- Not Responsive to Medication: If your headache does not respond to over-the-counter medications or if you find yourself using headache medication more than twice a week, seek medical advice.
Consulting a healthcare provider for headaches that are unusual, severe, or persistent can help ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. Don"t hesitate to seek medical help if you"re concerned about your headaches.
Exploring the various kinds of headaches enriches our understanding and empowers us to manage them effectively, ensuring a better quality of life and well-being.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-PaigeMcLaughlin-WhatisaClusterHeadache-Standard-87c962b6a28d4b1ab0359ed3ae5b696f.jpg)