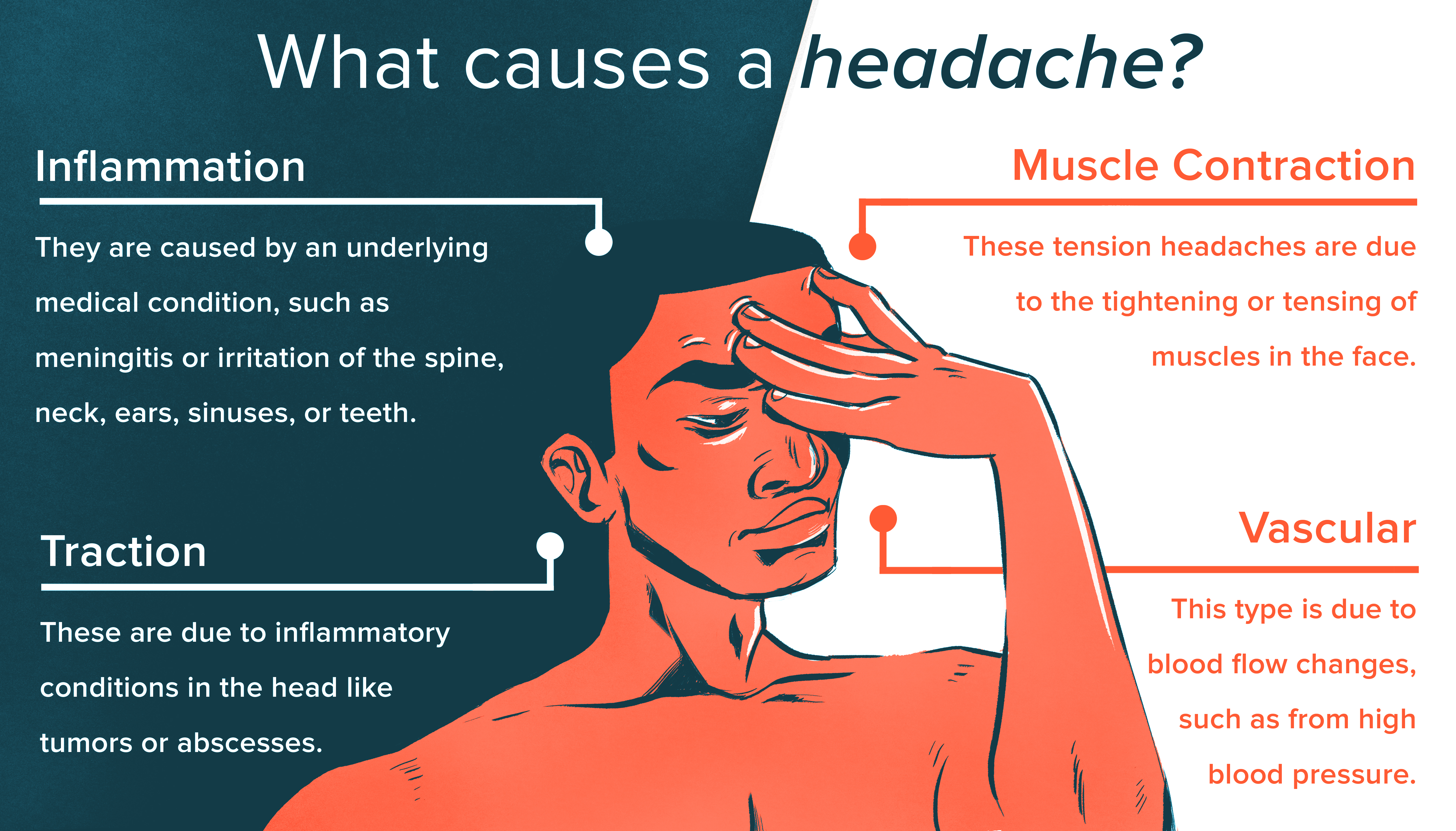
Topic what makes you get a headache: Discover the myriad factors behind headaches, from stress and diet to environmental triggers. This guide illuminates causes and offers proactive solutions to keep headaches at bay, enhancing your well-being.
Table of Content
- What are the potential triggers for headaches?
- Altitude-Induced Headaches
- Travel-Related Stress
- Work-Related Headaches
- Dehydration and Dietary Factors
- Physical and Emotional Stress
- Sleep Patterns and Headaches
- YOUTUBE: 5 Fast Ways to Fix Your Headache – Dr. Mandell
- Environmental Triggers
- Medical Conditions and Headaches
- Medications and Chemicals
- Preventative Measures and Treatments
What are the potential triggers for headaches?
Some potential triggers for headaches include:
- Stress
- Diet factors, such as certain foods or caffeine withdrawal
- Alcohol, particularly red wine
- Processed meats that contain nitrates
- Changes in sleep patterns or lack of sleep
- Poor posture
These triggers can vary from person to person, and what causes a headache for one individual may not affect another. It\'s important to identify your own personal triggers and try to avoid or manage them to reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches.
READ MORE:
Altitude-Induced Headaches
Altitude-induced headaches are a common ailment affecting individuals who travel to high elevations. These headaches are a primary symptom of acute mountain sickness (AMS), resulting from the body"s response to the lower oxygen levels found at high altitudes. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial for travelers seeking to enjoy high-altitude destinations without discomfort.
- Cause: The primary cause of altitude-induced headaches is the reduced oxygen saturation in the blood, which can lead to hypoxia. This condition triggers blood vessels in the brain to dilate, leading to increased blood flow and swelling, which can cause pressure and pain.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include a throbbing headache that typically worsens at night and when waking up. It may be accompanied by nausea, dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
- Prevention: To prevent altitude-induced headaches, individuals can ascend gradually to high altitudes to allow their bodies to acclimatize. Staying hydrated, avoiding strenuous exercise early on, and eating a balanced diet can also help.
- Treatment: Treatment options include over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. In more severe cases, prescription medications like acetazolamide can help reduce symptoms by accelerating acclimatization.
For those planning to travel to high altitudes, it"s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and potential pre-acclimatization strategies. Taking proactive steps can significantly enhance comfort and enjoyment of high-altitude adventures.

Travel-Related Stress
Travel, while exciting, can also be a significant source of stress, leading to headaches for many people. Factors such as changes in routine, the physical demands of travel, and sensory overload contribute to this condition. Understanding and managing these triggers can help minimize travel-related headaches and enhance the overall travel experience.
- Planning Ahead: Organizing your itinerary, packing essentials early, and ensuring all travel documents are ready can significantly reduce pre-travel stress.
- Staying Hydrated: Dehydration is a common issue during travel, especially on long flights. Drinking plenty of water can help prevent headaches.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: Eating nutritious meals and avoiding excessive caffeine or alcohol can stabilize your energy levels and reduce the risk of headaches.
- Getting Adequate Rest: Lack of sleep can exacerbate stress and lead to headaches. Try to maintain a regular sleep schedule before and during your trip.
- Managing Sensory Overload: Airports and crowded tourist spots can be overwhelming. Using noise-cancelling headphones and taking breaks can help manage sensory input.
- Practicing Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, or gentle stretching exercises can help reduce stress levels during travel.
By addressing these aspects of travel, individuals can significantly reduce their exposure to stress-induced headaches and make their journeys more enjoyable. Embracing a mindful approach to travel, focusing on self-care, and adjusting expectations can transform the travel experience into a more positive and headache-free adventure.
Work-Related Headaches
Work-related headaches are a frequent complaint among professionals, often resulting from a combination of stress, poor posture, and prolonged screen time. Recognizing and addressing the factors contributing to these headaches can lead to more productive and pain-free workdays.
- Stress Management: Stress is a primary cause of tension headaches. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular breaks can alleviate mental strain.
- Ergonomic Workspace: Adjusting your workstation to promote good posture can prevent strain on your neck and shoulders, reducing the risk of headaches.
- Regular Breaks: Taking short breaks to stretch and look away from the screen helps to prevent eye strain and tension headaches.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Staying hydrated and eating balanced meals can stave off headaches caused by dehydration or poor diet.
- Proper Lighting: Ensuring your workspace is well-lit without glare can reduce eye strain and headaches.
- Limiting Caffeine: While small amounts of caffeine can alleviate headache symptoms, excessive consumption can lead to rebound headaches.
By proactively managing these aspects of your work environment and habits, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of work-related headaches. Implementing these strategies not only benefits your physical well-being but also enhances focus and productivity.

Dehydration and Dietary Factors
Dehydration and certain dietary habits are well-known triggers for headaches. Understanding how hydration and nutrition impact headache occurrence can guide you towards making choices that may reduce headache frequency and severity.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake is crucial for preventing dehydration-related headaches. Drinking water regularly throughout the day is recommended, especially in hot weather or during physical activity.
- Electrolyte Balance: Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, play a vital role in hydration. Consuming electrolyte-rich foods or beverages can help maintain balance and prevent headaches.
- Caffeine Consumption: While caffeine can offer temporary headache relief, overuse can lead to rebound headaches. Moderation is key to avoiding this cycle.
- Food Triggers: Certain foods may trigger headaches in sensitive individuals. Common culprits include aged cheeses, processed meats, alcohol, and foods containing MSG or artificial sweeteners.
- Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and may reduce headache occurrence.
- Meal Timing: Regular, balanced meals help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Skipping meals or fasting can trigger headaches in some people.
By focusing on hydration and mindful eating, you can potentially lessen the frequency and severity of headaches. Tailoring your diet to suit your body"s needs and observing how different foods affect you personally can be a proactive way to manage headache triggers.
Physical and Emotional Stress
Both physical and emotional stress are significant contributors to headache development. Understanding the relationship between stress and headaches can empower individuals to implement effective management strategies.
- Recognition of Stressors: Identifying sources of stress, whether work-related, personal, or environmental, is the first step towards managing stress-induced headaches.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can reduce stress and tension, lowering the likelihood of stress-related headaches. Activities like walking, yoga, or swimming are particularly beneficial.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help alleviate emotional stress and prevent headaches.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring sufficient sleep is crucial for stress management. Lack of sleep can exacerbate stress and increase the frequency of headaches.
- Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Developing healthy ways to cope with stress, such as talking to a friend, journaling, or engaging in a hobby, can reduce its impact on your well-being.
- Seeking Professional Help: If stress and headaches are significantly impacting your life, consulting with a healthcare provider or therapist can provide additional strategies and support.
By addressing both physical and emotional stress through comprehensive strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the occurrence of stress-related headaches and enhance their overall quality of life.
Sleep Patterns and Headaches
Poor sleep patterns are closely linked to the development of headaches, including both tension-type headaches and migraines. Understanding and optimizing your sleep habits can play a critical role in reducing headache frequency and severity.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body"s internal clock, reducing the likelihood of headaches.
- Quality Sleep Environment: Ensuring a comfortable, quiet, and dark sleep environment can improve sleep quality. Consider using blackout curtains, eye masks, and white noise machines if necessary.
- Avoid Stimulants: Caffeine and nicotine can disrupt sleep patterns if consumed late in the day. Try to limit their intake in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Limited Screen Time: The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with your ability to fall asleep. Limiting screen time before bed can help prevent this issue.
- Pre-sleep Routine: Establishing a relaxing pre-sleep routine, such as reading or taking a warm bath, can signal to your body that it"s time to wind down.
- Address Sleep Disorders: Conditions such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless legs syndrome can disrupt sleep and increase headache risk. Seeking treatment for these disorders can improve sleep quality and reduce headaches.
By prioritizing healthy sleep habits, you can significantly impact your overall well-being and decrease the frequency and intensity of headaches related to sleep patterns.
5 Fast Ways to Fix Your Headache – Dr. Mandell
Are persistent headaches making your days unbearable? Discover natural remedies and effective techniques to quickly relieve headaches and gain back control of your life. Watch our video now!
What Causes Headache? | The Dr. Binocs Show – Best Learning Videos For Kids | Peekaboo Kidz
Curious about the causes behind those recurring headaches? Our video will unveil the surprising triggers that could be sabotaging your well-being. Don\'t miss out on this eye-opening exploration of headache causes!
Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers play a significant role in the onset of headaches for many individuals. These triggers can vary widely from person to person, but understanding common environmental factors can help in identifying and avoiding potential headache triggers.
- Lighting: Bright or flickering lights, including sunlight and fluorescent lights, can induce headaches. Using soft, natural light when possible can mitigate this trigger.
- Weather Changes: Shifts in barometric pressure, temperature, and humidity are known to trigger headaches in some people. Monitoring weather changes and taking preventive measures can be helpful.
- Air Quality: Poor air quality, including pollution, smoke, and strong odors, can also lead to headaches. Ensuring good ventilation and avoiding known irritants can reduce this risk.
- Noise: Loud or persistent noise can trigger tension headaches and migraines. Using earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones can offer relief in noisy environments.
- Visual Strain: Extended periods of screen time or exposure to glare can strain the eyes and lead to headaches. Taking regular breaks and using anti-glare screens can help.
- Altitude: As previously discussed, high altitudes can trigger headaches due to lower oxygen levels. Acclimatization and hydration are key in these environments.
By recognizing and minimizing exposure to these environmental triggers, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headache episodes, leading to improved overall well-being.
Medical Conditions and Headaches
Various medical conditions can lead to headaches, acting either as direct causes or significant contributors. Identifying underlying health issues is crucial for effective headache management and treatment.
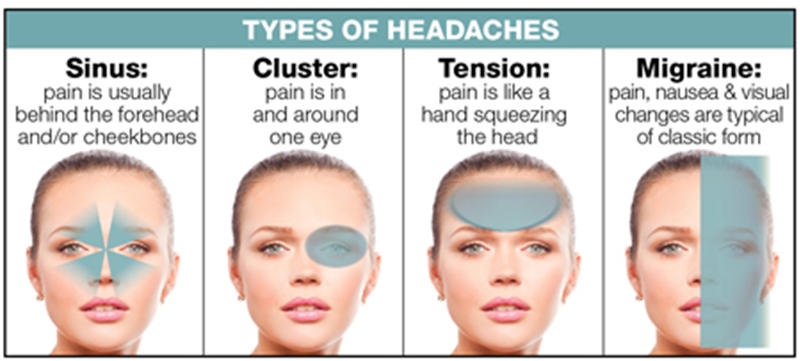
- Migraines: A neurological condition characterized by intense, often unilateral headaches accompanied by nausea, light and sound sensitivity.
- Tension-Type Headaches: The most common headache disorder, marked by mild to moderate pain, often described as a tight band around the head.
- Cluster Headaches: Known for their severe pain around one eye or temple, occurring in groups or "clusters" over weeks or months.
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinus cavities can cause pressure and pain in the forehead, cheeks, and nasal areas, leading to sinus headaches.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can lead to headaches, especially when reaching critical levels, often felt in the morning.
- Dehydration: A lack of adequate hydration can lead to a dehydration headache, characterized by a dull, widespread ache.
- Sleep Disorders: Conditions such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless legs syndrome can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to headaches.
Addressing these medical conditions with the help of healthcare professionals can significantly reduce headache frequency and severity, improving quality of life.
Medications and Chemicals
Medications and certain chemicals can induce headaches either as a side effect or due to withdrawal after long-term use. Understanding the substances that can contribute to headaches is important for managing and preventing them effectively.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Frequent use of pain relievers like ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen can lead to rebound headaches when they are stopped abruptly.
- Prescription Medications: Certain prescription drugs, including those for hypertension or depression, may have headaches as a side effect.
- Caffeine: Both excessive consumption and sudden withdrawal from caffeine can cause headaches.
- Alcohol: Headaches are a common symptom of alcohol hangovers, attributed to dehydration and the body"s reaction to toxins in alcoholic beverages.
- Nitrites and Nitrates: Found in processed meats, these preservatives can dilate blood vessels and cause headaches in some people.
- Monosodium Glutamate (MSG): This food additive, found in some processed foods and restaurant meals, can trigger headaches in sensitive individuals.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Aspartame, a common artificial sweetener, has been linked to headaches in some people.
Being aware of these triggers and monitoring your response to certain substances can help in reducing the incidence of headaches. Consulting with a healthcare provider is recommended for headaches induced by medication or chemical sensitivities.

READ MORE:
Preventative Measures and Treatments
Effective management and prevention of headaches involve a combination of lifestyle adjustments, home remedies, and medical treatments. Tailoring these strategies to your specific needs can significantly reduce both the frequency and severity of headaches.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and sufficient sleep are foundational to preventing headaches.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and reduce the occurrence of stress-induced headaches.
- Environmental Adjustments: Minimizing exposure to known headache triggers such as bright lights, loud noises, and strong odors can prevent onset.
- Medication Management: Overuse of headache medication can lead to rebound headaches. It"s important to follow a doctor’s advice on medication use and explore preventative medications if headaches are frequent.
- Regular Medical Checkups: For those with chronic headaches, regular checkups with a healthcare provider can help monitor and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and cognitive behavioral therapy have shown effectiveness in treating and preventing certain types of headaches.
- Hydration and Diet: Avoiding dehydration and potential food triggers can play a crucial role in headache prevention.
By integrating these preventative measures and treatments into your daily routine, you can achieve better control over headaches and improve your overall quality of life.
Understanding the myriad causes of headaches and implementing tailored preventative measures can greatly enhance your life quality. Embrace these insights for a healthier, more vibrant lifestyle free from the shadows of headaches.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Natural-Remedies-for-Managing-Headaches_Paige-McLaughlin_Final-461a780622884c479edf3dc01234692c.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Getting-Rid-of-a-Migraine_Illustrator_Ellen-Lindner_Final-a245985cbf4645a7874d573991fb6cbb.jpg)