Topic cervicogenic headache: Discover the essentials of cervicogenic headache, a prevalent cause of chronic pain, focusing on its symptoms, diagnosis, and effective treatment strategies for lasting relief.
Table of Content
- What are the causes and symptoms of cervicogenic headaches?
- Diagnosis and Treatment
- Management Strategies
- Interventional Treatments
- Additional Considerations
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Cervicogenic Headache
- Understanding Cervicogenic Headaches
- Signs and Symptoms
- Causes and Diagnosis
- Treatment Options
- Physical Therapy and Exercises
- Managing Pain and Preventing Recurrence
- Differential Diagnosis
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Conclusion and Patient Education
What are the causes and symptoms of cervicogenic headaches?
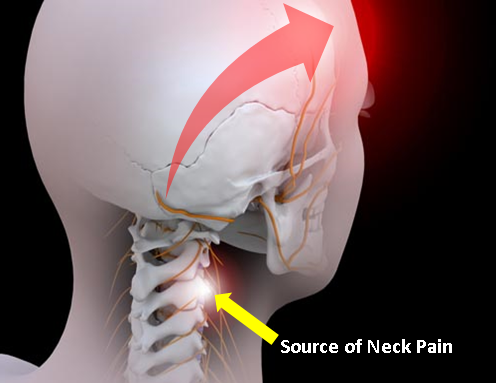
A cervicogenic headache (CGH) is a type of headache that originates from the cervical spine (neck) and is referred to the head. It is important to understand the causes and symptoms of cervicogenic headaches:
Causes of Cervicogenic Headaches:
- Trauma or injury to the neck, such as whiplash
- Arthritis or degenerative changes in the cervical spine
- Herniated or bulging discs in the neck
- Poor posture and muscle imbalances
- Tension in the neck and shoulder muscles
- Abnormalities in the structure of the neck
- Inflammation of the cervical nerves or blood vessels
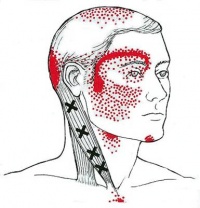
Symptoms of Cervicogenic Headaches:
- Unilateral (one-sided) headache pain
- Pain starting from the neck and spreading to the head
- Continuous, steady pain without throbbing
- Pain worsens with certain neck movements or positions
- Pain triggered by coughing, sneezing, or taking a deep breath
- Neck stiffness and limited range of motion
- Tenderness or sensitivity in the neck and shoulder area
Cervicogenic headaches can often be misdiagnosed as migraines or tension headaches, as the symptoms can overlap. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan based on the underlying cause.
READ MORE:
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in identifying lesions in the cervical spine or neck tissues indicative of cervicogenic headaches. It is essential to differentiate these headaches from migraines and traumatic brain injuries during evaluation.
Management Strategies
Effective management involves a combination of interventions, including moist heat application, spinal and cervical manipulations, neck massages, and specifically tailored neck exercises. Craniocervical flexion exercises, for instance, have been shown to improve muscular stability in the head and neck region, potentially reducing pain.
Interventional Treatments
Interventional treatments, such as cervical epidural steroid injections, have shown benefits in managing pain associated with cervicogenic headaches by addressing nerve root and microvascular inflammation. These interventions are relatively safe and can significantly reduce the need for daily NSAID use.
Additional Considerations
- Differential diagnosis is crucial to rule out conditions like occipital neuralgia, tension-type headaches, and migraines.
- Long-term management may require regular monitoring and possibly psychotherapy to address the chronic nature of the condition.
- Physical therapy, including manipulative therapy and therapeutic exercise, is considered the first line of treatment.
Conclusion
While cervicogenic headaches can be debilitating, proper diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Early intervention and a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies are key to managing this condition effectively.

Cervicogenic Headache
Discover the fascinating world of cervicogenic pain and its causes in this eye-opening video. Gain a deeper understanding of how this condition can affect your daily life and find out effective ways to alleviate the discomfort.
Cervicogenic Headache Symptoms
Dive into a comprehensive video that unravels the complexity of symptoms associated with various health conditions. Learn about their underlying causes and uncover practical tips to manage these symptoms, empowering you to live a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
Understanding Cervicogenic Headaches
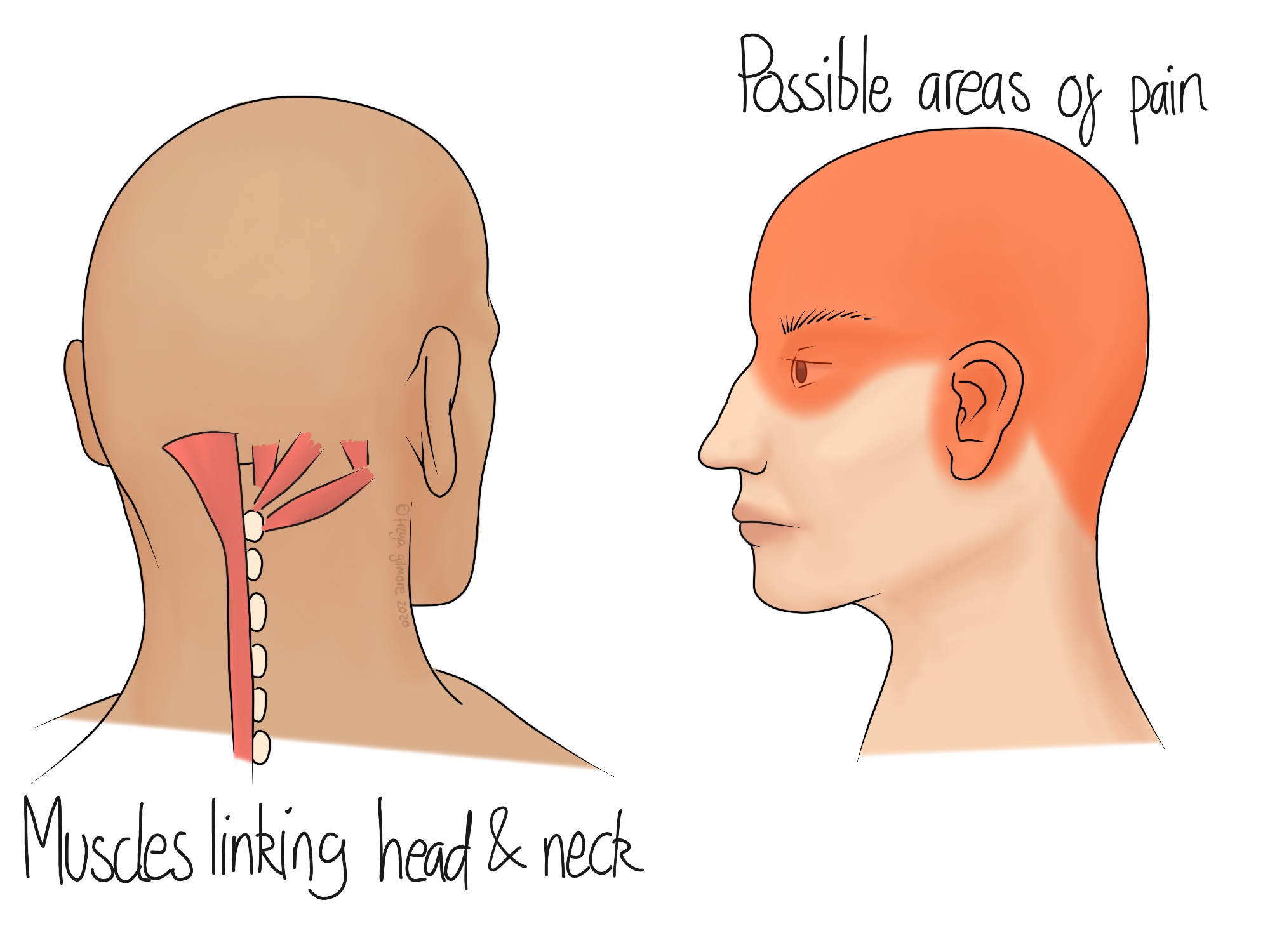
Cervicogenic headaches are a type of secondary headache, meaning they are caused by underlying conditions, particularly issues related to the neck. Unlike tension headaches or migraines, cervicogenic headaches originate from the cervical spine or associated structures, including discs, bones, or muscles.
- Origin: These headaches are referred pain from the neck to the head. The pain can be triggered by neck movement, posture, or specific neck positions.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include unilateral headache, pain radiating from the back to the front of the head, neck stiffness, and pain that worsens with certain neck movements or positions.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a physical examination, patient history, and sometimes imaging tests to rule out other causes of headache. Diagnostic nerve blocks can also be a part of the assessment.
- Treatment: Management strategies focus on treating the source of the headache in the neck. This can include physical therapy, chiropractic care, medication, and in some cases, interventional procedures like nerve blocks or injections.
Understanding the nature of cervicogenic headaches is crucial for effective management and relief. Since these headaches stem from physical issues in the neck, targeted treatments aimed at the cervical spine can offer significant improvements.
Signs and Symptoms
Cervicogenic headaches are characterized by specific signs and symptoms that differentiate them from other types of headaches. Recognizing these can help in seeking appropriate treatment and management strategies.
- Pain on one side of the head: Unlike tension headaches, cervicogenic headaches typically cause pain on one side of the head, originating from the neck and spreading towards the front.
- Neck movement or pressure triggers pain: Pain may worsen with certain neck movements or when pressure is applied to specific areas of the neck or base of the skull.
- Reduced range of motion in the neck: Individuals may experience stiffness or a reduced ability to move the neck, often accompanied by pain during attempted movements.
- Shoulder or arm pain: Pain may extend from the neck into the shoulders or arms on the same side as the headache.
- Sensitivity to light and noise: While not as common as in migraines, some individuals may experience sensitivity to light and noise.
- Blurred vision or dizziness: In some cases, cervicogenic headaches can cause blurred vision or a sense of dizziness.
Identifying these symptoms is crucial for diagnosis and treatment, as cervicogenic headaches require specific management approaches targeting the cervical spine and its associated structures.

Causes and Diagnosis
Cervicogenic headaches stem from various causes related to the cervical spine and its components. Accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment, involving a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests.
- Causes:
- Cervical degeneration: Aging or wear and tear leading to arthritis or spondylosis.
- Cervical disc problems: Herniated or bulging discs pressing on nerves.
- Whiplash injuries: Sudden movement causing neck strain and injuries.
- Postural issues: Long-term poor posture straining cervical spine structures.
- Diagnosis:
- Medical history: Discussing symptoms, history of neck pain or injuries.
- Physical examination: Assessing neck motion, pain trigger points.
- Imaging tests: MRI or CT scans to identify structural issues in the cervical spine.
- Nerve block injections: Temporarily relieving pain to confirm the source.
Understanding the underlying cause of cervicogenic headaches is crucial for developing a targeted treatment plan. Diagnosis may require a multi-faceted approach to accurately identify the source of pain.
Treatment Options
Treating cervicogenic headaches involves a multi-disciplinary approach, focusing on relieving pain, restoring function, and addressing the underlying causes. Here are some of the most effective treatment options:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises to improve neck strength, flexibility, and posture can significantly reduce symptoms.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or muscle relaxants may be used to manage pain and inflammation.
- Manual Therapies: Chiropractic adjustments, osteopathy, or spinal manipulation can help alleviate symptoms by improving spinal function and reducing stress on the cervical spine.
- Injections: Nerve blocks or steroid injections directly into the affected cervical spine area can provide temporary relief.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the structural issues causing the headache.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Changes in daily activities, ergonomics, and posture can help prevent the recurrence of headaches.
Successful management of cervicogenic headaches often requires a combination of treatments tailored to the individual"s specific condition and symptoms.

Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy and specific exercises play a crucial role in the treatment of cervicogenic headaches by improving posture, increasing flexibility, and strengthening the muscles around the neck and shoulders. Here"s a guide to effective strategies:
- Neck Stretches: Gentle stretching exercises can help relieve tension and stiffness in the neck muscles.
- Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the muscles in the neck, shoulders, and upper back can support the cervical spine and reduce the frequency of headaches.
- Posture Training: Correcting posture, especially during activities that involve prolonged sitting or standing, can significantly reduce strain on the neck and prevent headaches.
- Mobilization Techniques: Physical therapists may use hands-on techniques to improve movement in the neck and upper back, enhancing flexibility and reducing pain.
- Aerobic Exercise: Regular low-impact aerobic exercise, such as walking or swimming, can improve overall physical health and reduce the risk of headaches.
Working with a physical therapist to develop a personalized exercise program is essential for the best outcomes. Consistency and proper technique are key to effectively managing cervicogenic headaches through physical therapy and exercise.
Managing Pain and Preventing Recurrence
Effective management of cervicogenic headache pain and prevention of its recurrence involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both symptoms and underlying causes. Here are key strategies to consider:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular, gentle exercises tailored to neck strength and flexibility can help manage pain and prevent future episodes.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Making ergonomic changes to your work and living environments can reduce neck strain and alleviate pain.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress, which is often a trigger for headaches.
- Nutrition and Hydration: Maintaining a healthy diet and staying hydrated can impact overall health and potentially reduce headache frequency.
- Sleep Hygiene: Ensuring adequate and quality sleep can help in the overall management of pain and prevent headaches.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Ongoing consultation with healthcare providers is crucial for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
By incorporating these strategies into daily life, individuals can effectively manage cervicogenic headache pain and reduce the likelihood of recurrence, leading to improved quality of life.
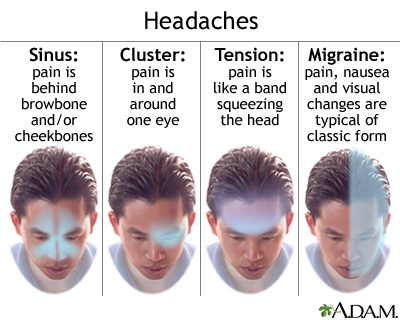
Differential Diagnosis
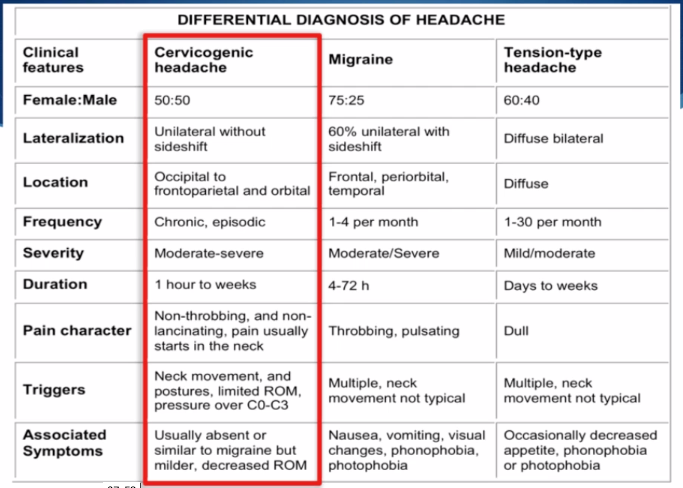
Distinguishing cervicogenic headache from other types of headaches is critical for effective treatment. The differential diagnosis process involves ruling out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms. Here are some key considerations:
- Migraines: Migraines often come with nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound, which are less common in cervicogenic headaches.
- Tension-Type Headaches: These headaches typically feature a band-like pressure around the head, not necessarily originating from the neck.
- Cluster Headaches: Characterized by severe, unilateral pain around the eye, these headaches occur in cyclical patterns or clusters.
- Occipital Neuralgia: This condition involves sharp, jabbing pain in the back of the head and neck, stemming from the occipital nerves.
- Secondary Headaches: Headaches resulting from other medical conditions, such as infection or high blood pressure, must also be considered.
Accurate diagnosis often requires comprehensive evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests. Identifying the precise cause of headache is crucial for selecting the appropriate treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many headaches can be managed with at-home treatments or lifestyle adjustments, certain symptoms associated with cervicogenic headaches may warrant prompt medical attention. Understanding when to seek help is crucial for your health and well-being.
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is severely painful can be a sign of a more serious condition.
- Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: If your headache persists longer than usual or worsens over time, it"s important to consult a healthcare provider.
- Neurological Symptoms: Symptoms such as confusion, difficulty speaking, vision changes, or weakness in the arms or legs should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
- Impact on Daily Life: Headaches that significantly impact your ability to perform daily tasks or enjoy life should be assessed by a professional.
- After Head Injury: If your headache follows a head injury, even if minor, it"s important to get evaluated to rule out concussion or other injury.
Early consultation with a healthcare provider can lead to a proper diagnosis and an effective treatment plan, ensuring the best possible outcomes for individuals suffering from cervicogenic headaches.
READ MORE:
Conclusion and Patient Education
Cervicogenic headaches, while challenging, can be effectively managed with the right approach and understanding. Educating patients about their condition is crucial for successful treatment and improving quality of life. Here are some key takeaways:
- Understanding Your Condition: Knowledge about cervicogenic headaches, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options, empowers patients to take an active role in their care.
- Comprehensive Treatment Plan: A multi-disciplinary approach, incorporating physical therapy, medication, lifestyle adjustments, and possibly interventional treatments, offers the best chance for relief.
- Regular Follow-Up: Ongoing communication with healthcare providers ensures that treatments are effective and adjusted as necessary.
- Self-Care Strategies: Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining good posture, and practicing stress-reduction techniques can help manage symptoms and prevent recurrences.
- Seek Support: Living with chronic headaches can be difficult. Support groups or counseling services can offer emotional support and additional coping strategies.
By staying informed and actively participating in treatment decisions, patients with cervicogenic headaches can achieve significant improvements in their symptoms and overall well-being.
Embracing a comprehensive approach to understanding and managing cervicogenic headaches can significantly enhance quality of life. With the right knowledge and treatments, overcoming this condition is within reach, promising a path to relief and well-being.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-PaigeMcLaughlin-WhatisaClusterHeadache-Standard-87c962b6a28d4b1ab0359ed3ae5b696f.jpg)