Topic headache back of head: Discover effective strategies for managing headaches at the back of the head, understanding their causes, and finding relief through practical tips and medical insights.
Table of Content
- What are the common causes of headaches in the back of the head?
- Common Causes of Headache at the Back of the Head
- Symptoms Associated with Headache at the Back of the Head
- When to See a Doctor for Headache at the Back of the Head
- Treatment Options for Headache at the Back of the Head
- YOUTUBE: Tips for Relieving Headaches at the Back of Your Head
- Prevention Tips for Headache at the Back of the Head
- Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- Understanding Occipital Neuralgia
- Tension Headaches and Their Management
- The Role of Posture in Headaches at the Back of the Head
- When Headache at the Back of the Head Indicates a Serious Condition
What are the common causes of headaches in the back of the head?
Common causes of headaches in the back of the head include:
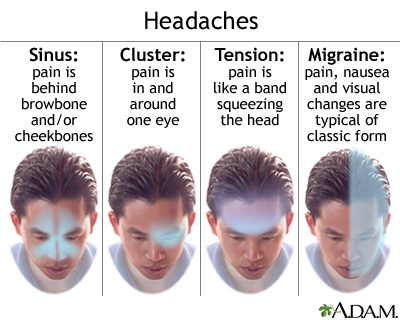
- Tension headaches: These are the most common type of headache and are often caused by muscle tension or stress. Tension headaches can cause pain or pressure in the back of the head or neck.
- Migraine headaches: Migraines can cause pain at the base of the skull or in the back of the head. They are typically characterized by moderate to severe throbbing pain, sensitivity to light and sound, and may be accompanied by nausea or aura.
- Cervicogenic headaches: These headaches stem from issues in the neck or upper spine. They can cause pain in the back of the head that may radiate to the forehead or temples.
- Occipital neuralgia: This condition involves irritation or inflammation of the occipital nerves, which run up the back of the head. It can cause sharp, shooting pain in the back of the head.
- Arthritis headache: Arthritis in the neck or upper spine can lead to headaches at the back of the head that worsen with movement.
- Low-pressure headaches: These occur when the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid surrounding the brain is too low, resulting in headaches at the back of the head that are often worsened by standing upright.
- Medication overuse: Overusing pain relievers or migraine medications can lead to rebound headaches, which may cause pain in the back of the head.
READ MORE:
Common Causes of Headache at the Back of the Head
Headaches at the back of the head can arise from a variety of causes, each requiring specific attention for effective management. Understanding these causes is the first step towards relief.
- Tension Headaches: Often resulting from stress, poor posture, or muscle strain, tension headaches produce a dull, aching sensation around the back of the head and neck.
- Occipital Neuralgia: This condition involves the occipital nerves, leading to sharp, jabbing pains in the back of the head that can mimic the shock-like sensation of electric shocks.
- Cervicogenic Headaches: Stemming from issues within the cervical spine, these headaches are felt at the back of the head, originating from the neck and often associated with neck movement or posture.
- Migraine: While migraines are typically known for affecting the front or side of the head, they can also cause pain at the back of the head, accompanied by sensitivity to light, sound, or nausea.
- Cluster Headaches: Although less common, cluster headaches can cause intense burning or piercing pain at the back of the head, typically occurring in cyclical patterns or clusters.
Identifying the specific cause of your headache is crucial for finding the most effective treatment. Lifestyle changes, medication, physical therapy, or professional medical advice may be recommended based on the underlying cause.

Symptoms Associated with Headache at the Back of the Head
Symptoms accompanying headaches at the back of the head can vary widely, providing clues to their underlying causes. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Dull, Aching Pain: Often associated with tension headaches, this symptom is characterized by a constant, mild to moderate pain that can feel like a tight band around the head.
- Sharp, Stabbing Pain: Symptoms of occipital neuralgia may include sharp, shooting pains that can be triggered by neck movement or even touching the scalp.
- Neck Stiffness and Pain: Cervicogenic headaches may be accompanied by stiffness and pain in the neck, sometimes spreading to the shoulders or upper back.
- Sensitivity to Light and Sound: Migraines can cause not only pain at the back of the head but also heightened sensitivity to light and sound, along with nausea or vomiting.
- Redness, Tearing, and Nasal Congestion: Cluster headaches may lead to symptoms such as red or watering eyes, nasal congestion, and swelling around the eye on the affected side.
- Visual Disturbances: Some headaches at the back of the head are accompanied by visual symptoms such as blurred vision or aura.
Understanding these symptoms and their patterns can significantly aid in determining the nature of your headache and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
When to See a Doctor for Headache at the Back of the Head
While many headaches can be managed with over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle adjustments, certain symptoms warrant prompt medical attention. Knowing when to see a doctor can help prevent complications and ensure appropriate care.
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is severe in intensity, often described as a "thunderclap" headache, can be a sign of a serious condition, such as an aneurysm or stroke.
- Changes in Pattern: Headaches that change in frequency, severity, or that present with symptoms not previously experienced should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Accompanied by Neurological Symptoms: If your headache is accompanied by symptoms such as confusion, difficulty speaking, weakness, or changes in vision, seek immediate medical attention.
- New Headache After Age 50: A new type of headache emerging after the age of 50 warrants a thorough medical examination to rule out more serious conditions.
- Impact on Daily Life: Headaches that increasingly interfere with daily activities or don"t improve with over-the-counter medications should be discussed with a doctor.
- Associated Symptoms: Headaches accompanied by fever, stiff neck, rash, persistent vomiting, or seizures should be assessed by a healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Timely consultation with a healthcare professional can lead to accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, ensuring your well-being and health safety.
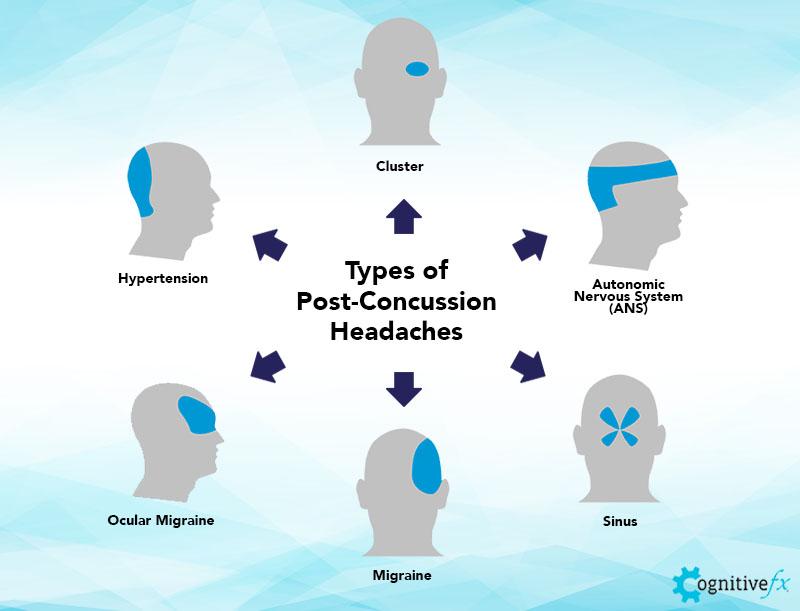
Treatment Options for Headache at the Back of the Head
Headaches at the back of the head can be managed through various treatment strategies, focusing on both medication and non-medication approaches to relieve pain and address the underlying causes.
Medications
- Over-the-counter options include ibuprofen, acetaminophen, or other anti-inflammatory medications for temporary relief.
- Prescription treatments may involve triptans or ergot alkaloids for severe headaches or migraines, anticonvulsants or antidepressants for occipital neuralgia, and muscle relaxants or cortisone injections for cervicogenic headaches.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can offer relief, especially for migraine, tension, and cervicogenic headaches, by providing personalized exercise plans.
Acupressure
Acupressure, particularly the stimulation of the LI-4 point between the thumb and forefinger, may help relieve headache symptoms by increasing blood flow and relaxing muscles.
Lifestyle Changes
- Ensuring adequate sleep, which aids in stress management and muscle tension relief.
- Applying ice packs to the back of the head to ease pain and reduce inflammation.
- Using a heating pad to relax muscles and alleviate pain.
- Practicing yoga, meditation, or other relaxation techniques to diminish muscle tension and pain.
It"s important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans, especially if headaches persist or worsen.
Tips for Relieving Headaches at the Back of Your Head
\"In this captivating video, you will discover effective and natural ways to relieve stress and tension in your daily life. From soothing techniques to calming exercises, this video will guide you towards a more peaceful and relaxed state of mind.\"
Causes of Headaches and Migraines in the Back of Your Head
\"Curious about what could be causing those unexplained headaches or sleepless nights? This intriguing video explores the various causes behind these common ailments, shedding light on factors you may have never considered. Get ready to uncover the mysteries and find potential solutions!\"
Prevention Tips for Headache at the Back of the Head
Experiencing headaches at the back of the head can be uncomfortable and affect your daily activities. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can adopt to reduce the frequency and severity of these headaches. Follow these prevention tips to help manage and possibly prevent headaches at the back of the head:
- Maintain Good Posture: Poor posture can contribute to tension headaches. Ensure your workstation is ergonomically set up, and take regular breaks to stretch and adjust your posture.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can trigger headaches. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day to keep hydrated and prevent headache episodes.
- Manage Stress: Stress is a common trigger for headaches. Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to help reduce stress levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce the frequency of headaches by improving overall health and reducing stress. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Limited Caffeine and Alcohol Intake: Both caffeine and alcohol can trigger headaches in some people. Limit your intake and monitor your response to these substances.
- Get Enough Sleep: Poor sleep patterns can lead to headaches. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night and try to maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Avoid Certain Foods: Some foods may trigger headaches in susceptible individuals. Keep a food diary to identify and avoid potential food triggers.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you experience frequent or severe headaches, consult a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and treatment options.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing headaches at the back of the head. Remember, lifestyle changes take time to show effects, so be patient and consistent with your efforts.

Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Adopting healthy lifestyle changes and applying home remedies can significantly improve the quality of life for those suffering from headaches at the back of the head. These adjustments and practices can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of headache episodes. Here are some effective strategies:
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Eating a nutritious, balanced diet can help prevent headaches. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise to improve blood circulation, reduce stress, and enhance your overall health. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can be particularly beneficial.
- Proper Hydration: Drink enough water throughout the day to avoid dehydration, a common headache trigger.
- Stress Management: Implement stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises to manage stress levels effectively.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough restful sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a comfortable, relaxing sleep environment.
- Limited Use of Pain Relievers: While over-the-counter pain medications can provide relief, excessive use can lead to rebound headaches. Use these medications sparingly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Heat or Cold Therapy: Applying a heat pad or cold pack to the area can help soothe muscle tension and reduce headache pain. Experiment with both to see which offers more relief.
- Avoid Headache Triggers: Identify and avoid personal headache triggers, which can include certain foods, smells, or environmental factors.
- Maintain a Headache Diary: Keeping a diary of your headaches can help identify patterns, triggers, and effective remedies for your headaches.
Implementing these lifestyle changes and home remedies can be a powerful approach to managing headaches at the back of the head. Remember, individual responses may vary, so it may be helpful to try different strategies to find out what works best for you.
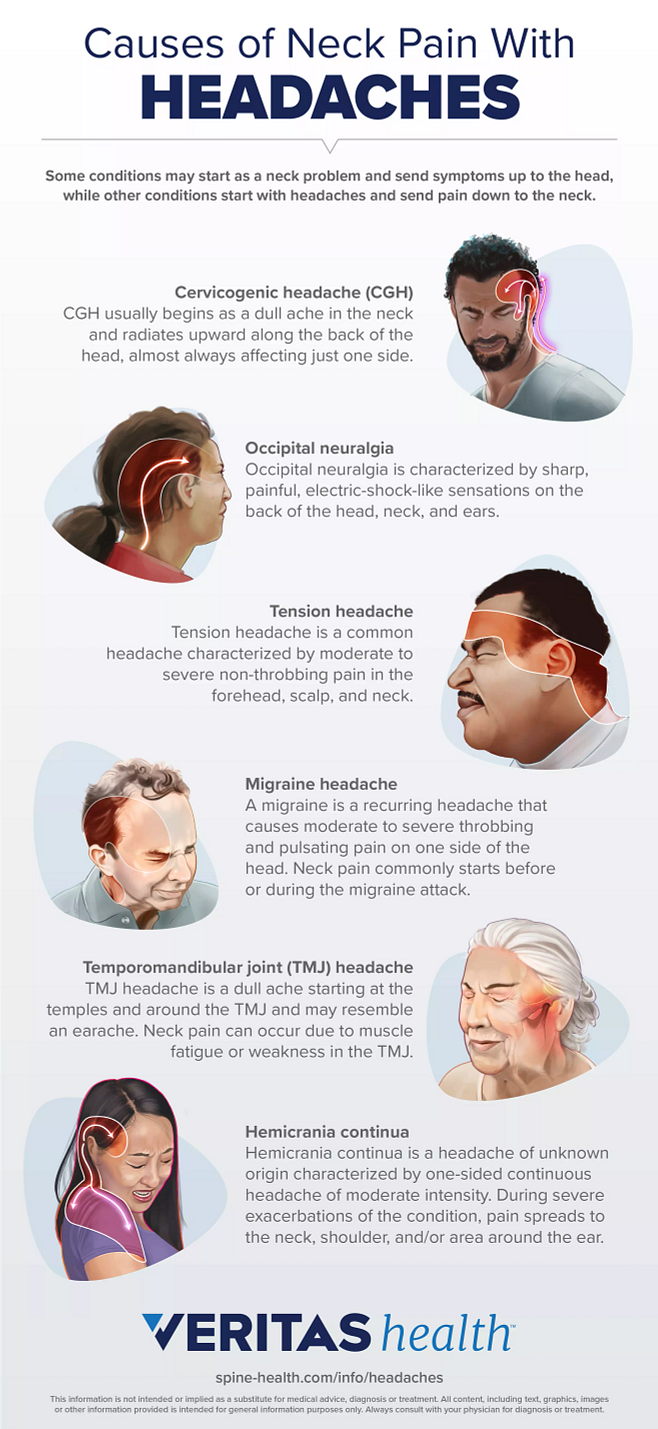
Understanding Occipital Neuralgia
Occipital neuralgia is a condition that results in chronic pain in the back of the head, neck, and behind the ears. This pain is often described as sharp, shooting, and sometimes follows a throbbing pattern. It is caused by irritation or injury to the occipital nerves, which run from the top of the spinal cord up through the scalp. Understanding this condition is crucial for managing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. Here are key aspects of Occipital Neuralgia:
- Causes: It can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle tension, injury, or inflammation, cervical spine disorders, or as a result of other medical conditions.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include sharp, shooting pain in the back of the head and neck, pain behind the eyes, and sensitivity to light. Some people may also experience a tender scalp and pain when moving the neck.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and possibly imaging tests to rule out other conditions. A nerve block injection can also be a diagnostic tool as well as a treatment option.
- Treatment Options: Treatment may include medication, physical therapy, massage, heat therapy, and in some cases, nerve blocks or surgery to relieve pressure on the nerves.
- Self-Care Strategies: Managing stress, maintaining good posture, and applying warm compresses can help alleviate symptoms. Regular physical activity and stretching exercises specifically designed for the neck and shoulders can also provide relief.
- Professional Care: Consulting with healthcare professionals, including neurologists and pain specialists, is important for a comprehensive treatment plan. They can offer guidance on the most effective treatment strategies tailored to individual needs.
Understanding and addressing occipital neuralgia involves a combination of medical intervention and lifestyle adjustments. With the right approach, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Tension Headaches and Their Management
Tension headaches, characterized by a dull, aching pain on both sides of the head, are among the most common types of headaches. They can also cause tenderness in the scalp, neck, and shoulder muscles. Tension headaches can be triggered by stress, poor posture, and lack of sleep, among other factors. Effective management of tension headaches involves a combination of lifestyle changes, home remedies, and medical treatments. Here"s how to manage tension headaches:
- Stress Management: Since stress is a major trigger, techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can be very effective in reducing headache frequency and severity.
- Improve Your Posture: Poor posture can contribute to tension headaches. Be mindful of your posture, especially if you sit for long periods. Consider ergonomic adjustments to your work environment.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise can help reduce the frequency of tension headaches by relieving stress and improving overall physical health.
- Adequate Rest: Ensure you get enough sleep each night. Lack of sleep can trigger tension headaches, so aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can lead to headaches. Drinking enough water throughout the day can help prevent them.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both caffeine and alcohol can affect your hydration status and can trigger headaches in some people. Moderation is key.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: For occasional tension headaches, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen can be effective. However, they should be used sparingly to avoid overuse headaches.
- Relaxation Techniques: Activities that promote relaxation, such as taking a warm bath, reading, or listening to soothing music, can help alleviate the symptoms of tension headaches.
- Massage: Gently massaging the temples, neck, and shoulders can help relieve the tension and pain associated with tension headaches.
While tension headaches can be bothersome, they are usually manageable with the right strategies. If you experience frequent or severe headaches, it"s important to consult a healthcare professional to rule out other causes and to discuss more specific treatment options.
The Role of Posture in Headaches at the Back of the Head
Poor posture is a significant contributor to headaches, particularly those that occur at the back of the head. This type of headache is often the result of muscle tension and strain in the neck and shoulder area, which can be exacerbated by maintaining a poor posture over extended periods. Understanding the role of posture can help in preventing and managing these headaches effectively. Here"s how posture affects headaches at the back of the head and what you can do about it:
- Understanding the Connection: Poor posture, especially while sitting or standing for long periods, can lead to muscle tension in the neck, shoulders, and scalp. This tension can then trigger headaches at the back of the head.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Keeping the spine in alignment can help reduce muscle strain. When sitting, ensure your back is straight, shoulders are back, and the computer screen is at eye level. Use a chair that supports your lower back.
- Take Regular Breaks: If you work at a desk, take short breaks every hour to stretch and walk around. This can help relieve muscle tension and prevent headache onset.
- Strengthen and Stretch: Regularly perform exercises that strengthen the muscles of your back, neck, and shoulders. Stretching exercises can also help maintain flexibility and reduce tension.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Make your work environment more ergonomic. Adjust your chair, desk, and computer setup to promote a better posture.
- Be Mindful of Your Posture: Regularly check in with your body to ensure that you"re maintaining a good posture. Reminders and posture correcting devices can be helpful.
- Seek Professional Help: If you"re experiencing chronic headaches due to poor posture, consider consulting with a physical therapist. They can offer exercises and advice tailored to your specific needs.
Improving your posture can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches at the back of the head. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can enjoy greater comfort and fewer headaches.

READ MORE:
When Headache at the Back of the Head Indicates a Serious Condition
While headaches at the back of the head are often due to benign causes like tension or poor posture, certain symptoms can indicate a more serious condition. Recognizing these signs is crucial for seeking timely medical intervention and preventing potential complications. Here"s what to look out for:
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is severely painful can be a sign of a serious issue, such as a stroke or aneurysm.
- Change in Pattern: A significant change in the pattern of your headaches, including increased frequency or intensity, warrants medical evaluation.
- Neurological Symptoms: Symptoms such as confusion, difficulty speaking, vision changes, weakness, or numbness on one side of the body accompanying a headache could indicate a neurological disorder and require immediate attention.
- Worsening with Activity: Headaches that worsen with physical activity or coughing may suggest a brain tumor or other serious conditions.
- Accompanied by Fever: A headache accompanied by fever, neck stiffness, or rash may be signs of an infection, such as meningitis.
- Persistent Nausea or Vomiting: These symptoms, especially when combined with headache, could indicate increased intracranial pressure and need prompt evaluation.
- After Head Injury: Headaches that develop after a head injury could signal a concussion or more severe brain injury.
- Age Over 50: New onset of headaches in individuals over 50 years old can be a sign of temporal arteritis, a condition that requires immediate treatment to prevent vision loss.
If you experience any of these warning signs, it"s important to seek medical care immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing serious conditions effectively. Remember, it"s better to be cautious and get a headache evaluated by a professional if you have concerns about its origin or severity.
Understanding the causes and solutions for headaches at the back of the head can significantly improve your quality of life. Explore our comprehensive guide to find relief and regain control over your well-being today.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-PaigeMcLaughlin-WhatisaClusterHeadache-Standard-87c962b6a28d4b1ab0359ed3ae5b696f.jpg)