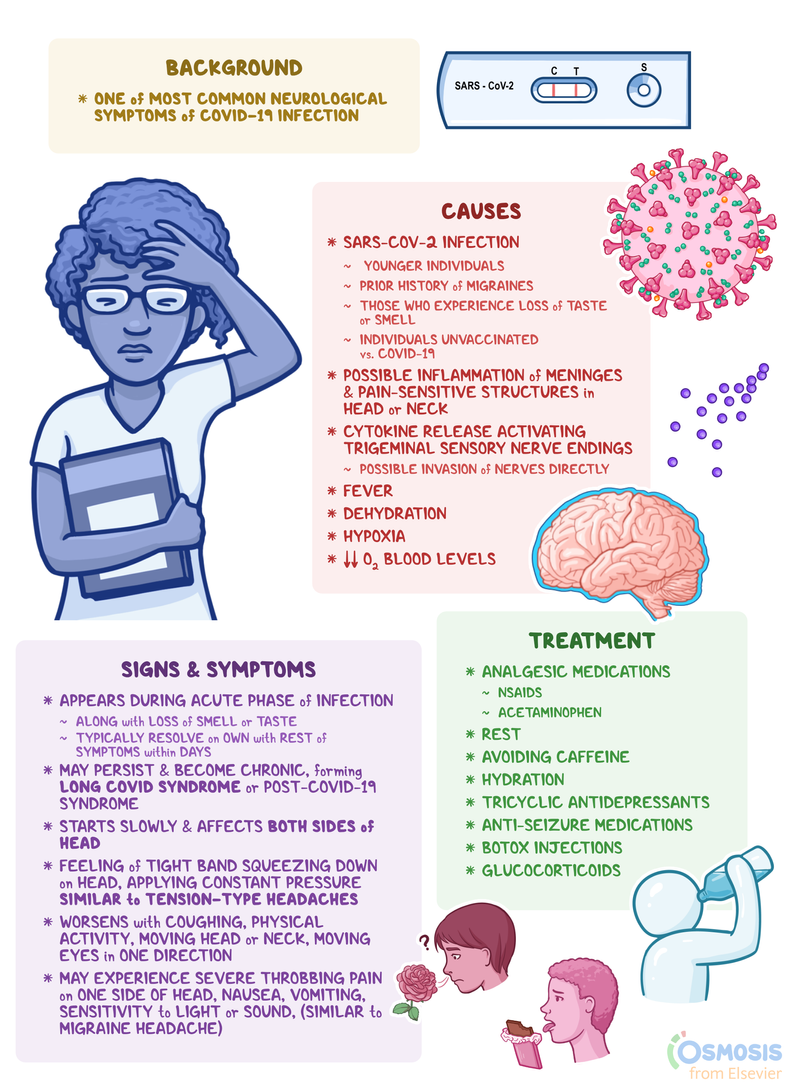
Topic types of headache: Explore the diverse world of headaches, from tension to migraines, and learn how to identify, prevent, and effectively manage each type for better health and well-being.
Table of Content
- What are the different types of headaches and their treatments?
- Understanding Different Types of Headaches
- Common Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Migraine Headaches: Symptoms, Triggers, and Treatment
- Tension-Type Headaches: Causes, Symptoms, and Relief Strategies
- YOUTUBE: Types of Headaches | Primary vs Secondary | Migraine Cluster Tension Headaches
- Cluster Headaches: Identification and Management
- Secondary Headaches: When to Seek Medical Attention
- Children and Headaches: Recognizing the Signs
- Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications for Headache Management
- When to See a Doctor: Warning Signs
- Latest Research and Developments in Headache Treatment
- Frequently Asked Questions About Headaches
What are the different types of headaches and their treatments?
There are several different types of headaches, each with their own characteristics and treatments. Here is a list of common types of headaches and how they can be treated:
- Tension headache - This is the most common type of headache. It typically causes a dull, aching pain on both sides of the head and can last for hours or even days. Treatment options include over-the-counter pain medications, relaxation techniques, and stress management.
- Migraine headache - Migraines are characterized by intense, throbbing pain, usually on one side of the head. They are often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. Treatment options include over-the-counter or prescription medications, rest in a quiet, dark room, and avoiding triggers such as certain foods or stress.
- Cluster headache - Cluster headaches are extremely painful headaches that occur in clusters or cycles. They usually occur on one side of the head and are accompanied by eye redness, tearing, and nasal congestion. Treatment options include prescription medications, oxygen therapy, and nerve blocks.
- Hemicrania continua - This is a chronic headache that usually affects one side of the head and is accompanied by continuous pain with occasional spikes in intensity. Treatment typically involves prescription medication.
- Ice pick headache - This is a sudden, intense pain that occurs as a sharp, stabbing sensation. It usually lasts for a few seconds to a few minutes. Treatment options may include medications to prevent future attacks.
- Thunderclap headache - This is a severe headache that reaches its peak intensity within seconds. It can be a symptom of a serious underlying condition and requires immediate medical attention.
It\'s important to note that these are just a few examples of the many types of headaches that exist. If you are experiencing frequent or severe headaches, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
READ MORE:
Understanding Different Types of Headaches
Headaches are a common health issue, impacting millions worldwide. Recognizing the type can be crucial for effective management. Here, we delve into various headache forms, each with unique characteristics and treatments.
- Migraines: Characterized by pulsating pain on one side of the head, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Tension-Type Headaches: Manifests as a constant, dull ache on both sides of the head, resembling a tight band around it. Stress and muscle strain often trigger these.
- Cluster Headaches: Known for their severe, burning pain around one eye or temple, occurring in groups or clusters over weeks or months.
- Secondary Headaches: Caused by underlying medical conditions, ranging from sinus infections to stroke, and necessitate prompt medical attention.
Understanding the symptoms and triggers of each type can guide towards the right treatment and prevention strategies, enhancing life quality.

Common Symptoms and Diagnosis
Headaches can manifest through a variety of symptoms, which often depend on the type of headache. Common symptoms include pain in the head that can vary in intensity, duration, and location, such as a throbbing, squeezing, or constant ache. Other symptoms might include nausea, sensitivity to light or sound, and changes in vision or aura.
Diagnosing headaches involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers may ask about the nature of the symptoms, their onset, duration, and any triggers or relieving factors. In some cases, additional tests such as MRI or CT scans are performed to rule out underlying conditions. The diagnosis is also based on the criteria established by the International Headache Society, which helps differentiate between types of headaches such as migraines, tension-type headaches, cluster headaches, and secondary headaches caused by other health issues.
- Migraines are often characterized by pulsating pain on one side of the head, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound. Some people experience auras before the headache begins.
- Tension-type headaches usually feature a pressing or tightening sensation around the head, with mild to moderate intensity, and are not worsened by routine physical activity.
- Cluster headaches are noted for severe, piercing pain around one eye or temple, occurring in clusters over weeks or months, often with eye watering or nasal congestion on the affected side.
- Secondary headaches are symptomatic of other conditions and can vary widely in their presentation. These require identifying and treating the underlying cause.
For children, headache symptoms might differ slightly and can include irritability, changes in sleep patterns, or vomiting. Pediatric headaches require careful assessment to avoid overlooking serious conditions.
Preventive measures and lifestyle modifications are often recommended for managing headache symptoms. These can include regular exercise, stress management techniques, and avoiding known triggers. For specific types of headaches, such as migraines or cluster headaches, medications and other treatments may be prescribed for both acute relief and prevention.
It is important for individuals to seek medical advice if headaches are frequent, severe, or accompanied by other symptoms like visual disturbances, weakness, or difficulty speaking, as these can be signs of more serious conditions.
Migraine Headaches: Symptoms, Triggers, and Treatment
Migraine headaches are a complex condition characterized by intense, often debilitating headaches, typically affecting one side of the head. They can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound. Migraines can significantly impact daily life, but understanding their symptoms, triggers, and available treatments can help manage this condition effectively.
- Symptoms: The primary symptom of a migraine is a throbbing or pulsating headache of moderate to severe intensity. Other common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, sound, and sometimes smells and touch. Some individuals experience auras—visual disturbances such as flashes of light or blind spots—before the onset of the headache.
- Triggers: Various factors can trigger migraines, including stress, hormonal changes (such as those related to menstruation), sleep disturbances, certain foods and drinks (aged cheeses, alcohol, and caffeine), sensory stimuli (bright lights, loud sounds), changes in the environment (weather changes), and medications.
- Treatment: While there is no cure for migraines, treatments are available to help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of attacks. Treatment strategies include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, triptans (prescription drugs that help counteract the changes in the brain that may lead to migraines), and preventive medications, which are often prescribed for frequent migraine sufferers to reduce the likelihood of future attacks.
- Lifestyle modifications: Identifying and avoiding individual triggers, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and managing stress can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
- Alternative therapies: Some people find relief through acupuncture, biofeedback, and supplements like magnesium, riboflavin (vitamin B2), and coenzyme Q10.
- Medical devices: Certain FDA-approved devices that use magnetic or electrical stimulation of specific areas of the head can be effective for some patients.
Working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan is crucial. This plan may include keeping a headache diary to track the occurrence of migraines and potential triggers, which can be invaluable for managing this condition.

Tension-Type Headaches: Causes, Symptoms, and Relief Strategies
Tension-type headaches are the most common form of headache, characterized by a dull, aching pain that is often described as a tight band around the head. They can vary in frequency and intensity but typically do not cause the same level of disability as migraines. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing effective relief strategies can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.
- Causes: The exact cause of tension-type headaches is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to their development. These include stress, poor posture, anxiety, lack of sleep, dehydration, eye strain, and certain environmental factors.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include a constant, dull ache on both sides of the head, pressure around the forehead, and tenderness around the forehead and scalp. Unlike migraines, tension-type headaches do not typically feature nausea or visual disturbances.
- Relief Strategies: Several strategies can help alleviate the symptoms of tension-type headaches and reduce their frequency:
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and reduce headache frequency.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve posture and relieve muscle tension can be beneficial, especially for individuals who spend long hours in one position.
- Proper Ergonomics: Adjusting the work environment to reduce strain on the body can prevent headaches caused by poor posture or eye strain.
- Hydration and Diet: Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can help prevent headaches. Avoiding foods and drinks known to trigger headaches in some people may also be helpful.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications such as ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen can offer temporary relief for tension-type headaches.
- Relaxation Techniques: Regularly practicing relaxation techniques such as massages or warm baths can help to relax muscles and reduce the likelihood of developing tension-type headaches.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can reduce stress and improve overall health, potentially decreasing the frequency of headaches.
For individuals who experience frequent or severe tension-type headaches, consulting a healthcare provider is important. They can help rule out underlying conditions and provide guidance on more specific treatment options, including prescription medications or other therapies tailored to individual needs.
Types of Headaches | Primary vs Secondary | Migraine Cluster Tension Headaches
Are you tired of dealing with pesky headaches that ruin your day? Watch this video to discover effective strategies and natural remedies to finally say goodbye to those head-pounding discomforts!
Cluster Headaches: Identification and Management
Cluster headaches are recognized as one of the most painful types of headache, characterized by intense burning or piercing pain around or behind one eye or on one side of the face. These headaches occur in series lasting weeks or months, known as "cluster periods," followed by remission periods when the headaches stop. Early identification and effective management are key to reducing their impact on a sufferer"s life.
- Identification: Cluster headaches are marked by sudden, severe pain on one side of the head, often around the eye. Other symptoms include red or watering eye, nasal congestion or runny nose, forehead or facial sweating, swelling around the eye on the affected side, and restlessness. Attacks typically last between 15 minutes to 3 hours and can occur up to several times a day during a cluster period.
- Triggers: While the exact cause of cluster headaches is unknown, certain factors like alcohol consumption, smoking, strong smells, and changes in sleep patterns can trigger attacks. Avoiding known triggers can help manage the condition.
- Oxygen Therapy: Breathing pure oxygen through a mask at the start of an attack can significantly reduce the duration and severity of the pain.
- Medications: Fast-acting treatments such as sumatriptan (injections or nasal spray) and zolmitriptan nasal spray are often effective in stopping attacks. Preventive medications may also be prescribed to decrease the frequency and severity of the headaches during cluster periods.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and avoiding alcohol and tobacco can help reduce the frequency of cluster headache attacks.
- Neurostimulation Techniques: In some cases, techniques such as occipital nerve stimulation or deep brain stimulation, where electrical impulses are used to target specific areas of the brain or nerves, have shown promise in treating cluster headaches.
Due to the intensity and frequency of cluster headaches, they can significantly affect an individual"s quality of life. It"s important for those affected to seek medical advice to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Support groups and counseling may also be beneficial in managing the psychological impact of living with this condition.

Headache Overview Types Signs and Symptoms Treatment
Curious about the topic but don\'t want to dive deep? This overview video provides a comprehensive yet concise summary of everything you need to know, saving you time and giving you a great starting point for further exploration.
Secondary Headaches: When to Seek Medical Attention
Secondary headaches are caused by underlying health conditions and can serve as warning signs of more serious issues. Unlike primary headaches, such as migraines or tension-type headaches, secondary headaches are symptoms of diseases that can affect the brain, arteries, and neck, among other parts of the body. Recognizing when to seek medical attention for secondary headaches is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment of the underlying condition.
- Causes: Secondary headaches can result from a variety of conditions, including sinus infections, brain tumors, strokes, blood vessel abnormalities, meningitis, and changes in intracranial pressure. They might also be triggered by medication overuse or certain life-threatening conditions.
- Warning Signs: Certain symptoms accompanying a headache necessitate immediate medical attention:
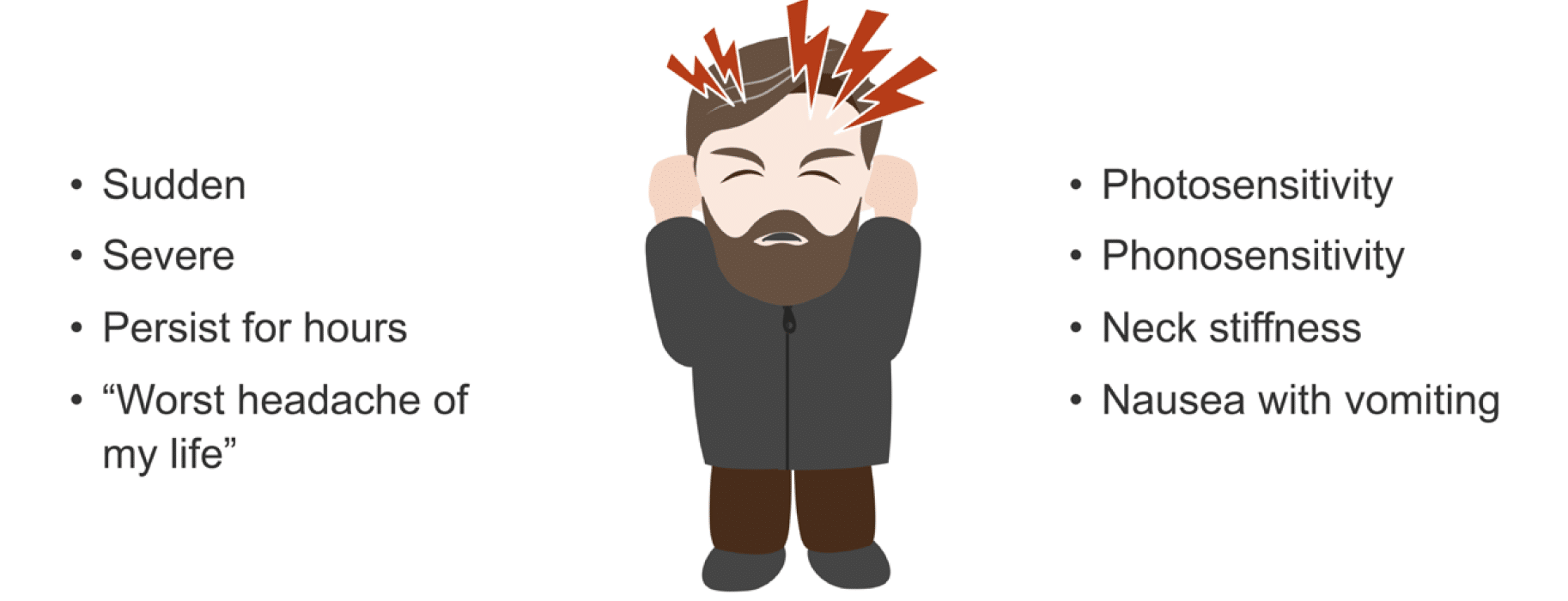
- Sudden, severe headache that peaks in intensity within seconds to minutes, often described as "the worst headache of my life."
- Headache accompanied by fever, neck stiffness, rash, confusion, seizure, double vision, weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking.
- Headache that worsens or changes pattern over time.
- Headache following a head injury, especially if it worsens.
- New headache pain if you are over 50 years old.
Secondary headaches may require different types of tests for accurate diagnosis, including MRI or CT scans, lumbar puncture, or blood tests, depending on the suspected underlying condition.
Treatment for secondary headaches focuses on addressing the root cause. This may involve medication to treat infection, surgery to remove obstructions or tumors, or other specialized treatments depending on the specific health issue.
It is essential not to ignore headaches that suddenly change in pattern or intensity, as they can be indicators of serious health conditions. Early consultation with healthcare professionals can lead to timely and effective treatment, significantly improving outcomes.
Children and Headaches: Recognizing the Signs
Headaches in children are common and can have various causes, ranging from minor ailments to more serious conditions. Recognizing the signs of headaches in children and understanding when to seek medical advice are important steps in managing their health and well-being. While children may not always communicate their symptoms effectively, there are key indicators that parents and caregivers can watch for.
- Common Symptoms: Similar to adults, children with headaches may experience pain in the head, sensitivity to light or sound, nausea, or vomiting. However, they might also exhibit less obvious signs such as irritability, mood changes, changes in sleep patterns, or a lack of appetite.
- Types of Headaches: Children can suffer from various types of headaches, including tension-type headaches, migraines, and cluster headaches, though the latter are less common in this age group. Secondary headaches, resulting from another medical condition, can also occur.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- If a headache is severe or occurs more frequently.
- If headaches worsen or change in pattern.
- If the headache is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, neck stiffness, rash, visual disturbances, weakness, or difficulty walking or talking.
- If a very young child is complaining of headaches.
Management and Treatment:
Managing headaches in children often involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, such as ensuring regular sleep patterns, healthy eating, staying hydrated, and managing stress. Over-the-counter pain relief medication can be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It is also beneficial to teach children to communicate their symptoms effectively and to maintain a headache diary to identify potential triggers or patterns.
In some cases, referral to a pediatric neurologist may be necessary for further evaluation and treatment, especially if headaches are frequent, severe, or associated with other worrying symptoms. With appropriate care and attention, most children can effectively manage their headaches and lead healthy, active lives.

Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications for Headache Management
Headaches can significantly impact daily life, but many can be managed or even prevented with the right lifestyle modifications and preventive measures. By understanding and implementing these strategies, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of headaches, improving their overall quality of life.
- Regular Sleep Schedule: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule helps regulate the body"s natural rhythms, reducing the likelihood of headaches. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can prevent headaches. It"s also important to eat regular meals to avoid low blood sugar levels, which can trigger headaches.
- Hydration: Dehydration is a common headache trigger. Drinking enough water throughout the day can help prevent headaches.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to tension-type headaches and migraines. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help manage stress.
- Limiting Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol can trigger headaches in some people. Moderating intake can help prevent these headache triggers.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches by improving overall health and stress management.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal headache triggers, which can include certain foods, smells, or environmental factors, is crucial for some individuals.
- Posture Improvement: Poor posture can contribute to tension headaches. Working on posture, especially if sitting for long periods, can help prevent headaches.
- Breaks from Screens: Taking regular breaks from screens can prevent headaches caused by eye strain.
In addition to these lifestyle modifications, consulting with a healthcare provider can help identify specific preventive medications or treatments for those with frequent or severe headaches. By taking proactive steps and making mindful lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage their headache symptoms and reduce their impact on daily life.
When to See a Doctor: Warning Signs
While most headaches are not indicative of a serious medical condition, certain symptoms can signal the need for immediate medical attention. Recognizing these warning signs is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment, potentially preventing serious complications. Here are key indicators that a headache requires a doctor"s evaluation:
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is extremely severe, often described as a "thunderclap" headache, can be a sign of a serious condition, such as a brain aneurysm or bleeding in the brain.
- Change in Pattern: A significant change in the frequency, severity, or pattern of headaches warrants a medical evaluation to rule out underlying causes.
- Accompanied by Other Symptoms: Headaches accompanied by symptoms such as confusion, fever, stiff neck, seizures, double vision, weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking should be assessed by a healthcare provider immediately.
- After a Head Injury: A headache following a head injury, especially if it worsens or continues to recur, could indicate a concussion or other serious injury.
- New Headaches After Age 50: New onset of headaches in individuals over the age of 50 can be a sign of temporal arteritis or other age-related conditions.
In addition to these warning signs, individuals who find their headaches are resistant to over-the-counter medications or significantly impact their quality of life should also consult a healthcare provider. Early intervention can help manage symptoms, identify any underlying conditions, and provide appropriate treatment strategies to manage or alleviate headaches.
It"s also advisable for individuals with a history of headaches to maintain regular check-ups with their healthcare provider, especially if their symptoms change or worsen. A healthcare professional can offer guidance on managing headaches and recommend further diagnostic tests if necessary.
Latest Research and Developments in Headache Treatment
The field of headache treatment is continually evolving, with new research and developments offering hope to those who suffer from chronic headaches and migraines. Advances in understanding the biological mechanisms behind headaches have led to the development of innovative treatments that target specific pathways involved in headache disorders. Here are some of the latest trends and breakthroughs in headache treatment:
- Monoclonal Antibodies for Migraine Prevention: Recent years have seen the approval of several monoclonal antibodies that target the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) pathway, a key player in migraine development. These treatments have shown promise in reducing the frequency and severity of migraine attacks.
- Neuromodulation Devices: Non-invasive neuromodulation devices, which use magnetic or electrical stimulation to modulate brain activity, are gaining traction as a treatment for both acute migraine attacks and preventative care. These devices offer an alternative for those who prefer not to take medication or have found pharmacological treatments ineffective.
- Digital Health Interventions: Mobile apps and online platforms that provide cognitive behavioral therapy, biofeedback, and relaxation techniques are becoming more prevalent. These digital tools help patients manage their headache symptoms by reducing stress, improving sleep, and tracking headache triggers.
- Genetic Research: Studies focused on the genetic underpinnings of migraines are underway, aiming to identify genetic factors that increase susceptibility to migraines. This research could lead to personalized medicine approaches to headache treatment.
- New Pharmacological Treatments: The development of new drugs, including gepants that block the CGRP receptor and ditans that target the 5-HT1F serotonin receptor, offers new options for acute migraine treatment.
Alongside these advancements, ongoing research is dedicated to improving the diagnosis and classification of headache disorders, enhancing the effectiveness of existing treatments, and exploring holistic approaches that consider lifestyle and environmental factors. As our understanding of headaches deepens, the potential for more effective and personalized treatments grows, providing hope for those affected by these debilitating conditions.
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions About Headaches
Headaches are a common health issue that affects people of all ages. They can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that interferes with daily activities. Understanding headaches can help you manage them better. Here are some frequently asked questions about headaches:
- What are the main types of headaches?
- There are several types of headaches, but the most common include tension-type headaches, migraines, cluster headaches, and secondary headaches, which are caused by underlying health conditions.
- What causes headaches?
- Headaches can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, lack of sleep, dehydration, poor posture, eye strain, certain foods and drinks, environmental changes, and medical conditions.
- How can I tell if my headache is serious?
- A headache can be considered serious if it is unusually severe or accompanied by other symptoms such as a stiff neck, fever, confusion, weakness, vision changes, or difficulty speaking. These signs warrant immediate medical attention.
- How are headaches treated?
- Treatment varies depending on the type of headache. It may include over-the-counter pain relief, prescription medications, lifestyle changes, stress management techniques, hydration, and avoiding known triggers. In some cases, alternative therapies like acupuncture or biofeedback may be helpful.
- Can headaches be prevented?
- While not all headaches can be prevented, many can be managed or reduced in frequency by identifying and avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, ensuring adequate hydration, regular physical activity, and managing stress.
- When should I see a doctor for a headache?
- You should consult a doctor if headaches are frequent, severe, disrupt your daily life, change in pattern or intensity, or are accompanied by other symptoms like those mentioned above.
- Are headaches hereditary?
- Some types of headaches, particularly migraines, can have a genetic component, meaning they can run in families. However, the exact influence of genetics on headaches varies among individuals.
Understanding headaches is the first step towards effective management and treatment. If you have concerns about your headaches, it"s important to seek advice from healthcare professionals who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation.
Understanding the different types of headaches and their treatments empowers you to manage symptoms effectively. Stay informed about the latest developments and strategies to improve your quality of life and navigate the challenges of headaches with confidence.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-dehydration-symptoms-7480908-Horiz-e2500f0828b746ee9d2e2b5257af60cb.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headache-on-the-right-side-5216756_final-b9d0145864d74706b0316a2e9b62dd37.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)