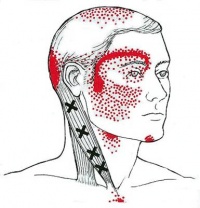
Topic back of head headache: Experiencing back of head headaches can be distressing, but understanding their causes and exploring effective treatments offers a pathway to relief and improved well-being.
Table of Content
- What are the causes of a headache at the back of the head?
- Common Causes of Back of Head Headaches
- Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
- When to See a Doctor
- Diagnostic Approaches
- Treatment Options for Relief
- Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
- YOUTUBE: Get Rid of Headaches at the Back of Your Head
- Prevention Strategies
- Understanding Tension Headaches
- Exploring Occipital Neuralgia
- The Role of Posture in Headaches
- Medication Overuse Headaches: A Common Culprit
- Physical Therapy and Exercises for Headache Relief
- Nutritional Considerations and Headaches
- Stress Management Techniques for Headache Sufferers
- Alternative Treatments: Acupuncture, Massage, and More
What are the causes of a headache at the back of the head?
A headache at the back of the head can be caused by various factors, including:
- Tension headaches: Tension headaches are one of the most common causes of pain in the back of the head. They are often triggered by stress, anxiety, or tight muscles in the neck and scalp.
- Migraines: Migraine headaches can cause pain at the back of the head, usually on one side. They are often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances.
- Arthritis headache: Arthritis can cause pain in the back of the head that worsens with movement. This type of headache is more common in older adults and may be associated with other symptoms of arthritis.
- Medication overuse: Overusing pain medications, such as over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications, can lead to rebound headaches, which can cause pain at the back of the head.
- Other possible causes: Other possible causes of a headache at the back of the head include sinusitis, occipital neuralgia (irritation of the nerves in the scalp), high blood pressure, and head or neck injuries.
If you are experiencing frequent or severe headaches at the back of your head, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
READ MORE:
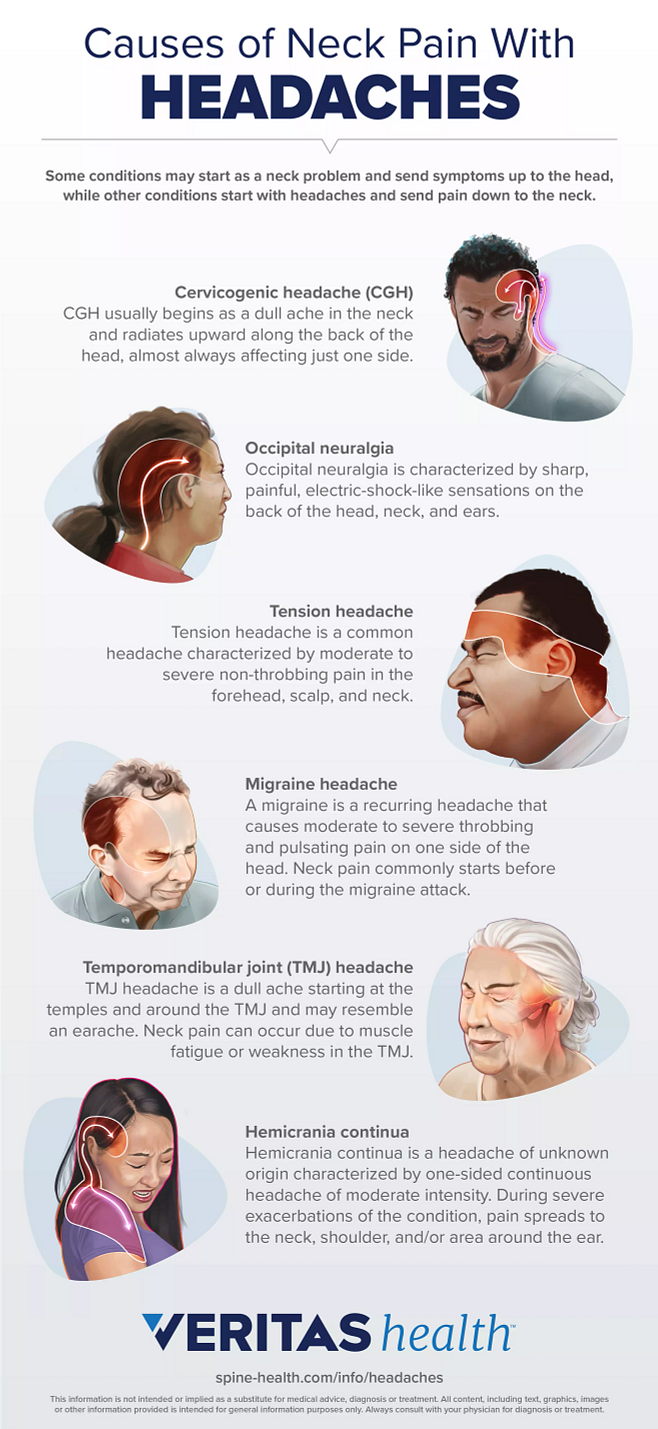
Common Causes of Back of Head Headaches
Headaches occurring at the back of the head can have various triggers. Understanding these can help identify the best approach for relief. Here are the most common causes:
- Tension Headaches: Often resulting from stress, poor posture, or muscle strain, these are the most frequent type of headache affecting the back of the head.
- Occipital Neuralgia: This condition involves the occipital nerves, which run from the top of the spinal cord up through the scalp, causing intense pain that feels like a sharp, jabbing, electric shock in the back of the head and neck.
- Cervicogenic Headaches: Originating from issues within the cervical spine, these headaches are often caused by neck disorders such as degenerative disease, injuries, or infections.
- Arterial Tension: High blood pressure can sometimes manifest as a headache in the back of the head, especially in the morning.
- Medication Overuse: Overuse of headache medication can lead to rebound headaches, which might occur at the back of the head.
- Poor Posture: Spending long hours in front of a computer or using a smartphone can strain the muscles in the neck and base of the skull, leading to headaches.
Identifying the underlying cause of your headache is crucial for effective treatment. If you experience frequent back of head headaches, consider consulting a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Headaches at the back of the head can be accompanied by various signs and symptoms that may indicate the underlying cause or severity of the condition. Being aware of these can help in seeking timely medical advice:
- Pain Severity and Type: The pain can range from dull and throbbing to sharp and stabbing, depending on the cause.
- Location of Pain: While focused at the back of the head, the pain may spread to the sides, front, or even into the neck.
- Sensitivity to Light and Sound: Some individuals may experience increased sensitivity to light and sound, especially during migraine episodes.
- Visual Disturbances: Blurry vision, aura, or visual phenomena can accompany headaches, particularly in cases of migraines.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms are more common with migraines but can occur with other types of headaches as well.
- Neck Pain and Stiffness: Often associated with tension and cervicogenic headaches, stiffness and pain in the neck can accompany the headache.
- Dizziness: Some headache disorders, like migraines, can lead to feelings of dizziness or vertigo.
- Numbness or Tingling: Occipital neuralgia may cause sensations of numbness, tingling, or a pins-and-needles feeling in the back of the head and neck.
It"s important to note that while some symptoms can be managed at home, others may require professional medical intervention, especially if they are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as confusion, fever, or sudden severe headache.
When to See a Doctor
While many headaches can be managed with over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle adjustments, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Knowing when to see a doctor can help prevent complications and address underlying conditions effectively:
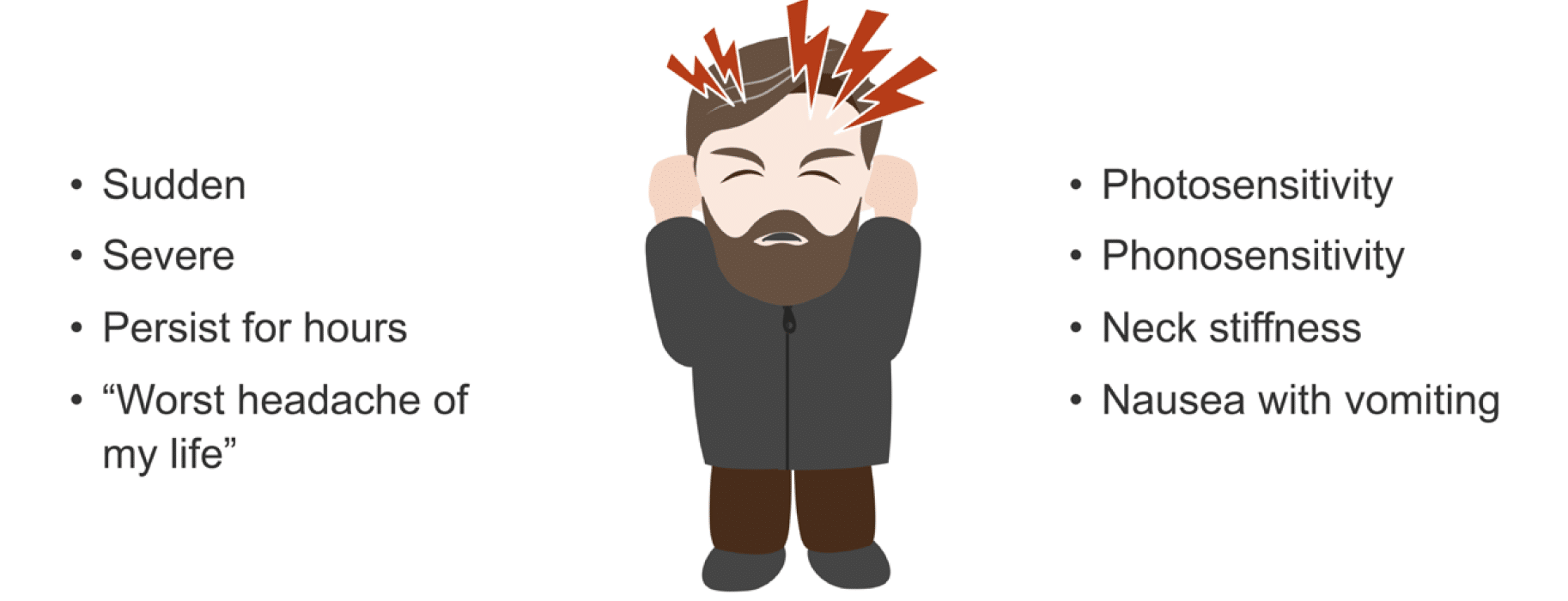
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is severely painful can be a sign of a serious condition, such as a stroke or aneurysm.
- Changes in Pattern: A significant change in the frequency, severity, or pattern of your headaches should be evaluated.
- Neurological Symptoms: Symptoms such as confusion, seizures, numbness, or weakness indicate the need for immediate medical care.
- Accompanied by Other Symptoms: Headaches accompanied by fever, stiff neck, rash, vomiting, or visual loss may suggest a more serious underlying condition.
- Impact on Daily Life: If your headaches are impacting your ability to work, sleep, or engage in daily activities, it’s time to seek professional advice.
- Not Responding to Medication: Headaches that do not improve with over-the-counter medication or require frequent doses for relief should be assessed by a healthcare provider.
- After a Head Injury: Headaches that develop after a head injury, even if minor, should be promptly evaluated to rule out concussion or other injury.
Consulting a healthcare professional can provide you with a diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan, ensuring the best possible outcome for your health.

Diagnostic Approaches
To accurately diagnose the cause of back of head headaches, healthcare professionals may use a combination of methods. A thorough diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment:
- Medical History: A detailed discussion of your symptoms, their onset, duration, and what alleviates or worsens them, as well as your medical history, is the first step.
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive physical exam, focusing on the head, neck, eyes, ears, nose, throat, and neurological functions, helps identify potential causes.
- Neurological Tests: Tests to assess reflexes, muscle strength, sensory perception, and coordination can help detect neurological disorders.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans of the head and neck can reveal structural issues, such as tumors or sinus problems, causing headaches.
- Blood Tests: These can uncover infections, inflammation, or other conditions that might lead to headaches.
- Spinal Tap (Lumbar Puncture): In certain cases, examining the cerebrospinal fluid can help diagnose infections or bleeding around the brain.
Depending on the initial findings, your doctor might refer you to a specialist, such as a neurologist, for further testing and treatment. The right diagnostic approach will guide the development of a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Relief
Finding relief for back of head headaches involves a variety of treatment options tailored to the underlying cause and the individual"s specific needs. Here are some effective strategies:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can alleviate occasional headaches. Prescription medications may be necessary for more severe or chronic conditions.
- Physical Therapy: For headaches caused by muscular tension or cervical spine issues, physical therapy can help improve posture and strengthen muscles, reducing headache frequency and intensity.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and biofeedback can help manage stress levels, a common trigger for headaches.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Regular exercise, adequate hydration, a healthy diet, and sufficient sleep are fundamental for headache prevention and overall well-being.
- Massage and Acupuncture: These alternative therapies can provide relief for some people by reducing muscle tension and promoting relaxation.
- Preventive Medications: For those with frequent or severe headaches, doctors may prescribe medications to reduce the number of headaches.
- Interventional Treatments: In certain cases, nerve blocks or Botox injections are used to treat chronic headache conditions.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals to identify the most suitable treatment approach is key to managing headaches effectively. It may take some time to find the best strategy, but with patience and professional guidance, relief is achievable.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Managing back of head headaches often involves simple home remedies and lifestyle changes that can significantly reduce their frequency and severity. Incorporating these practices can promote overall health and well-being:
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can trigger headaches, so ensure you drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce tension and stress, both of which are common headache triggers. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Improve Sleep Habits: Establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a restful environment to enhance sleep quality, as poor sleep can exacerbate headaches.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and yoga can help manage stress levels, potentially reducing the occurrence of headaches.
- Optimize Your Workstation: Adjust your computer monitor to eye level and take regular breaks to stretch, reducing neck and eye strain.
- Apply Heat or Cold: Applying a warm compress or ice pack to the back of your neck can provide immediate relief from headache pain.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Regular, nutritious meals can prevent headaches triggered by hunger or certain food sensitivities.
- Limited Caffeine and Alcohol: Both substances can be headache triggers. Limiting intake may help reduce headache frequency.
These adjustments not only aid in managing headaches but also contribute to a healthier lifestyle. If your headaches persist despite these measures, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended.
Get Rid of Headaches at the Back of Your Head
Experience relief like never before with this incredible video! Discover the secrets to finding calm and relaxation in the midst of a hectic day. Let soothing visuals and serene music wash over you, bringing a sense of peace and tranquility. You deserve this moment of relief, so click play and let the stress melt away.
Causes of Headaches and Migraines at the Back of Your Head
Uncover the causes behind the challenges you face every day by diving into this eye-opening video. Gain a deeper understanding of the root causes that hold you back from living your best life. With valuable insights and practical solutions, this video will empower you to overcome obstacles and create a life filled with joy and success. Don\'t let the causes control you - take control by watching now!
Prevention Strategies
Preventing back of head headaches involves a proactive approach to managing potential triggers and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Here are key strategies that can help minimize the occurrence of headaches:
- Maintain Good Posture: Proper alignment of your body, especially while sitting or standing for long periods, can reduce strain on your neck and head.
- Manage Stress: Engaging in stress-reduction activities, such as mindfulness, meditation, or hobbies, can lower the likelihood of stress-induced headaches.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise promotes overall health and can prevent tension build-up in the muscles that might lead to headaches.
- Healthy Eating Habits: A balanced diet supports overall health and can prevent headaches related to nutritional deficiencies or food triggers.
- Adequate Hydration: Drinking enough water throughout the day helps prevent dehydration, a common headache trigger.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Ensuring you get enough quality sleep each night can help avoid headaches caused by sleep disturbances.
- Limiting Stimulants: Reducing the consumption of caffeine and alcohol can decrease the frequency of headaches for some individuals.
- Screen Time Management: Taking regular breaks from screens and using proper lighting can reduce eye strain and prevent headaches.
Adopting these strategies not only helps in preventing back of head headaches but also enhances overall health and well-being. It"s important to be consistent with these practices for the best results.

Understanding Tension Headaches
Tension headaches, one of the most common types of headaches, often manifest as a dull, aching pain around the head, particularly at the back of the head. Understanding their characteristics can help in managing them effectively:
- Symptoms: These headaches are typically characterized by a pressing or tightening sensation on both sides of the head, without pulsating. They can last from 30 minutes to several days.
- Triggers: Stress, anxiety, poor posture, and lack of physical activity are among the primary triggers. Eye strain, dehydration, and certain dietary habits can also contribute.
- Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can provide relief. Stress management techniques, regular physical activity, and maintaining good posture are key preventive measures.
- Prevention: Identifying and avoiding personal headache triggers, taking regular breaks during prolonged periods of work or screen time, and engaging in relaxation activities can help prevent tension headaches.
While tension headaches are generally not indicative of underlying serious health issues, frequent or severe headaches should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other causes and to receive tailored treatment advice.
Exploring Occipital Neuralgia
Occipital Neuralgia is a condition characterized by sharp, stabbing pains in the back of the head, neck, and behind the ears, often resulting from irritation or injury to the occipital nerves. Understanding this condition is crucial for those affected:
- Symptoms: Sufferers may experience intense jabbing pain that can mimic the shock-like sensation of an electric shock, scalp sensitivity, and pain when moving the neck.
- Causes: It can be caused by trauma, prolonged neck tension, or compression of the occipital nerves due to osteoarthritis, cervical disc disease, or tumors.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, nerve block injections to confirm the condition, and imaging tests to identify underlying causes.
- Treatment: Treatments include nerve block injections, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, surgery to decompress the affected nerve.
- Management: Warm compresses, massage, and relaxation techniques can help manage symptoms. It"s also important to maintain good posture and avoid activities that strain the neck.
While occipital neuralgia can be painful and disruptive, proper diagnosis and treatment can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.

The Role of Posture in Headaches
Posture plays a significant role in the development and exacerbation of headaches, particularly those occurring at the back of the head. Understanding how posture affects headaches can lead to more effective prevention and management strategies:
- Poor Posture and Muscle Tension: Poor posture, especially while sitting or standing for extended periods, can lead to increased muscle tension in the neck, shoulders, and back, contributing to headache development.
- Neck Strain: Forward head posture, commonly seen with prolonged use of computers and mobile devices, can strain neck muscles and lead to tension headaches.
- Ergonomic Solutions: Adjusting workstations to promote good posture, using ergonomic chairs, and ensuring screens are at eye level can help reduce the risk of headaches.
- Regular Breaks and Stretching: Taking frequent breaks to move and stretch can alleviate muscle stiffness and prevent tension headaches.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can be beneficial in improving posture and strengthening the muscles that support the head and neck, reducing the likelihood of headaches.
- Yoga and Pilates: These activities can improve overall posture, flexibility, and muscle strength, contributing to reduced headache frequency and severity.
By addressing posture and making necessary adjustments to daily habits and work environments, individuals can significantly reduce the occurrence of headaches related to muscle tension and neck strain.
Medication Overuse Headaches: A Common Culprit
Medication overuse headaches (MOH), also known as rebound headaches, occur from the frequent use of headache medication. They are a common and often overlooked cause of chronic headaches, including those at the back of the head:
- Definition: MOH are headaches that occur 15 or more days a month in people who regularly use headache medications for more than three months.
- Common Medications Involved: Over-the-counter pain relievers like aspirin, ibuprofen, and acetaminophen, as well as prescription drugs, can all contribute to MOH.
- Symptoms: The headaches may present as dull, persistent pain that worsens in the morning or after medication wears off.
- Prevention: Limiting the use of headache medications to no more than two days a week can help prevent MOH.
- Treatment: The primary treatment involves reducing or stopping the overused medication, a process that should be supervised by a healthcare professional to manage withdrawal symptoms and develop alternative headache management strategies.
- Alternative Therapies: Non-pharmacological treatments, such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and stress management techniques, can be effective in managing headaches without the risk of MOH.
Understanding the risks of medication overuse and seeking guidance from healthcare providers can help prevent the cycle of rebound headaches, leading to better headache management and improved quality of life.
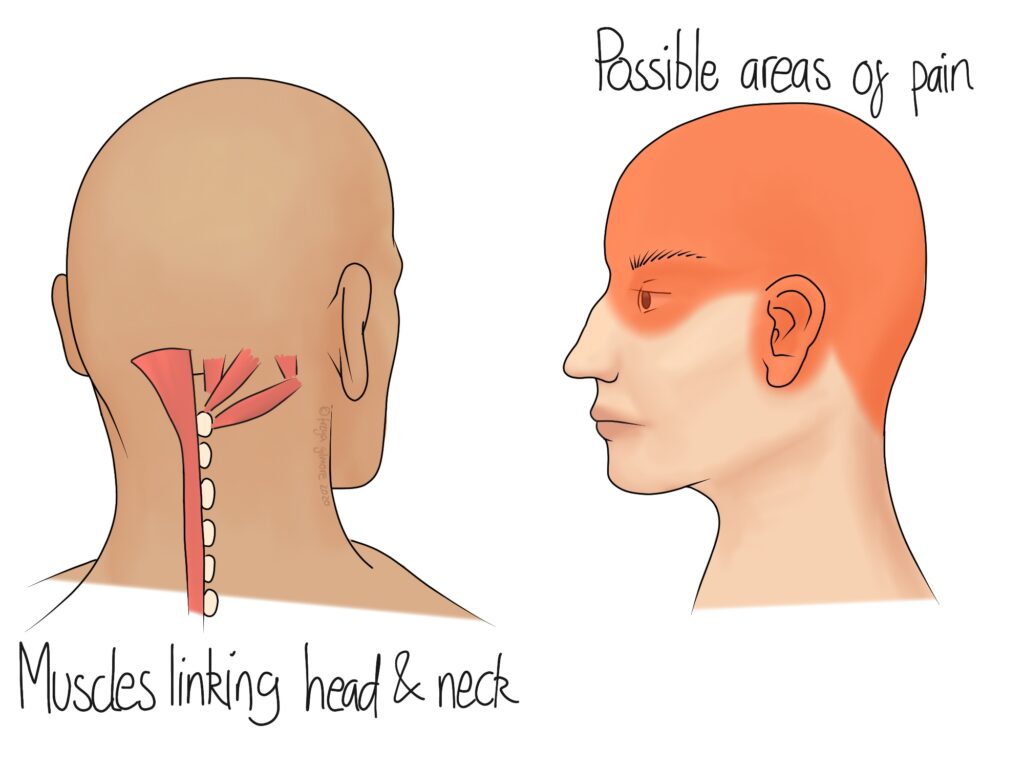
Physical Therapy and Exercises for Headache Relief
Physical therapy and targeted exercises can be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of back of head headaches by addressing the underlying muscle tension and postural issues. Here are some strategies and exercises that can offer relief:
- Neck Stretches: Gentle stretching exercises for the neck can relieve tension and reduce headache symptoms. Examples include neck tilts and rotations.
- Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the muscles in the neck, shoulders, and upper back can improve posture and decrease the likelihood of headaches.
- Posture Training: Physical therapists can provide guidance on maintaining proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking to prevent tension headaches.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage and mobilization of the spine by a physical therapist can help alleviate muscle tightness and improve spinal function.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold to the neck and shoulders can reduce muscle spasms and pain associated with headaches.
- Biofeedback: Learning to control physiological responses to stress through biofeedback can reduce the frequency of tension headaches.
- Relaxation Techniques: Incorporating relaxation exercises, such as deep breathing and meditation, into your routine can help manage stress and reduce headache occurrences.
Engaging in a regular program of physical therapy and exercises, tailored to your specific needs, can be a powerful tool in managing and preventing back of head headaches.
Nutritional Considerations and Headaches
Diet plays a crucial role in the management and prevention of headaches, including those at the back of the head. Certain foods can trigger headaches in susceptible individuals, while others may help reduce their frequency and severity:
- Avoid Known Triggers: Common dietary triggers include aged cheeses, processed foods, red wine, chocolate, and foods high in MSG, nitrates, or artificial sweeteners. Identifying and avoiding these can help reduce headache occurrences.
- Maintain Stable Blood Sugar: Skipping meals or fasting can trigger headaches in some people. Eating regular, balanced meals helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent headaches.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration is a known headache trigger. Drinking sufficient water throughout the day can help prevent headaches.
- Increase Magnesium Intake: Low levels of magnesium have been linked to headaches and migraines. Foods rich in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, can be beneficial.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both can be headache triggers. Reducing intake may help, especially if you notice a link between your consumption and headache patterns.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These have anti-inflammatory properties and can be found in fish, flaxseed, and walnuts, potentially reducing headache frequency.
- Consider a Food Diary: Tracking what you eat can help identify potential food triggers and the effect of dietary changes on your headaches.
Adopting a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and being mindful of food triggers can play a significant role in headache management. Consultation with a healthcare provider or a nutritionist can provide personalized dietary advice.
.png)
Stress Management Techniques for Headache Sufferers
Stress is a common trigger for headaches, including those at the back of the head. Implementing effective stress management techniques can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being, helping to decrease the likelihood of stress-induced headaches.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices promote relaxation and have been shown to be effective in managing stress and reducing headache frequency.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep, controlled breathing can help calm the nervous system and reduce stress, offering relief from headache symptoms.
- Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to reduce stress and tension, which can help prevent headaches.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves tensing and then slowly relaxing different muscle groups, which can help alleviate stress and headache pain.
- Adequate Sleep: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and ensuring you get enough rest can reduce stress levels and the occurrence of headaches.
- Time Management: Organizing your schedule and setting realistic goals can help prevent the stress that comes from feeling overwhelmed, potentially reducing headache frequency.
- Seeking Social Support: Talking with friends, family, or a professional can provide emotional support and reduce stress.
By incorporating these stress management techniques into your daily routine, you can create a more balanced lifestyle and effectively manage headache symptoms.
READ MORE:
Alternative Treatments: Acupuncture, Massage, and More
For those seeking relief from back of head headaches, alternative treatments can offer effective solutions without the need for medication. These methods have been shown to reduce headache frequency and severity for many individuals:
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It"s thought to stimulate the nervous system and promote pain relief, including for headaches.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help reduce muscle tension in the neck, shoulders, and back, which is often associated with tension headaches. Regular sessions may help decrease headache occurrence.
- Chiropractic Care: Adjustments and manipulations by a chiropractor can help relieve structural issues and improve spinal health, potentially reducing headache symptoms.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs, such as feverfew and butterbur, have been used to prevent and treat headaches. However, it"s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any herbal treatment.
- Aromatherapy: Essential oils, such as lavender or peppermint, used in aromatherapy can provide relaxation and reduce stress, which may help alleviate headache symptoms.
- Biofeedback: This technique teaches control over certain bodily processes that are typically involuntary, such as muscle tension and blood pressure, which can be beneficial for headache sufferers.
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): This program incorporates mindfulness meditation and yoga to reduce stress and improve pain management, including for headaches.
Exploring these alternative treatments, possibly in conjunction with conventional therapies, can provide a comprehensive approach to managing back of head headaches and enhancing overall well-being.
Understanding the complexities of back of head headaches empowers you to find relief and improve your quality of life. Embrace the journey toward wellness with knowledge, positive lifestyle changes, and the support of healthcare professionals.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headache-on-the-right-side-5216756_final-b9d0145864d74706b0316a2e9b62dd37.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)