Topic headache right side of head: Discover the causes and solutions for headaches on the right side of your head, offering you insights into effective relief and prevention strategies for improved well-being.
Table of Content
- What are the common causes of a headache on the right side of the head?
- Common Causes of Right-Side Headaches
- Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
- Differentiating Between Migraine, Cluster, and Tension Headaches
- When to See a Doctor: Red Flags and Serious Symptoms
- Diagnosis Techniques and Tests
- Treatment Options: Medication, Therapy, and Home Remedies
- YOUTUBE: Causes of a Right-Sided Headache
- Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
- Understanding Cluster Headaches and Their Unique Characteristics
- Impact of Dehydration and Dietary Factors
- Neurological Conditions and Other Underlying Causes
- Managing Pain: Tips for Immediate Relief
- Long-Term Management and Coping Strategies
What are the common causes of a headache on the right side of the head?
The common causes of a headache on the right side of the head can include:
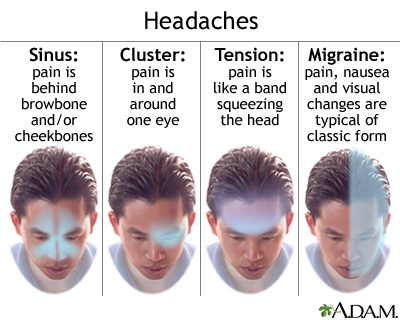
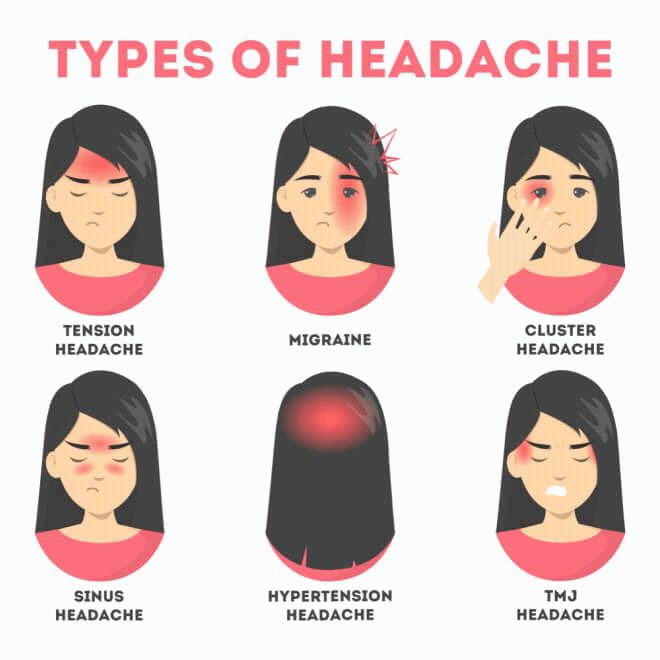
- Migraine: A neurological condition that often causes throbbing pain on one side of the head, accompanied by symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Tension headache: A common type of headache characterized by a dull, aching pain or pressure on both sides of the head, but it can also occur on one side.
- Cluster headache: A severe headache that typically occurs on one side of the head, often around the eye area, and is characterized by intense pain, usually accompanied by other symptoms like eye redness, nasal congestion, and tearing.
It is important to note that these are just common causes, and a headache on the right side of the head can also be a result of other factors such as sinusitis, stress, eye strain, dehydration, or even medication side effects. If you\'re experiencing chronic or severe headaches, it\'s recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
READ MORE:
Common Causes of Right-Side Headaches
Headaches on the right side of the head can stem from various causes, each affecting individuals differently. Understanding these can help in managing and preventing discomfort.
- Migraine: Characterized by intense, throbbing pain, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Tension Headaches: Manifests as a constant pressure or ache around the head, especially at the temples or back of the head and neck.
- Cluster Headaches: Known for their severe, piercing pain behind one eye or the temple area, occurring in clusters over weeks or months.
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses, leading to pain on one side of the head, can cause pressure-like pain in specific areas.
- Dehydration: Lack of adequate fluids can lead to a dehydration headache, often felt on one side of the head.
- Eye Strain: Prolonged periods of screen use without breaks can lead to headaches predominantly on the right side, if that side is more strained.
- Dental Issues: Problems such as TMJ disorders or toothaches can refer pain to the right side of the head.
- Caffeine Withdrawal: Sudden decrease in caffeine intake can trigger headaches on one side of the head.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, especially in women, can lead to migraines and headaches on one side.
Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and relief. Lifestyle changes, medication, or professional medical advice may be recommended based on the cause.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
When experiencing a headache on the right side of your head, certain signs and symptoms can indicate the severity and cause of your discomfort. Paying attention to these can help in seeking the appropriate treatment.
- Severity of Pain: From a mild, annoying ache to severe, debilitating pain that interferes with daily activities.
- Location of Pain: Pain localized to the right side, potentially radiating to the face, neck, or shoulders.
- Type of Pain: Can vary from throbbing, pulsating pain to a constant, steady ache.
- Duration: Headaches that last from 30 minutes to several hours, or even days, indicating different conditions.
- Frequency: Occasional headaches versus chronic patterns that may require professional attention.
- Trigger Factors: Specific triggers such as food, stress, weather changes, or lack of sleep that precede the headache.
- Associated Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, visual disturbances, or dizziness accompanying the headache.
- Changes in Vision: Blurry vision, partial vision loss, or aura (visual disturbances indicating a migraine).
- Neurological Symptoms: Difficulty speaking, weakness, or numbness on one side of the body, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Impact on Daily Life: The extent to which the headache affects your ability to perform daily tasks and enjoy life.
Recognizing these signs and symptoms can aid in understanding the nature of your headache and deciding when to seek medical advice for effective management and treatment.
Differentiating Between Migraine, Cluster, and Tension Headaches
Understanding the differences between migraine, cluster, and tension headaches can be crucial for effective treatment and management. Each type has distinct characteristics that help in their identification.
- Migraines: Often characterized by throbbing or pulsing pain on one side of the head, migraines can last from 4 to 72 hours. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Some individuals experience auras, such as flashes of light or blind spots, before the onset of the headache.
- Cluster Headaches: Known for their extreme pain, cluster headaches occur in cyclical patterns or clusters. The pain is typically located around or behind one eye and can be very severe. These headaches are often accompanied by redness in the eye, nasal congestion, or a runny nose on the affected side. Cluster periods can last from weeks to months, followed by remission periods.
- Tension Headaches: These are the most common type of headache and are characterized by a constant ache or pressure around the head, especially at the temples or back of the head and neck. Tension headaches can last from 30 minutes to several days, and the pain is usually mild to moderate in intensity, without the specific accompanying symptoms seen in migraines and cluster headaches.
By identifying the specific type of headache you"re experiencing, you can better understand how to manage your symptoms and seek out the most appropriate treatments. Lifestyle adjustments, medications, and other therapies may vary significantly based on the type of headache.
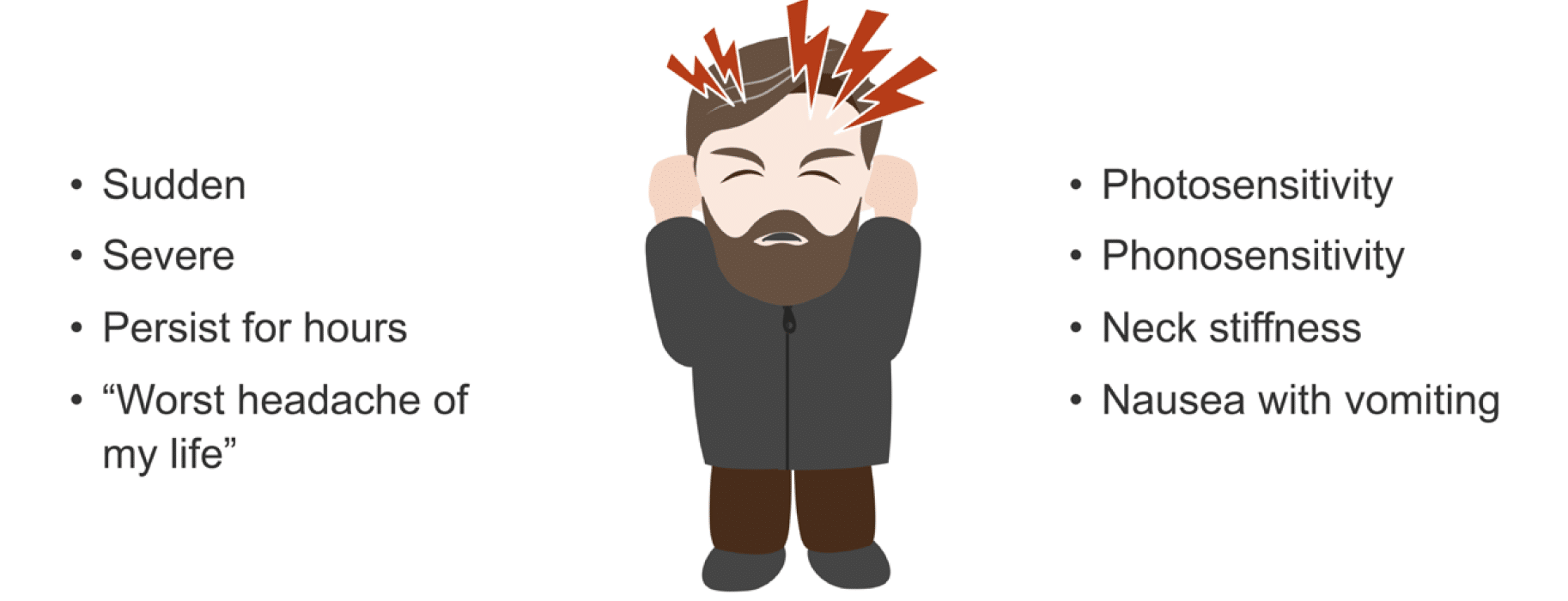
When to See a Doctor: Red Flags and Serious Symptoms
While most headaches are not indicative of a serious medical condition, certain symptoms can signal a need for immediate medical attention. Recognizing these red flags is essential for your health and safety.
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is severe, often described as a "thunderclap" headache, could indicate a serious condition such as an aneurysm.
- Progressive Pain: Headaches that progressively worsen over days or weeks can be a sign of a tumor, abscess, or increased pressure inside the skull.
- Neurological Symptoms: Symptoms such as confusion, seizures, difficulty speaking, or weakness in the arms or legs warrant immediate evaluation.
- Change in Pattern: A significant change in the frequency, severity, or characteristics of your headaches should be assessed by a healthcare provider.
- Headache after Head Injury: A headache that develops after a head injury, even if it seems minor, requires prompt medical attention.
- Associated Symptoms: Headaches accompanied by fever, stiff neck, rash, vomiting, or visual loss can be signs of serious conditions like meningitis or glaucoma.
- Impact on Daily Activities: If headaches are affecting your ability to function in your daily life, seek medical advice for management strategies.
- First or Worst Headache: Your first-ever severe headache or one that is significantly worse than your usual headaches should be evaluated promptly.
- Age Factor: New onset of headaches in individuals over 50 years old can indicate temporal arteritis or other age-related conditions.
Listening to your body and seeking medical advice when experiencing these symptoms can lead to early diagnosis and treatment of potentially serious conditions.
Diagnosis Techniques and Tests
To accurately diagnose the cause of headaches on the right side of the head, healthcare professionals may employ a variety of techniques and tests. These diagnostic measures help to rule out underlying conditions and ensure appropriate treatment.
- Medical History: A comprehensive review of your medical history, symptoms, and any factors that exacerbate or relieve your headaches.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical exam, including checking your blood pressure, and assessing your head, neck, eyes, ears, nose, and throat.
- Neurological Examination: Tests to assess your reflexes, muscle strength, sensation, balance, and coordination.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans can provide detailed images of the brain, helping to identify tumors, bleeding, or other abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Can detect infections, blood vessel problems, or toxins that might be contributing to headaches.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): In cases where infection or bleeding in the brain is suspected, a lumbar puncture may be performed to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Eye Exam: An examination by an ophthalmologist to check for vision problems or pressure on the optic nerve.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): Though less common, an EEG might be conducted if seizures are a suspected cause of headaches.
Diagnosing the cause of right-side headaches often requires a combination of these techniques to provide a comprehensive overview of the patient"s condition, guiding effective treatment plans.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headache-on-the-right-side-5216756_final-b9d0145864d74706b0316a2e9b62dd37.jpg)
Treatment Options: Medication, Therapy, and Home Remedies
Effective management of headaches on the right side of the head involves a multifaceted approach, including medications, therapies, and home remedies. Tailoring the treatment to the type of headache and individual needs is crucial for relief.
- Medications:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen for mild headaches.
- Prescription medications, including triptans for migraines or oxygen therapy for cluster headaches.
- Preventive medications such as beta-blockers or anticonvulsants, particularly for frequent headaches.
- Therapies:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to manage pain perception and reduce stress, which can trigger headaches.
- Physical therapy, especially for tension headaches caused by muscle strain or poor posture.
- Acupuncture or massage therapy, offering relief for some individuals by reducing stress and muscle tension.
- Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes:
- Maintaining a headache diary to identify and avoid potential triggers.
- Regular physical activity, which can reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches over time.
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises.
- Adequate hydration and a balanced diet, avoiding foods known to trigger headaches.
- Ensuring sufficient sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.
Combining these treatments under the guidance of healthcare professionals can significantly improve quality of life for those suffering from right-side headaches.
Causes of a Right-Sided Headache
Causes: Curious about the causes behind certain phenomena? This captivating video explores the fascinating world of causes, shedding light on the intricate web of factors that shape our lives and offering eye-opening insights you won\'t want to miss!
Migraines 101: Understanding Symptoms
Migraines: Are migraines a constant struggle in your life? Find relief and understanding through this informative video, as it delves into the mysteries of migraines, providing valuable tips and techniques to manage and potentially even overcome these debilitating headaches.
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting effective prevention strategies and making lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches on the right side of the head. These proactive measures focus on maintaining overall health and identifying headache triggers.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can reduce stress and prevent headache occurrences.
- Healthy Eating Habits: Maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding known headache triggers, such as alcohol, caffeine, and certain foods, can help manage headache symptoms.
- Adequate Hydration: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, a common headache trigger.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels, reducing the likelihood of stress-induced headaches.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Ensuring you get enough sleep and maintaining a regular sleep pattern can prevent headaches.
- Avoiding Smoking: Smoking can trigger headaches in some individuals; quitting smoking can reduce the frequency of headaches.
- Limiting Screen Time: Reducing time spent in front of screens and taking regular breaks can prevent eye strain and associated headaches.
- Posture Improvement: Maintaining good posture, especially when sitting for long periods, can prevent tension headaches.
- Regular Eye Checkups: Eye strain can lead to headaches; regular checkups can ensure that prescription glasses or contacts are up to date.
Implementing these strategies can help minimize the impact of headaches on your daily life, improving your overall well-being.
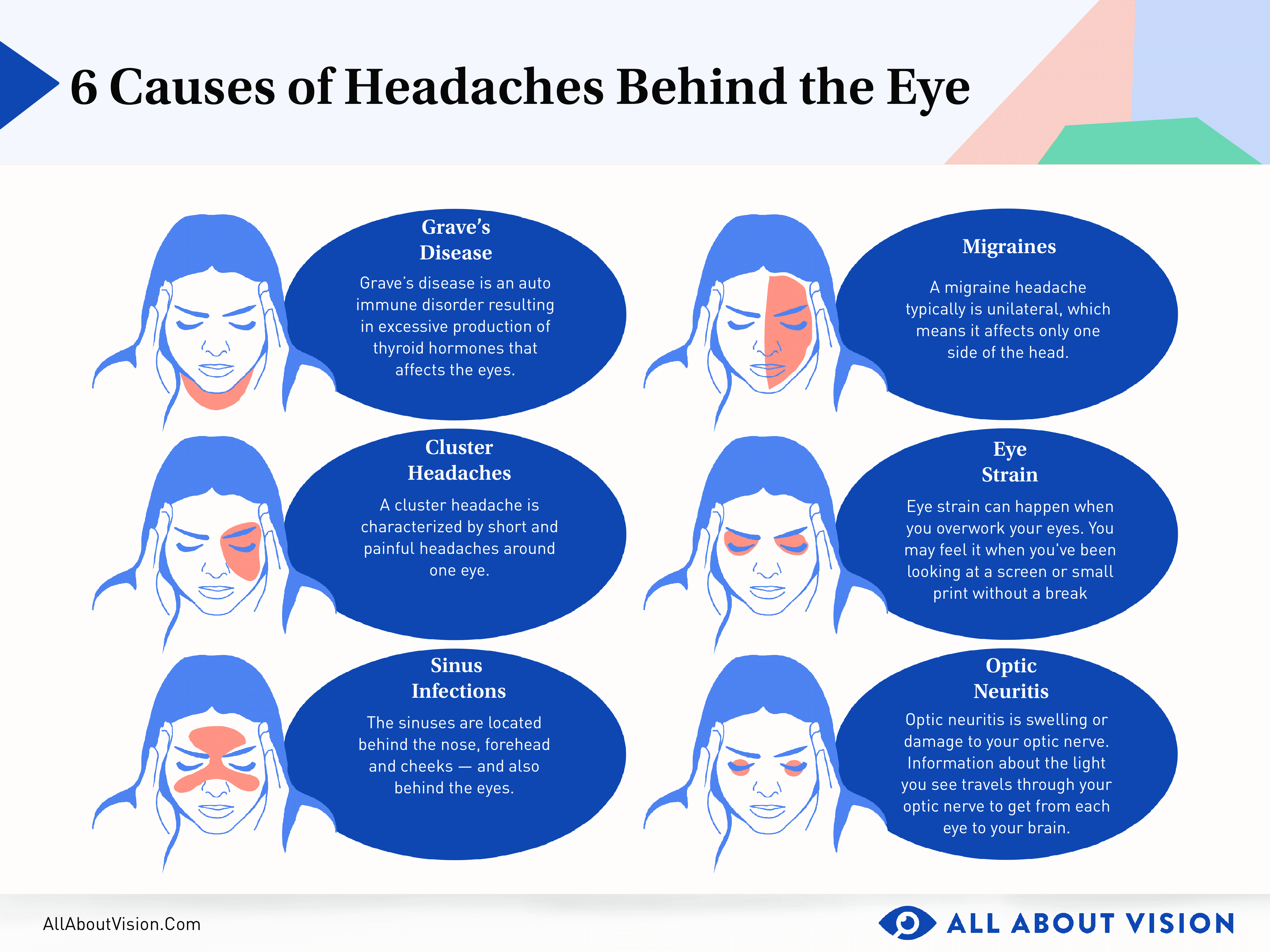
Understanding Cluster Headaches and Their Unique Characteristics
Cluster headaches are a severe form of headache known for their unique characteristics and patterns, which significantly impact those affected. Understanding these features can help in identifying and managing this painful condition.
- Intense Pain: Cluster headaches are marked by extremely severe pain, often described as burning or piercing, typically located around or behind one eye.
- Cluster Periods: These headaches occur in groups or clusters, appearing suddenly and lasting for weeks or months, followed by remission periods when no headaches occur.
- Frequency: During a cluster period, headaches can occur up to several times a day, each lasting from 15 minutes to 3 hours.
- Unilateral Symptoms: Symptoms are often one-sided, including redness of the eye, nasal congestion, runny nose, or sweating on the affected side of the face.
- Triggers: Alcohol, cigarettes, and certain foods or environmental factors can trigger attacks during a cluster period.
- Restlessness: Unlike migraines, individuals experiencing cluster headaches may become very restless or agitated.
- Time of Occurrence: Attacks often occur at the same time each day, frequently waking sufferers from sleep.
- Gender Prevalence: Cluster headaches are more common in men than women and typically start between the ages of 20 and 40.
Due to the intensity and pattern of pain, cluster headaches require specific treatment strategies, including oxygen therapy, triptans, and preventive medications, to manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of headache clusters.
Impact of Dehydration and Dietary Factors
The role of hydration and diet is crucial in the management and prevention of headaches on the right side of the head. Understanding how dehydration and certain dietary factors affect headaches can guide better lifestyle choices.
- Dehydration: Even mild dehydration can lead to headaches by causing the brain to temporarily contract or shrink, pulling away from the skull. Staying well-hydrated is essential for headache prevention.
- Caffeine: Both excessive consumption and withdrawal from caffeine can trigger headaches. Moderating intake and reducing caffeine gradually can help prevent these headaches.
- Alcohol: Certain types of alcohol, especially red wine, contain substances like tyramine and histamine that can trigger headaches in sensitive individuals.
- Processed Foods: Foods high in nitrates, nitrites, MSG, and artificial sweeteners may trigger headaches in some people. Opting for fresh, whole foods can reduce the risk of headache.
- Meal Skipping: Irregular eating patterns and skipping meals can lead to low blood sugar levels, which might trigger headaches. Maintaining regular meal times can help prevent this.
- Hydration Tips: Drinking water throughout the day, consuming hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables, and minimizing diuretic beverages can keep dehydration at bay.
- Dietary Management: Identifying and avoiding personal headache triggers through a food diary can be an effective strategy for some individuals.
By paying attention to hydration and dietary habits, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches, leading to better overall health and well-being.

Neurological Conditions and Other Underlying Causes
Headaches on the right side of the head can sometimes be symptomatic of underlying neurological conditions or other health issues. Identifying these causes is crucial for targeted treatment and management.
- Brain Tumors: Though rare, headaches can be a symptom of a brain tumor. The headache may worsen in the morning or change intensity with changes in position.
- Stroke: A sudden, severe headache can be a sign of stroke, especially if accompanied by other symptoms such as difficulty speaking, weakness, or vision problems.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): Abnormal connections between arteries and veins in the brain can cause headaches due to the increased pressure.
- Temporal Arteritis: Inflammation of the blood vessels (arteries) in and around the scalp can cause a sharp, throbbing headache.
- Trigeminal Neuralgia: This chronic pain condition affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain, leading to intense facial pain that can be mistaken for headaches.
- Intracranial Hypertension: Increased pressure inside the skull can lead to headaches, often accompanied by visual disturbances.
- Infections: Meningitis, encephalitis, and other infections can cause headaches as part of their symptomatology.
- Medication Overuse Headaches: Overuse of headache medication can lead to rebound headaches, worsening headache symptoms over time.
Due to the potential severity of these conditions, it"s important to seek medical evaluation if your headache patterns change or if headaches are accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Managing Pain: Tips for Immediate Relief
When a headache strikes, especially on the right side of your head, knowing how to manage the pain quickly can provide much-needed relief. Here are some effective strategies to alleviate headache pain.
- Apply Cold or Warm Compress: For some, a cold pack to the forehead for 15 minutes can relieve pain, while others may find a warm compress or heating pad on the back of the neck more beneficial.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water can sometimes alleviate headache pain, especially if dehydration is a factor.
- Limit Screen Time: Taking a break from screens can reduce headaches caused by eye strain.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga can help reduce stress-related headaches.
- Try Caffeine: In small amounts, caffeine can enhance the pain-relieving effects of ibuprofen and acetaminophen. But be cautious, as too much can lead to withdrawal headaches.
- Adjust Lighting: Dimming or turning off bright lights can help if your headache is triggered by light sensitivity.
- Over-the-Counter Medication: For some, over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or aspirin can provide quick relief. Use these medications as directed to avoid overuse headaches.
- Essential Oils: Peppermint and lavender essential oils can be applied to the temples to help soothe headache pain for some people.
- Maintain Good Posture: Improving your posture can reduce headaches caused by neck strain, especially if you spend long hours at a desk.
While these tips can provide immediate relief, understanding and addressing the underlying causes of your headaches is crucial for long-term management.
READ MORE:
Long-Term Management and Coping Strategies
Effectively managing headaches on the right side of the head over the long term involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medical treatment, and coping strategies. These approaches aim to reduce the frequency, severity, and impact of headaches on daily life.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Ongoing communication with your healthcare provider can help adjust treatments as needed and address any emerging issues.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress is a common trigger for headaches. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness, and stress reduction exercises can be beneficial.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can decrease the frequency and intensity of headaches by improving overall health and stress resilience.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep schedule and ensuring adequate sleep can significantly impact headache management.
- Diet and Hydration: Eating a balanced diet, avoiding known triggers, and staying well-hydrated can prevent headache episodes.
- Medication Management: Proper use of prescribed medications, avoiding overuse, and regular reviews with a healthcare provider can optimize headache control.
- Educational Resources: Learning about your condition and staying informed on the latest treatments and management strategies can empower you to take an active role in your care.
- Support Networks: Connecting with support groups or online communities can provide valuable advice, empathy, and coping strategies shared by others experiencing similar issues.
- Environmental Adjustments: Minimizing exposure to headache triggers in your environment, such as bright lights, strong odors, or loud noises, can help reduce the likelihood of headache onset.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices such as yoga, acupuncture, and biofeedback can offer relief for some individuals by promoting relaxation and pain management.
By adopting these long-term management strategies, individuals can improve their quality of life and gain greater control over their headache symptoms.
Empower yourself with knowledge and proactive measures to manage right-side headaches effectively. Embrace a healthier lifestyle, seek timely medical advice, and explore various treatments to find your path to relief and well-being.


.png)
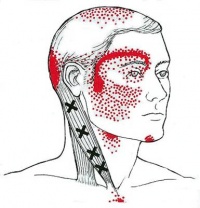
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)
