Topic different types of headache: Explore the realm of "Different Types of Headache", a comprehensive guide to understanding, diagnosing, and managing the various headache forms, tailored to provide relief and insights for sufferers seeking a healthier, more comfortable life.
Table of Content
- What are the different types of headache?
- Understanding Headache Types and Symptoms
- Diagnosis and Evaluation of Headaches
- Common Headache Triggers and How to Manage Them
- Treatment Options for Various Headache Types
- When to Seek Medical Attention for Your Headache
- Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments
- YOUTUBE: Different Types of Headaches
- Exploring Alternative Treatments and Therapies
- Headache Management: Diet, Exercise, and Stress Reduction
- The Impact of Sleep and Hydration on Headaches
- Understanding Secondary Headaches and Underlying Conditions
What are the different types of headache?
There are several different types of headaches that individuals can experience:
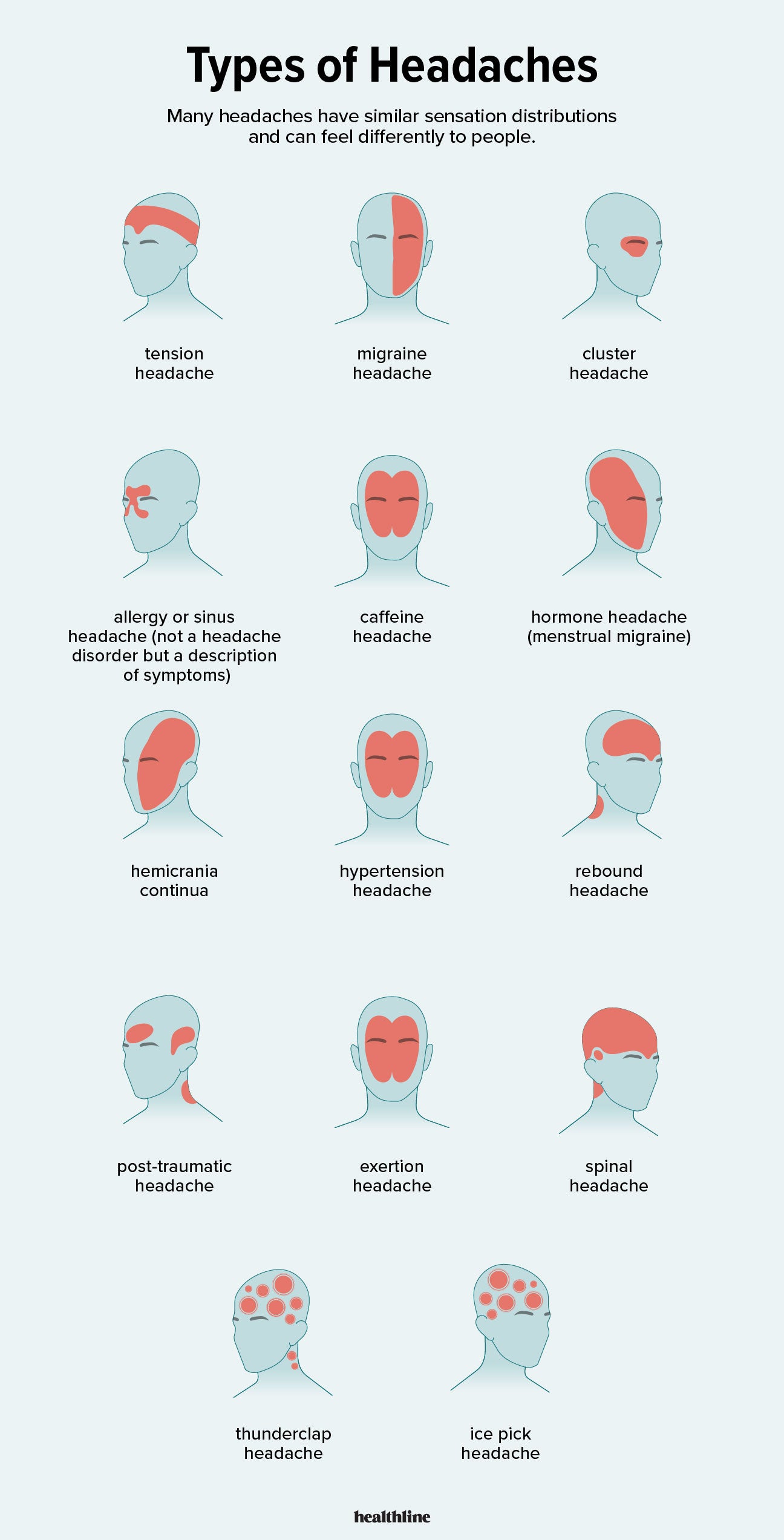
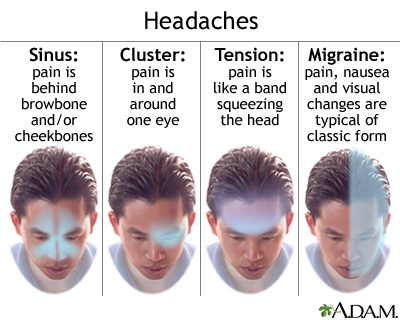
- Tension Headaches: These are the most common type of headache and are typically characterized by a dull, aching pain on both sides of the head or neck.
- Migraine Headaches: Migraines are severe headaches that can cause throbbing or pulsating pain, often on one side of the head. They may also be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
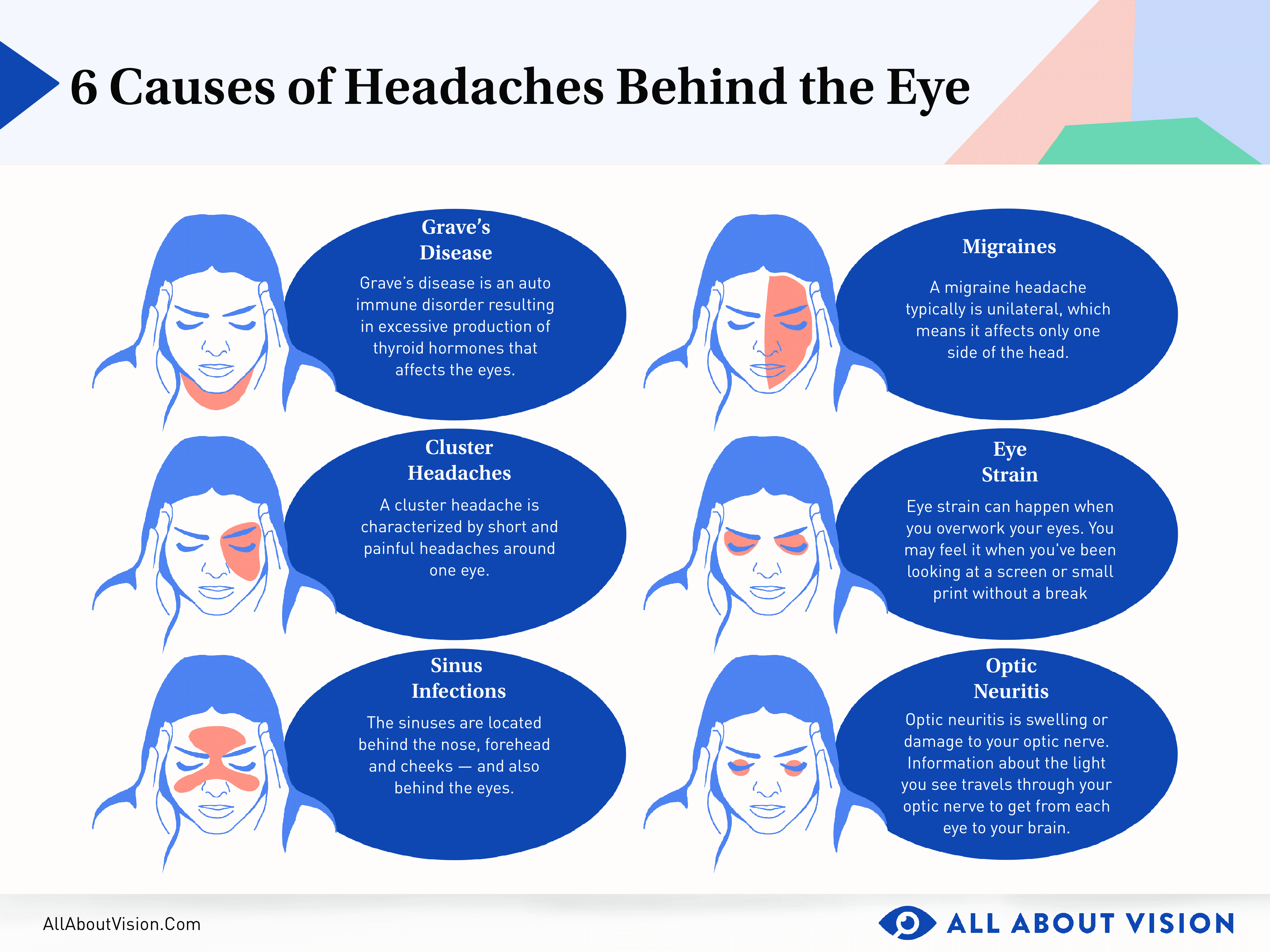
- Cluster Headaches: Cluster headaches are excruciatingly painful and occur in cycles or clusters. They usually affect one side of the head and are accompanied by symptoms like eye redness, tearing, and nasal congestion.
- Hypnic Headaches: Hypnic headaches are rare primary headaches that typically occur during sleep and wake individuals up. They are usually short-lived but can be very intense.
- Sinus Headaches: Sinus headaches are associated with sinus infections or allergies and are characterized by a constant pain or pressure in the forehead, cheeks, or bridge of the nose.
- Hormone Headaches: These headaches are often experienced by women and are triggered by hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause.
It\'s important to note that there are many other types of headaches as well, and it\'s always recommended to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
READ MORE:
Understanding Headache Types and Symptoms
Headaches come in various forms, each with unique characteristics and symptoms. Recognizing the differences is crucial for effective management and treatment. Below, we explore the most common types of headaches and their symptoms.
- Migraine: Characterized by intense, throbbing pain usually on one side of the head. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and sometimes aura—visual disturbances signaling the headache"s onset.
- Tension-Type Headache: The most common type, featuring a constant, dull ache on both sides of the head. Often associated with stress, tension headaches may also involve sensitivity around the neck and scalp.
- Cluster Headaches: Known for their severe, burning pain around one eye or temple. These headaches occur in clusters, happening frequently over weeks or months, followed by remission periods. Symptoms include watery eye, nasal congestion, or swelling around the eye on the affected side.
- Hypnic Headache: A rare condition that wakes individuals from sleep, typically occurring at the same time every night. The pain is mild to moderate and affects both sides of the head.
- Secondary Headaches: Caused by underlying conditions, such as sinus infection, high blood pressure, or brain tumors. Symptoms vary widely depending on the cause.
Identifying the type of headache you"re experiencing is a step toward finding relief. Note the patterns, triggers, and symptoms, and consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.

Diagnosis and Evaluation of Headaches
Proper diagnosis and evaluation are key to effective headache management. This process helps distinguish between different types of headaches and identifies any underlying conditions that may require treatment. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how healthcare professionals typically diagnose and evaluate headaches:
- Patient History: A detailed patient history is taken to understand the frequency, duration, and characteristics of the headache. Patients are often asked about the nature of the pain (throbbing, constant, piercing), location, time of onset, and any associated symptoms (nausea, light sensitivity).
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive physical exam can help rule out physical factors contributing to headaches. This may include checking blood pressure, signs of infection, or neurological abnormalities.
- Neurological Assessment: To exclude neurological disorders, a series of tests may be conducted to examine the brain and nerve function, including reflexes, muscle strength, eye and coordination tests.
- Diagnostic Tests: While not always necessary, diagnostic tests such as MRI or CT scans can be used to identify any structural problems in the brain that may be causing the headache.
- Headache Diaries: Keeping a headache diary is often recommended to track the occurrence of headaches, their severity, duration, associated symptoms, and potential triggers. This information is invaluable in making an accurate diagnosis.
- Referral to Specialists: In cases where headaches are complex or difficult to diagnose, referral to a neurologist or headache specialist may be necessary for further evaluation and treatment.
Understanding the cause of your headaches is the first step towards finding effective treatment and relief. Always consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Common Headache Triggers and How to Manage Them
Identifying and managing triggers is a crucial step in preventing headaches. While triggers can vary from person to person, some are widely recognized. Here"s a look at common headache triggers and tips for managing them:
- Stress: Stress is a common trigger for many types of headaches. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises, can help reduce the frequency of headaches.
- Diet: Certain foods and drinks, like aged cheeses, processed foods, alcohol, and caffeine, can trigger headaches in some people. Keeping a food diary can help identify and avoid these triggers.
- Sleep Patterns: Both too much and too little sleep can provoke headaches. Establishing a regular sleep schedule and ensuring you get 7-9 hours of sleep each night can help.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water is a common headache trigger. Aim for at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water a day to stay hydrated.
- Bright Lights and Loud Noises: Bright, flickering lights, or loud noises can induce headaches for some. Reducing screen time, using anti-glare screens, and wearing earplugs in loud environments can mitigate these triggers.
- Hormonal Changes: For some, especially women, hormonal fluctuations can trigger headaches. If you suspect hormonal changes are causing headaches, consult with a healthcare provider for management strategies.
- Weather Changes: Changes in weather or barometric pressure can trigger headaches in some individuals. While you can"t control the weather, staying hydrated and taking over-the-counter pain relief at the first sign of a headache can help.
- Physical Activity: Intense physical activity can lead to exertion headaches for some people. Gradually warming up and staying hydrated can help prevent these types of headaches.
Understanding your headache triggers and how to manage them is a proactive way to reduce their impact on your life. Remember, if you"re experiencing frequent or severe headaches, it"s important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.

Treatment Options for Various Headache Types
Effective headache treatment varies depending on the type of headache. Understanding the specific type of headache you"re dealing with is crucial for finding the most effective treatment. Below are general guidelines for treating different headache types:
- Migraine Headaches: Treatment often involves a combination of medications to relieve symptoms and prevent future attacks. Over-the-counter pain relievers, triptans, anti-nausea medications, and preventive medications such as beta-blockers or antidepressants may be used.
- Tension-Type Headaches: These are commonly treated with over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Stress management techniques, physical therapy, and sometimes prescription medications are also effective.
- Cluster Headaches: Treatment can include oxygen therapy, triptans, and preventative medications such as verapamil. Due to the severity of the pain, fast-acting treatments are preferred.
- Secondary Headaches: Treatment targets the underlying cause. For example, if a headache is due to sinus infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. For hypertension-related headaches, blood pressure medication might be necessary.
- Lifestyle and Home Remedies: For all types of headaches, lifestyle modifications can play a key role in management. Adequate hydration, regular sleep patterns, exercise, and stress reduction can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
- Alternative Therapies: Some people find relief through acupuncture, massage, biofeedback, or cognitive behavioral therapy. These can be especially helpful for those looking to minimize medication use.
Always consult with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan tailored to your specific condition and needs. They can provide guidance on the best combination of treatments based on your individual symptoms and headache type.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Your Headache
While most headaches are not indicative of a serious medical condition, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Recognizing these signs can help you decide when it"s time to consult a healthcare professional.
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is severe, often described as a "thunderclap" headache, can be a sign of a serious condition, such as an aneurysm.
- Changes in Pattern: Any significant changes in the frequency, severity, or patterns of your headaches should be evaluated.
- Neurological Symptoms: Headaches accompanied by symptoms such as confusion, difficulty speaking, vision loss, or weakness on one side of the body may indicate a stroke or other neurological conditions.
- After Head Injury: Headaches that develop after a head injury can signify a concussion or other serious injury.
- Associated Symptoms: Headaches with a fever, stiff neck, rash, vomiting, or a significant lack of energy could suggest an infection like meningitis.
- Persistent Headaches in Children: Persistent or recurring headaches in children always warrant a medical evaluation to rule out underlying conditions.
- Worsening Headaches: Headaches that progressively worsen over days or weeks need to be checked out to exclude tumors or hydrocephalus (fluid accumulation in the brain).
Consulting a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is crucial if you experience any of these symptoms. Early intervention can be key in managing serious conditions effectively.

Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments
Adopting certain preventive measures and making lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Tailoring these strategies to fit your life can help manage and even prevent headaches.
- Regular Sleep Schedule: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule helps prevent headaches by stabilizing your body"s natural rhythm.
- Healthy Diet: Eating balanced meals at regular intervals prevents low blood sugar levels, which can trigger headaches.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake is essential to prevent dehydration, a common headache trigger.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can reduce stress levels and the likelihood of stress-induced headaches.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity increases overall health and reduces stress, which can help prevent headaches.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal headache triggers, such as certain foods, drinks, or environmental factors, is crucial.
- Limiting Stimulants: Reducing intake of caffeine and alcohol can prevent headaches associated with withdrawal or overuse.
- Regular Breaks: Taking regular breaks from screen time and ensuring proper posture can prevent tension and eye strain headaches.
By integrating these preventive measures and lifestyle adjustments into your routine, you can significantly reduce the impact of headaches on your daily life. Consultation with a healthcare provider can offer additional personalized strategies.
Different Types of Headaches
Are persistent headaches affecting your daily life? Learn effective strategies to alleviate headaches and find relief through this informative video. Say goodbye to discomfort and embrace a pain-free lifestyle!
Primary vs. Secondary Headaches | Migraine, Cluster, Tension Headaches
Suffering from debilitating migraines? Unlock the secrets to managing migraines and regain control of your life. Discover helpful tips, remedies, and expert advice in this eye-opening video that promises to offer relief and prevent future episodes. Don\'t let migraines hold you back any longer!
Exploring Alternative Treatments and Therapies
Alongside traditional medical treatments, many individuals find relief from headaches through alternative treatments and therapies. These approaches can complement conventional treatments, offering holistic relief and prevention strategies.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It"s widely used for pain relief and can be effective for migraines and tension headaches.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help reduce stress and relieve tension in the muscles of the neck, shoulders, and head, thereby alleviating headache symptoms.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, such as feverfew and butterbur, have been studied for their potential to prevent migraines and reduce headache severity.
- Essential Oils: Aromatherapy using essential oils like lavender or peppermint can be applied topically or inhaled to provide relief from headache symptoms.
- Yoga and Meditation: These practices can help manage stress, a common headache trigger, and incorporate physical postures, breath control, and meditation to promote overall well-being.
- Biofeedback: A technique that teaches control over certain physiological processes that can influence headache activity, such as muscle tension and blood pressure.
- Magnesium Supplements: Magnesium deficiency has been linked to headaches, especially migraines. Supplementing with magnesium may reduce the frequency of migraine attacks.
Before starting any alternative treatment, it"s important to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it"s safe and suitable for your specific health situation. Integrating these therapies with conventional treatments can offer a comprehensive approach to headache management.
Headache Management: Diet, Exercise, and Stress Reduction
Effective headache management often involves more than just medication. Diet, exercise, and stress reduction play a crucial role in reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. Implementing lifestyle changes can significantly improve your quality of life by minimizing headache symptoms.
- Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet helps stabilize blood sugar levels, which can prevent headaches. Avoid known dietary triggers such as aged cheeses, alcohol, caffeine, and processed foods. Incorporating foods rich in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, and seeds, may also help.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves overall health and reduces stress, which can decrease the frequency of headaches. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are beneficial. It"s important to start slowly and gradually increase intensity to avoid exercise-induced headaches.
- Stress Reduction: Since stress is a common trigger for headaches, finding effective ways to manage stress is key. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels and potentially lessen the occurrence of headaches.
- Hydration: Dehydration can trigger headaches, so it"s essential to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day. Aim for at least 8 cups of water daily, more if you"re active or in hot environments.
- Sleep: Poor sleep patterns can contribute to headaches. Establishing a regular sleep schedule and ensuring you get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night can help manage headache frequency.
By addressing diet, exercise, and stress, you can take proactive steps toward managing your headaches more effectively. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant lifestyle changes, especially if you have ongoing health conditions.
The Impact of Sleep and Hydration on Headaches
Sleep and hydration play crucial roles in the prevention and management of headaches. Inadequate sleep can lead to tension-type headaches and exacerbate migraine symptoms. Establishing regular sleep patterns and ensuring a sufficient amount of sleep each night can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Similarly, dehydration is a common trigger for headaches, including migraines. Maintaining proper hydration by drinking adequate amounts of water throughout the day can help prevent dehydration-related headaches and improve overall brain health.
- Ensure consistent sleep schedules to avoid triggering headaches.
- Drink plenty of water daily to prevent dehydration and associated headaches.
Addressing these lifestyle factors can serve as an effective strategy for reducing the occurrence of headaches and improving quality of life.

READ MORE:
Understanding Secondary Headaches and Underlying Conditions
Secondary headaches are caused by underlying medical conditions and require careful diagnosis to address the root cause. Unlike primary headaches, which include migraines and tension-type headaches, secondary headaches signal other health issues.
- Dehydration Headaches: Occur when the body loses essential fluids and electrolytes, leading to reduced blood volume and brain hydration.
- Sinus Headaches: Caused by sinus infection or inflammation, leading to pressure and pain in the forehead, cheeks, and nasal areas.
- Medication Overuse Headaches: Result from the frequent use of headache medication, leading to a rebound effect.
- Spinal Headaches: Arise from leakage of spinal fluid, often after a lumbar puncture, causing a drop in spinal fluid pressure.
- Thunderclap Headaches: Extremely severe headaches that develop suddenly and may indicate life-threatening conditions like subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Understanding the specific symptoms and causes of secondary headaches is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management strategy.
Understanding the various types of headaches is crucial for effective management and treatment. This comprehensive guide explores everything from symptoms and triggers to diagnosis and lifestyle adjustments, offering valuable insights for those seeking relief and prevention strategies.
.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-PaigeMcLaughlin-WhatisaClusterHeadache-Standard-87c962b6a28d4b1ab0359ed3ae5b696f.jpg)