Topic thunderclap headache: Discover the crucial insights into thunderclap headaches, a sudden and severe headache that demands immediate attention, highlighting its significance, symptoms, and the importance of timely medical intervention.
Table of Content
- How long does the pain of a thunderclap headache typically last?
- What is a Thunderclap Headache?
- Symptoms of Thunderclap Headaches
- Causes and Risk Factors
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Diagnosis of Thunderclap Headaches
- YOUTUBE: Brain Aneurysms: \"Sudden Onset Thunderclap Headaches\"
- Treatment Options
- Potential Complications
- Prevention and Management Strategies
- Living with Thunderclap Headaches
- Research and Future Directions
How long does the pain of a thunderclap headache typically last?
The pain of a thunderclap headache typically lasts for a short duration, ranging from minutes to a few hours.
READ MORE:
What is a Thunderclap Headache?
A thunderclap headache is a severe, sudden headache that strikes like a clap of thunder, reaching its peak intensity within 60 seconds. It is characterized by its abrupt onset and can be a symptom of potentially life-threatening conditions, such as bleeding around the brain, aneurysm, or stroke. Unlike other types of headaches, a thunderclap headache is often described by sufferers as the worst headache of their life, indicating its extreme severity and the immediate need for medical evaluation.
- Strikes suddenly and intensely, often without warning.
- Can indicate serious underlying medical conditions.
- Requires immediate medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the nature of thunderclap headaches is crucial for recognizing the urgency of seeking medical care to rule out or address any underlying conditions that may be life-threatening.
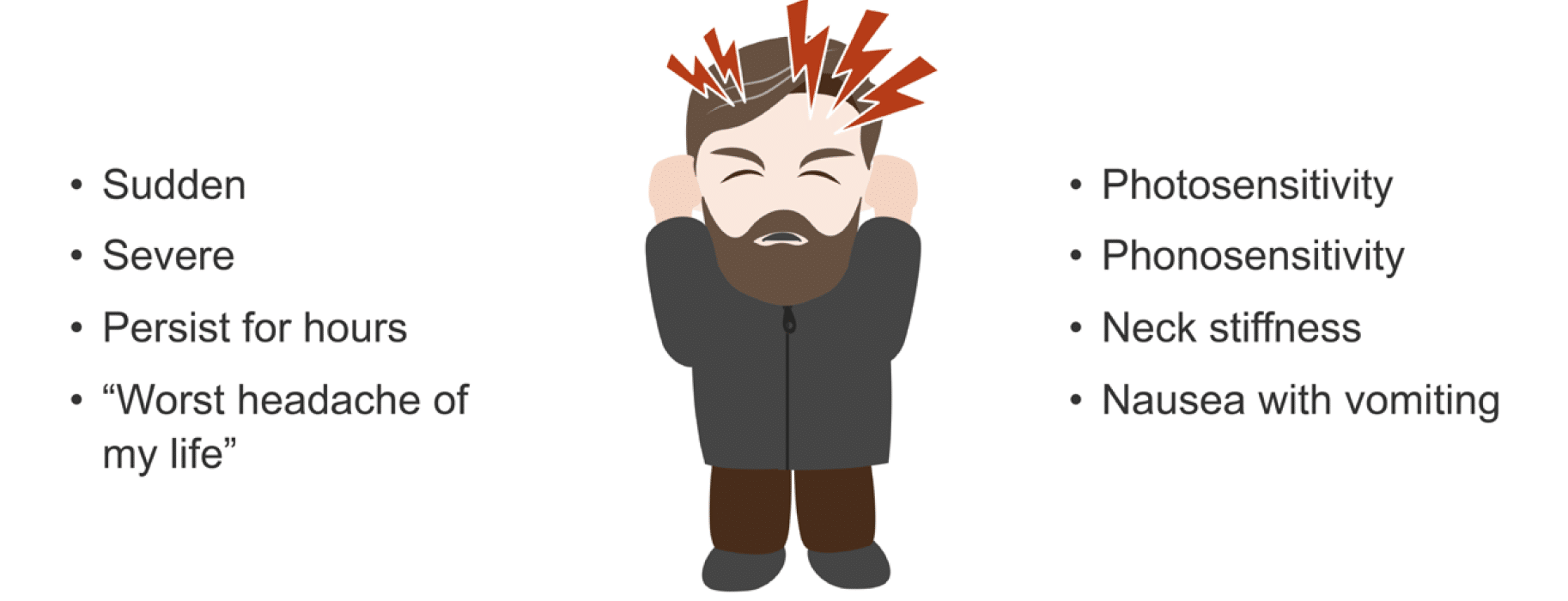

Symptoms of Thunderclap Headaches
Thunderclap headaches are distinguished by their sudden onset and severe intensity, often described as the most intense headache experience. Key symptoms include:
- Sudden, severe headache that peaks within 60 seconds
- Pain often accompanied by nausea or vomiting
- Possible altered mental state or consciousness
- Fever and seizures in some cases
- Neck stiffness or pain, indicating possible meningitis
- Visual disturbances or sensitivity to light
- Weakness, confusion, or difficulty speaking, suggesting a stroke
These symptoms require immediate medical attention as they may signal a serious underlying condition such as a subarachnoid hemorrhage, arterial dissection, or cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Thunderclap headaches are acute, severe headaches that can be primary or signal underlying serious conditions. Common causes include:
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) - bleeding in the space around the brain.
- Cerebral aneurysm - a bulge in a blood vessel in the brain that can leak or burst.
- Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) - sudden narrowing of the brain’s blood vessels.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage - bleeding within the brain tissue.
- Arterial dissection - a tear in the lining of an artery in the neck or brain.
- Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis - a blood clot in the brain’s venous sinuses.
- Infections such as meningitis or encephalitis.
Risk factors enhancing the likelihood of experiencing a thunderclap headache include:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Certain genetic conditions
- Use of illicit drugs, especially cocaine and amphetamines
- History of migraines
Recognizing these causes and risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention of conditions that could lead to thunderclap headaches.

When to Seek Medical Attention
Thunderclap headaches require immediate medical evaluation due to their potential association with life-threatening conditions. It"s critical to seek emergency medical attention if you experience:
- A sudden, severe headache that peaks within seconds or minutes.
- Headache accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or loss of consciousness.
- Signs of a neurological deficit, such as confusion, weakness, or difficulty speaking.
- Seizures or convulsions.
- Stiff neck or other symptoms suggesting meningitis.
- Visual changes or sensitivity to light.
Immediate evaluation can help identify and treat potential causes such as subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral aneurysm, or other critical conditions. Timely intervention can be crucial for a positive outcome.
Diagnosis of Thunderclap Headaches
Diagnosing a thunderclap headache involves ruling out potential serious causes to determine the appropriate treatment. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Initial assessment to understand the headache"s characteristics and any associated symptoms.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: An urgent CT scan of the head to look for signs of bleeding or other abnormalities in the brain.
- Lumbar Puncture: If the CT scan is normal but suspicion for subarachnoid hemorrhage remains, a lumbar puncture may be performed to detect blood in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI may be used to identify other causes of headaches, such as arterial dissection or stroke.
- CT Angiography or Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): These imaging tests are used to examine the blood vessels in the brain for any signs of aneurysm or other vascular anomalies.
These diagnostic tests are critical in identifying any serious underlying conditions that may be causing the thunderclap headache, enabling timely and appropriate treatment.

Brain Aneurysms: \"Sudden Onset Thunderclap Headaches\"
Are you familiar with the term \"Sudden Onset Thunderclap Headaches\"? If not, it\'s time to learn about the alarming symptoms that could be a sign of brain aneurysms. This informative video will shed light on this condition, ensuring you are well-informed and prepared for any potential medical emergencies.
Thunderclap Headache
Experiencing excruciating headaches that strike suddenly like a thunderclap? This intriguing video tackles the mystery behind thunderclap headaches, delving into their causes, symptoms, and possible treatments. Don\'t let these intense headaches go unnoticed - find out more by watching this enlightening video now.
Treatment Options
The treatment for thunderclap headaches depends on the underlying cause. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Immediate Care: Emergency evaluation to rule out life-threatening conditions.
- Medication: Pain relievers, and in some cases, medications to address the specific cause (e.g., antihypertensive drugs for blood pressure).
- Monitoring: Hospitalization for observation and further testing may be required.
- Surgical Intervention: For certain conditions like aneurysms, surgery might be necessary.
- Preventive Medication: In cases of recurrent thunderclap headaches with identifiable triggers, preventive medications can be prescribed.
It"s crucial to follow a healthcare professional"s guidance for a tailored treatment plan based on the specific diagnosis and individual health needs.
Potential Complications
Thunderclap headaches can indicate serious underlying conditions, leading to potential complications if not promptly diagnosed and treated. These complications may include:
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A life-threatening type of stroke caused by bleeding on the surface of the brain.
- Cerebral Aneurysm: The risk of a ruptured aneurysm increases, which can lead to stroke, brain damage, and potentially death.
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome (RCVS): Can cause stroke or seizures if not treated promptly.
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Bleeding within the brain tissue, leading to stroke, coma, or death.
- Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: Blood clots in the brain"s venous sinuses can lead to increased intracranial pressure and hemorrhage.
- Arterial Dissection: Tears in the walls of arteries supplying blood to the brain can lead to ischemic stroke.
Early detection and treatment of the cause of a thunderclap headache are crucial to prevent these serious complications.

Prevention and Management Strategies
Preventing thunderclap headaches can be challenging due to their sudden onset, but managing risk factors and triggers may help. Strategies include:
- Maintaining regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, especially if you have a history of headaches or vascular problems.
- Managing blood pressure and avoiding activities known to trigger sudden increases in blood pressure or strain.
- Avoiding illicit drug use, such as cocaine or amphetamines, which can provoke thunderclap headaches.
- Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of headaches in general.
- Being aware of the symptoms and seeking immediate medical attention if a thunderclap headache occurs, especially if it"s the first occurrence.
While it may be difficult to prevent a thunderclap headache completely, being informed about the potential triggers and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk. Immediate medical evaluation is crucial for any sudden, severe headache to rule out serious conditions.
Living with Thunderclap Headaches
Living with thunderclap headaches can be challenging, but understanding and managing the condition can improve quality of life. Strategies for coping include:
- Seeking regular medical care to monitor the condition and any underlying causes.
- Developing a plan for when a thunderclap headache occurs, including when to seek emergency care.
- Identifying and avoiding potential triggers, if known, to prevent future episodes.
- Maintaining a support network of friends, family, and healthcare providers.
- Educating oneself about the condition to better understand the symptoms and treatment options.
- Considering psychological support or therapy to cope with the stress and anxiety that may accompany the condition.
Adapting to life with thunderclap headaches involves a combination of medical management, lifestyle adjustments, and support, aiming to reduce the impact on daily life and enhance overall well-being.

READ MORE:
Research and Future Directions
Research into thunderclap headaches is ongoing, aiming to better understand their causes, improve diagnostic methods, and find effective treatments. Future directions include:
- Exploring the genetic and molecular basis of conditions leading to thunderclap headaches to identify potential targets for therapy.
- Developing advanced imaging techniques for quicker, more accurate diagnosis of underlying causes.
- Investigating new medications and interventions to manage and treat the causes of thunderclap headaches more effectively.
- Conducting long-term studies to understand the prognosis of patients with thunderclap headaches and to improve patient care.
These research efforts aim to provide better outcomes for patients, through improved understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of thunderclap headaches and their associated conditions.
Thunderclap headaches, though daunting, can be managed with prompt medical attention and care. Understanding their signs, seeking timely treatment, and ongoing research promise hope for those affected by this intense condition.
.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-PaigeMcLaughlin-WhatisaClusterHeadache-Standard-87c962b6a28d4b1ab0359ed3ae5b696f.jpg)