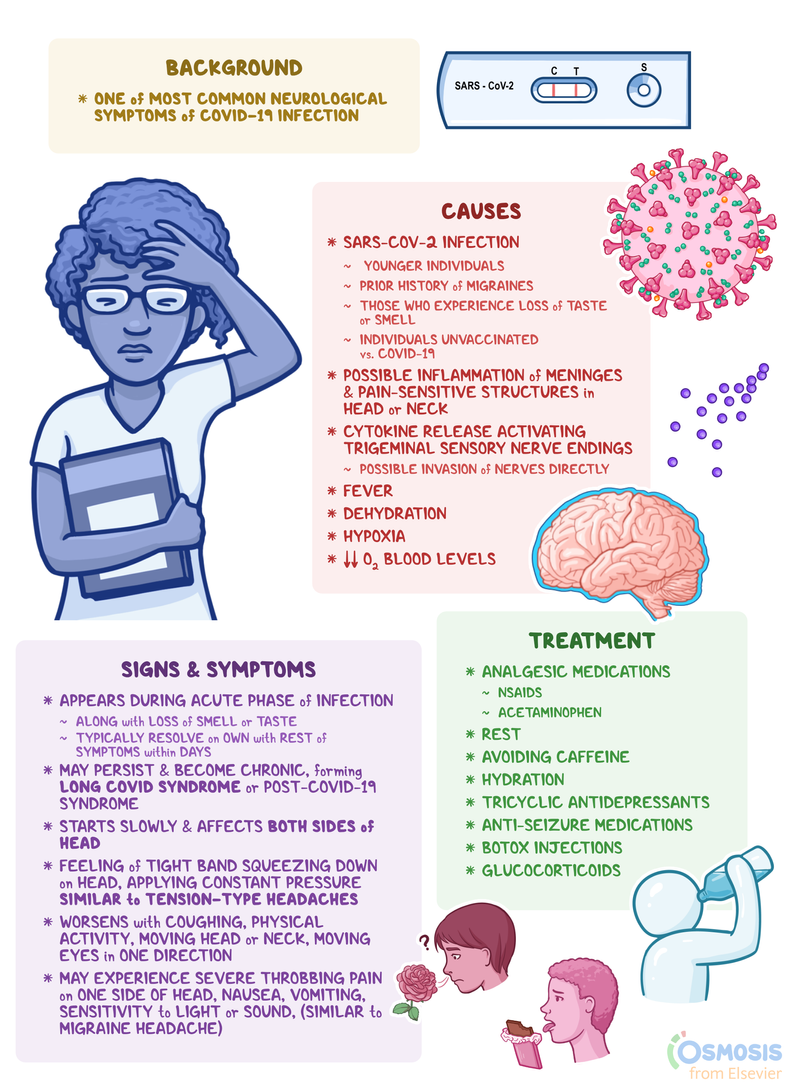
Topic temple headache: Experiencing temple headaches can be unsettling, but understanding their causes and treatments can lead to effective relief and improved well-being. Discover key insights into managing and preventing these discomforts for a healthier lifestyle.
Table of Content
- Can tension headaches cause pain in the temples?
- Common Causes of Temple Headaches
- Symptoms Indicating Serious Conditions
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Diagnosis of Temple Headaches
- Treatment Options for Temple Headaches
- Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
- YOUTUBE: Techniques for Quick Relief from Temporal Headaches
- Preventive Measures to Avoid Temple Headaches
- Understanding Tension Headaches vs. Migraines
- Impact of Stress and Anxiety on Temple Headaches
- Temporal Arteritis: A Critical Condition
Can tension headaches cause pain in the temples?
Yes, tension headaches can cause pain in the temples.
Tension headaches are characterized by a feeling of a tight band or pressure around the head. This pressure can be felt on the forehead, temples, or the back of the head. The pain is usually dull and achy, and it can be mild to moderate in intensity.
The exact cause of tension headaches is not known, but they are believed to be related to muscle tension or stress. Factors such as poor posture, emotional stress, eyestrain, or fatigue can trigger tension headaches.
When tension headaches occur, the muscles in the scalp, neck, and face may contract or tighten, leading to pain and discomfort. The pain may radiate from the back of the head to the temples or forehead.
- Symptoms of tension headaches include:
- Headache pain that is mild to moderate in intensity
- A feeling of pressure or tightness around the head
- Pain in the temples, forehead, or back of the head
- Tenderness or sensitivity of the scalp, neck, or shoulder muscles
- Difficulty sleeping or concentrating
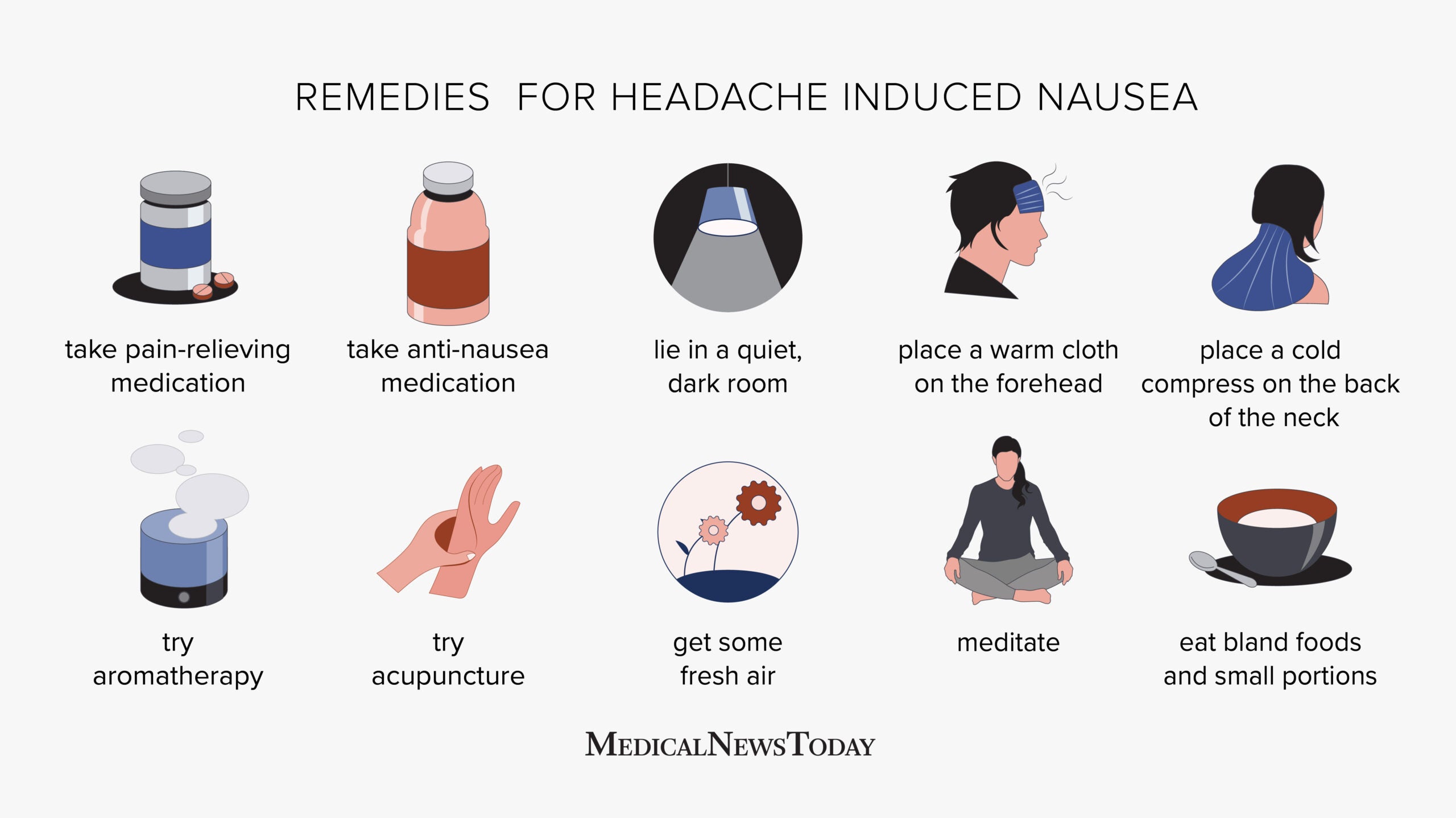
- Mild nausea
To relieve tension headaches, there are several self-care measures you can try:
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga
- Apply a warm or cold compress to the painful area
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Improve your posture and ergonomic setup at work or home
- Manage stress through exercise, regular sleep, and stress management techniques
If tension headaches persist or worsen despite self-care measures, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance. They can help determine the underlying cause of the headaches and suggest appropriate treatment options.
READ MORE:
Common Causes of Temple Headaches
Temple headaches can be caused by a variety of factors, each leading to discomfort in different ways. Understanding these causes is the first step towards effective management and relief.
- Tension Headaches: The most common form, resulting from muscle strain, stress, or fatigue.
- Migraines: Intense, throbbing pain often accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light or sound, and sometimes aura.
- Cluster Headaches: Severe, recurrent headaches on one side of the head, often around the eye.
- Temporal Arteritis: An inflammatory condition affecting the arteries in the temples, potentially serious without treatment.
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses can cause pressure and pain in the temples.
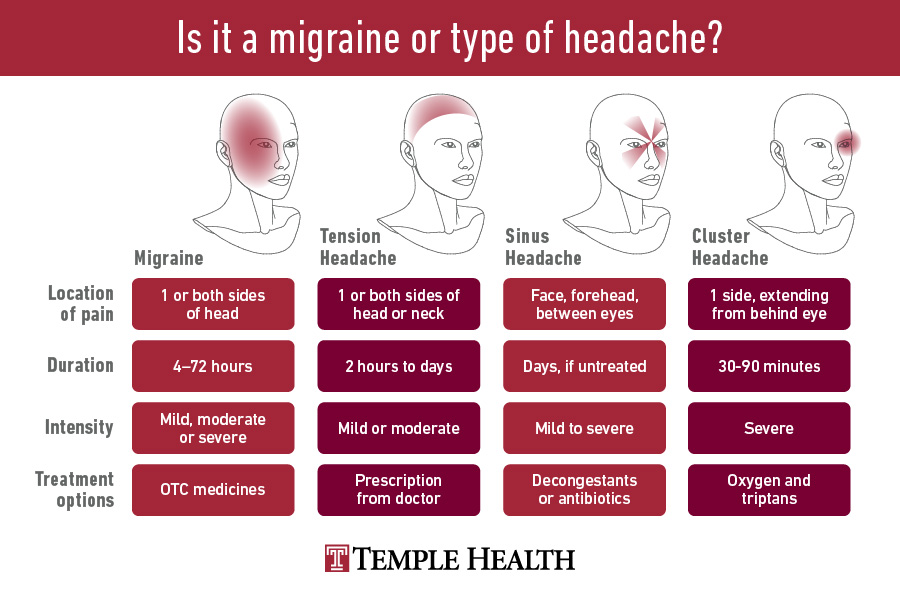
- Cervicogenic Headaches: Originating from disorders of the neck and leading to pain in the temple region.
- Dental Issues: Problems with teeth or jaw alignment can manifest as pain in the temples.
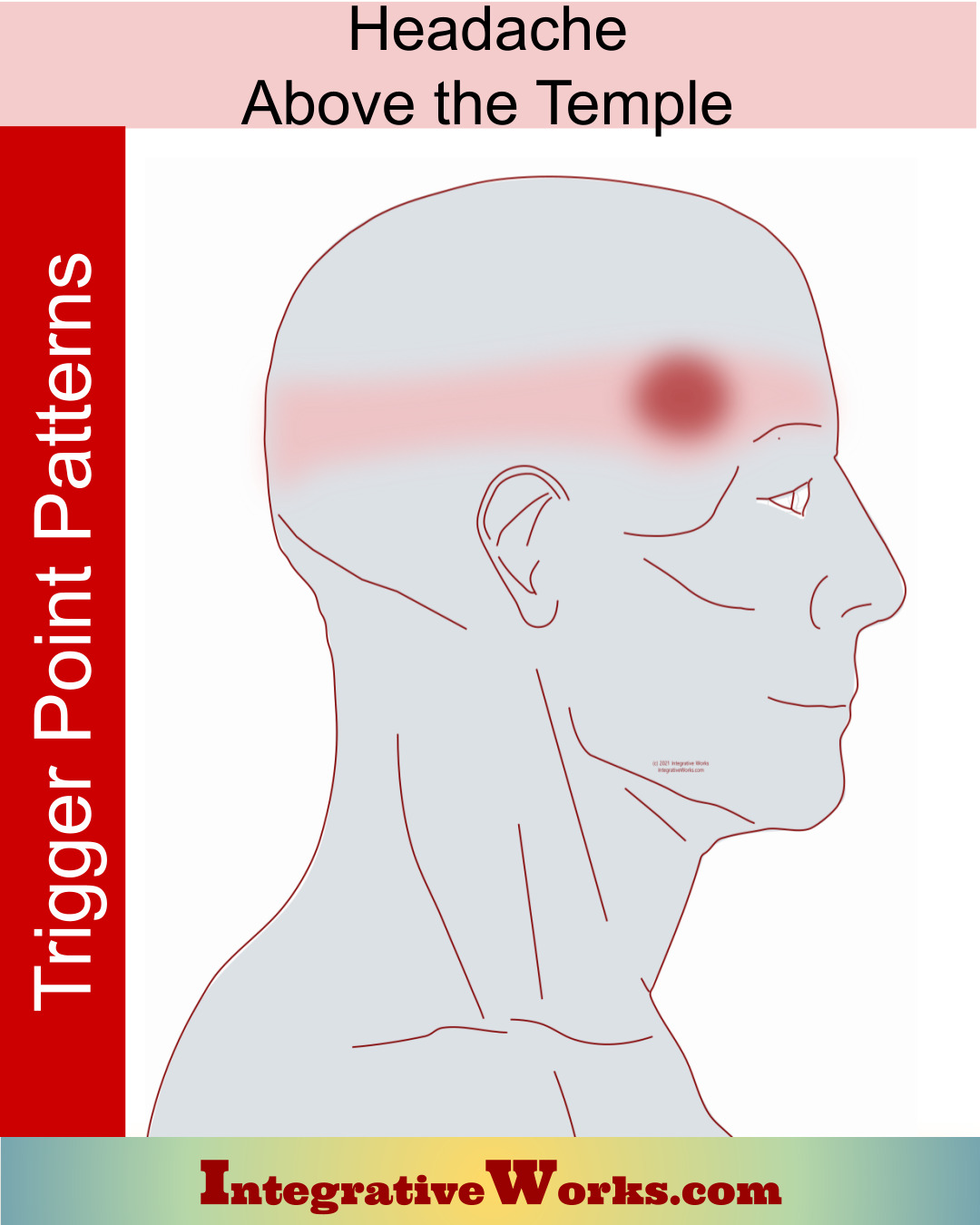
- Eyestrain: Long periods of screen time without rest can lead to temple headaches.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can cause headaches, including pain in the temples.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations, especially in women, can trigger headaches in the temple area.
Recognizing the specific cause of your temple headache is crucial for choosing the right treatment approach.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headaches-as-a-symptom-of-multiple-sclerosis-2440798-01-ac13321fbd2d4dca99f899a63b8ea265.png)
Symptoms Indicating Serious Conditions
While many temple headaches are benign, certain symptoms alongside a temple headache can indicate a more serious condition requiring immediate medical attention. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention.
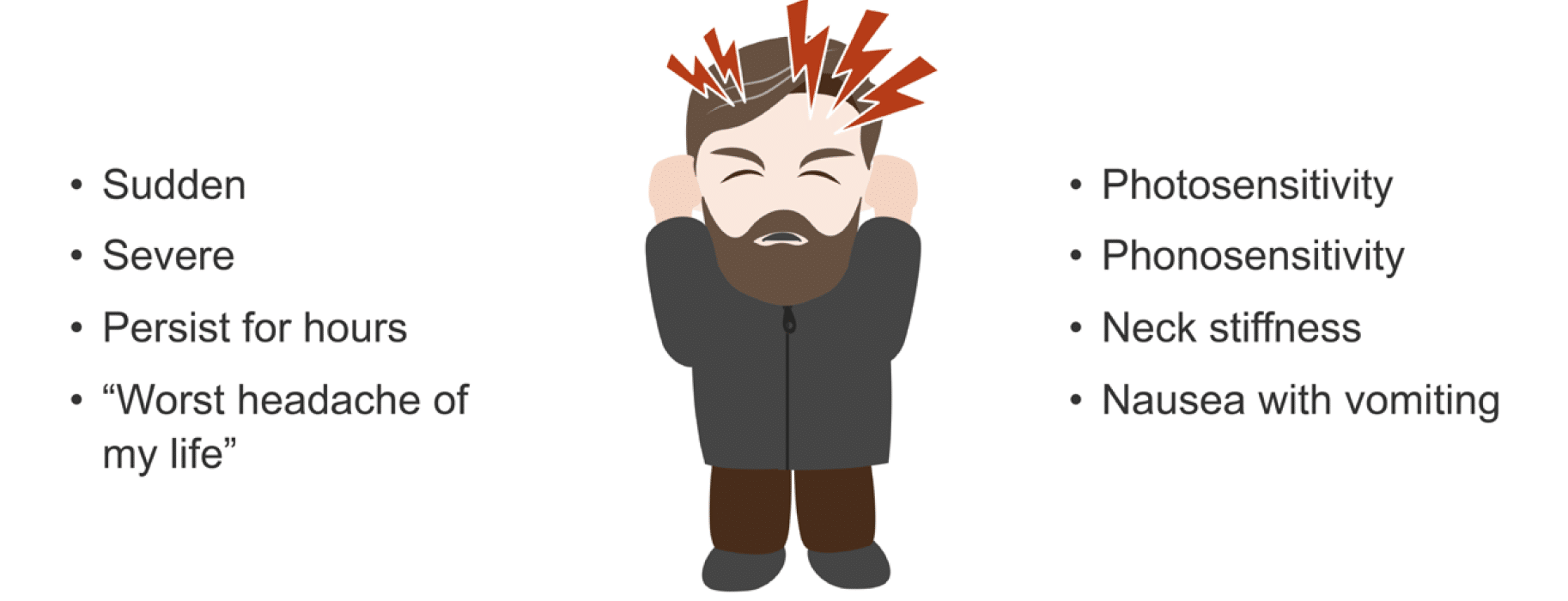
- Sudden, severe headache: A headache that comes on abruptly and is severe in nature, often described as a "thunderclap" headache.
- Headache with neurological symptoms: Symptoms such as confusion, difficulty speaking, weakness, or changes in vision accompanying a headache.
- Persistent or escalating headache: Headaches that persist or worsen over time, especially if they do not respond to usual headache remedies.
- Headache after head injury: A headache developing after a head injury can signal a concussion or more serious brain injury.
- Changes in pattern: A significant change in the pattern of headaches, including frequency, severity, or symptoms.
- Fever and stiff neck: Accompanying fever and stiffness in the neck could indicate meningitis, especially if the headache is severe.
- Scalp tenderness: Tenderness or pain when touching the scalp, particularly in older adults, could suggest temporal arteritis.
- Visual disturbances: Sudden visual problems, including blurred vision, double vision, or vision loss, especially if occurring with a headache.
- Headache with nausea or vomiting: While this can be a symptom of many types of headaches, when severe, it can also indicate a more serious condition.
- Seizures: Experiencing a seizure for the first time, accompanied by a headache, requires immediate medical evaluation.
These symptoms could potentially indicate conditions such as brain aneurysms, strokes, meningitis, or other critical issues. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential if you experience any of these symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It"s essential to know when a temple headache signals a need for professional medical evaluation. Here are guidelines to help you determine when it"s time to consult a healthcare provider.
- Sudden, Severe Onset: If your headache comes on suddenly and is more severe than any you"ve experienced before, seek immediate medical attention.
- Change in Headache Pattern: Noticeable changes in the frequency, severity, or characteristics of your headaches warrant a doctor"s visit.
- Neurological Symptoms: Symptoms such as confusion, difficulty speaking, weakness, numbness, or changes in vision alongside a headache require urgent care.
- Headache After Head Injury: Any headache that develops after a head injury, especially if it worsens, should be evaluated by a doctor immediately.
- Accompanied by Other Serious Symptoms: Headaches with a fever, stiff neck, rash, persistent vomiting, or drowsiness can indicate a serious condition.
- Impact on Daily Life: If your headache is severe enough to disrupt your daily activities or does not improve with over-the-counter medication, see a healthcare professional.
- First-time Migraine Symptoms: If you experience what appears to be a migraine for the first time, especially if over 50, seek medical advice to rule out other causes.
- Existing Health Conditions: Individuals with a history of cancer, HIV/AIDS, or a weakened immune system experiencing new or changing headaches should consult their doctor.
Listening to your body and recognizing these signs can lead to early diagnosis and treatment of potentially serious conditions.
Diagnosis of Temple Headaches
Diagnosing temple headaches involves several steps to identify the underlying cause and determine the most effective treatment plan.
- Medical History: A comprehensive review of the patient"s medical history, including the nature, duration, and pattern of headaches.
- Physical Examination: A physical exam, focusing on the head, neck, eyes, ears, and sometimes the nasal passages and throat.
- Neurological Assessment: Tests to assess the nervous system function, including reflexes, muscle strength, eye and mouth movement, and sensory function.
- Blood Tests: Blood work can reveal signs of infection, inflammation, or other conditions that might be causing the headaches.
- Imaging Tests: CT scans or MRIs can help detect any structural issues, such as tumors or sinus disease, contributing to headaches.
- Temporal Artery Ultrasound: For suspected cases of temporal arteritis, an ultrasound may be performed to examine the temporal arteries for signs of inflammation.
- Temporal Artery Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy of the temporal artery is the most definitive way to diagnose temporal arteritis. A small section of the artery is removed and examined under a microscope for signs of inflammation.
- Lumbar Puncture: If an infection or bleeding in the brain is suspected, a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) might be conducted to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid.
Based on the findings from these assessments, healthcare providers can diagnose the cause of temple headaches and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Options for Temple Headaches
The approach to treating temple headaches can vary based on their cause. Here are some commonly recommended treatments:
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and aspirin can be effective for mild to moderate headaches.
- Prescription Medications: For more severe cases, especially migraines or cluster headaches, prescription medications may be necessary.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and biofeedback can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches caused by stress.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and hydration can prevent headaches. Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake is also beneficial.
- Physical Therapy: For headaches caused by muscular tension or cervical issues, physical therapy can help relieve pain.
- Hot or Cold Compresses: Applying heat or cold to the area can alleviate the pain of tension headaches and migraines.
- Migraine Specific Treatments: Triptans and other migraine-specific medications can be effective for those diagnosed with migraines.
- Preventive Medications: In cases of frequent, chronic headaches, doctors may prescribe medication to reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help individuals manage the pain and stress that may trigger headaches.
- Dietary Adjustments: Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger headaches can be a crucial part of managing symptoms.
Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment based on the individual"s symptoms and headache type.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Managing temple headaches often involves simple home remedies and lifestyle adjustments that can significantly reduce their frequency and severity. Here are effective strategies:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, a common headache trigger.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to help reduce the risk of headaches.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help manage stress levels and reduce headache occurrence.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can decrease the frequency and intensity of headaches.
- Dietary Adjustments: Identify and avoid foods that trigger your headaches. Common triggers include caffeine, alcohol, and certain preservatives.
- Muscle Relaxation Techniques: Progressive muscle relaxation, massage, and gentle stretching can alleviate tension in the neck and shoulders, reducing headache risk.
- Limit Screen Time: Reduce eye strain by taking regular breaks from screens and ensuring proper lighting when using digital devices.
- Proper Posture: Maintaining good posture, especially while sitting for long periods, can prevent headaches caused by neck and shoulder strain.
- Essential Oils: Aromatherapy using lavender or peppermint oil can provide relief from headache pain when applied to the temples or inhaled.
- Hot or Cold Compress: Applying a hot or cold compress to the head or neck area can soothe pain and relax tense muscles.
These home remedies, combined with a healthy lifestyle, can be effective in managing temple headaches. However, if headaches persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.
Techniques for Quick Relief from Temporal Headaches
\"Experience instant relief as you watch this amazing video that reveals proven techniques to relieve stress and tension. Say goodbye to aches and pains and hello to a relaxed and rejuvenated body!\"
Relieve TMJ-Related Tension Headaches
\"If you suffer from TMJ or jaw pain, this video is a must-watch. Discover effective exercises and tips to alleviate discomfort and restore proper function. Get ready to say goodbye to jaw pain and hello to a pain-free smile!\"
Preventive Measures to Avoid Temple Headaches
Adopting certain preventive measures can significantly reduce the occurrence of temple headaches. Here are key strategies to incorporate into your daily life:
- Maintain a Regular Sleep Schedule: Ensuring consistent sleep times and aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep per night can help prevent headaches.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink adequate water throughout the day to avoid dehydration, a common trigger for headaches.
- Manage Stress: Utilize stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to lower the risk of headaches.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol can trigger headaches, so it"s beneficial to consume these in moderation.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise helps reduce tension and prevent headaches.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Avoiding foods known to trigger headaches and maintaining a healthy diet can be effective in preventing them.
- Improve Posture: Good posture, especially during long periods of sitting, can prevent headaches caused by neck and shoulder strain.
- Avoid Headache Triggers: Identify and steer clear of specific activities or foods that have previously triggered your headaches.
- Regular Breaks from Screens: Taking frequent breaks from computer and smartphone screens can prevent eye strain and related headaches.
- Relaxation Techniques: Regular practice of relaxation techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation can help in preventing headaches.
Implementing these preventive measures into your lifestyle can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of temple headaches, leading to a more comfortable and productive life.

Understanding Tension Headaches vs. Migraines
Tension headaches and migraines are common causes of head pain but differ significantly in their symptoms, triggers, and treatments. Understanding these differences can help in managing them effectively.
- Symptoms:
- Tension Headaches: Often described as a constant, dull ache on both sides of the head, resembling a tight band around the forehead.
- Migraines: Characterized by a throbbing or pulsating pain on one side of the head, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Triggers:
- Tension Headaches: Triggered by stress, poor posture, and muscle strain.
- Migraines: Can be triggered by hormonal changes, certain foods and beverages, stress, and environmental factors.
- Duration:
- Tension Headaches: Can last from 30 minutes to several days.
- Migraines: Typically last from 4 hours to 3 days.
- Treatment:
- Tension Headaches: Often managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, stress management, and physical therapy.
- Migraines: May require specific medication, such as triptans, and preventive treatments, including lifestyle changes and prescription medications.
- Prevention:
- Tension Headaches: Beneficial to maintain good posture, manage stress, and adopt a healthy lifestyle.
- Migraines: Identifying and avoiding specific triggers, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and possibly using preventive medication.
Knowing whether you are experiencing a tension headache or a migraine is crucial for effective treatment and relief. Consultation with a healthcare provider can help in proper diagnosis and management.
Impact of Stress and Anxiety on Temple Headaches
Stress and anxiety are significant contributors to temple headaches, affecting both their frequency and intensity. Understanding the connection between stress, anxiety, and headaches can guide effective management strategies.
- Stress as a Trigger: Stress can trigger muscle tension around the neck and scalp, leading to tension headaches that often present as pain in the temples.
- Anxiety-Related Symptoms: Anxiety can exacerbate the perception of pain and lead to increased frequency of headaches, including migraines and tension headaches that affect the temples.
- Physiological Effects: The body"s response to stress and anxiety includes the release of chemicals like adrenaline and cortisol, which can contribute to headache development.
- Behavioral Factors: Stress and anxiety can lead to behaviors that trigger headaches, such as poor sleep patterns, inadequate hydration, excessive caffeine consumption, and skipping meals.
- Management Techniques: Stress and anxiety reduction techniques, such as relaxation exercises, deep breathing, yoga, and mindfulness, can effectively reduce the occurrence of temple headaches.
- Professional Support: For those with chronic stress and anxiety, seeking professional help from a psychologist or psychiatrist can provide strategies to manage these conditions and reduce headache frequency.
Addressing stress and anxiety not only helps in managing temple headaches but also improves overall well-being and quality of life.
READ MORE:
Temporal Arteritis: A Critical Condition
Temporal arteritis, also known as giant cell arteritis, is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. It involves the inflammation of the temporal arteries, which can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly.
- Who is at Risk: Primarily affects individuals over the age of 50, with a higher incidence in women and those with a northern European heritage.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include severe headache, scalp tenderness, jaw pain when chewing, vision problems, and sometimes fever, fatigue, and weight loss.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosed through patient history, physical examination, blood tests indicating inflammation, and often confirmed with a temporal artery biopsy.
- Treatment: Immediate treatment with high-dose corticosteroids is crucial to prevent vision loss. Long-term treatment may be necessary to manage the condition.
- Monitoring and Management: Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to adjust medications and monitor for side effects.
- Importance of Early Detection: Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent serious complications, including irreversible vision loss and stroke.
Understanding the signs and seeking prompt medical care can significantly impact the outcome for those with temporal arteritis, highlighting the importance of awareness and early intervention.
Understanding temple headaches is key to effective management and relief. By recognizing symptoms, causes, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps towards improving your health and well-being, ensuring a happier, headache-free life.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-dehydration-symptoms-7480908-Horiz-e2500f0828b746ee9d2e2b5257af60cb.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headache-on-the-right-side-5216756_final-b9d0145864d74706b0316a2e9b62dd37.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)