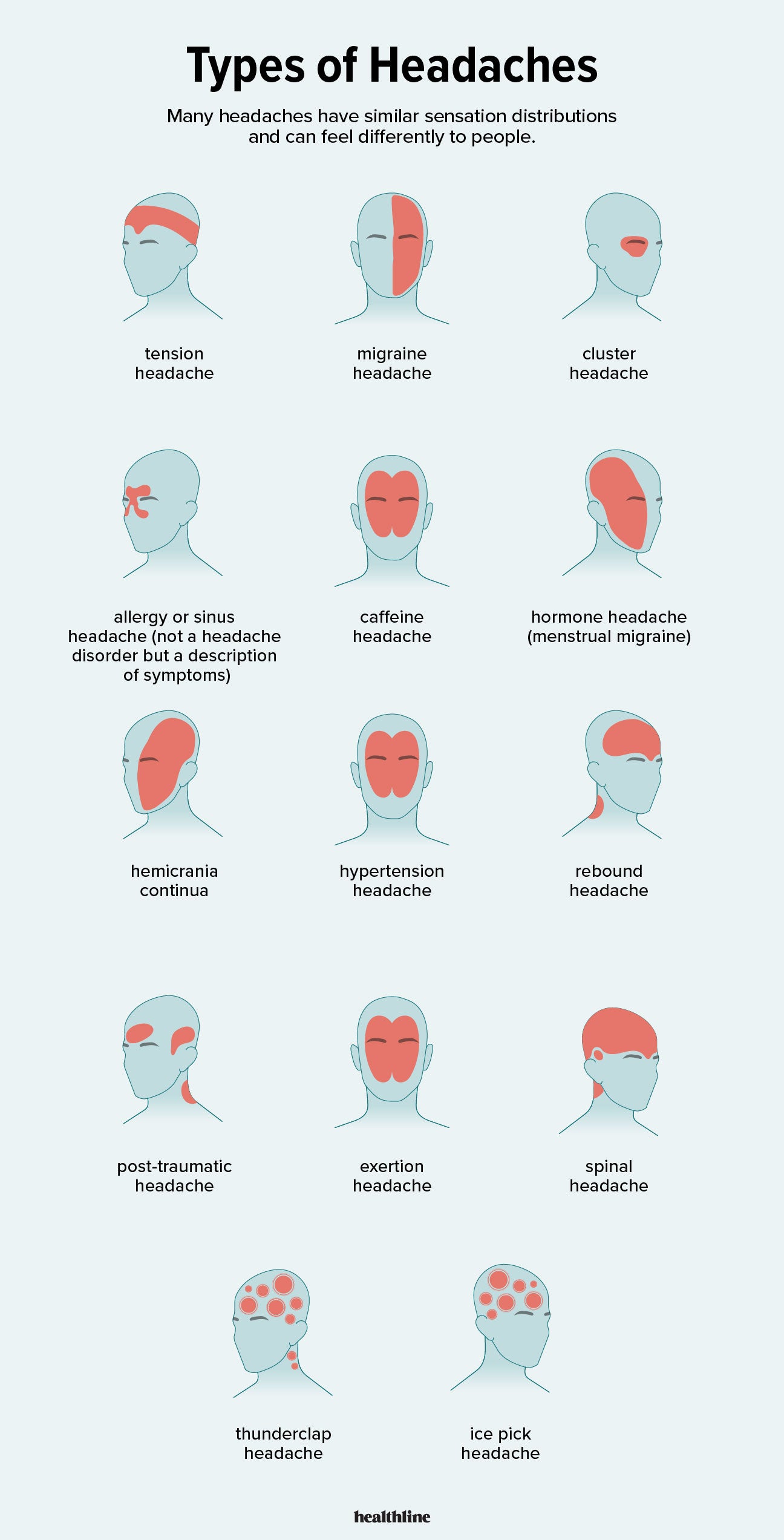
Topic headache placement meaning: Discover how the location of your headache reveals its causes and guides effective remedies, enhancing your well-being and health management strategies.
Table of Content
- What does headache placement mean?
- Understanding Different Headache Locations and Their Implications
- Cluster Headaches: Identification and Treatment Options
- Cervicogenic and Occipital Neuralgia Headaches: Symptoms and Causes
- Hormonal Headaches: Recognizing and Managing Menstrual and Pregnancy-Related Headaches
- Sinus Headaches: Distinguishing Features and Effective Treatments
- Dehydration Headaches: Symptoms, Prevention, and Relief Strategies
- YOUTUBE: Primary vs Secondary Headache with Red Flags: Tension Type, Migraine, Cluster Headache
- Tension Headaches: Common Causes and Relief Methods
- Migraine Management: Understanding Triggers and Treatment
- When to Seek Medical Attention for Your Headache
What does headache placement mean?
The placement or location of a headache can provide valuable information about its underlying cause or type. Different headache placements indicate different types of headaches:
- Sinus headache: This type of headache is felt in the front of the head and face. It is often caused by sinusitis or sinus infections.
- Migraine headache: Migraines typically affect one side of the head. They are often intense and come with additional symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances.
- Whole-head headache: This type of headache affects the entire head and feels like there is a tight band around it. It is commonly associated with tension headaches, which are often caused by stress, muscle tension, or poor posture.
Understanding the placement of a headache can help in diagnosis and selecting the most appropriate treatment or management strategy.
READ MORE:
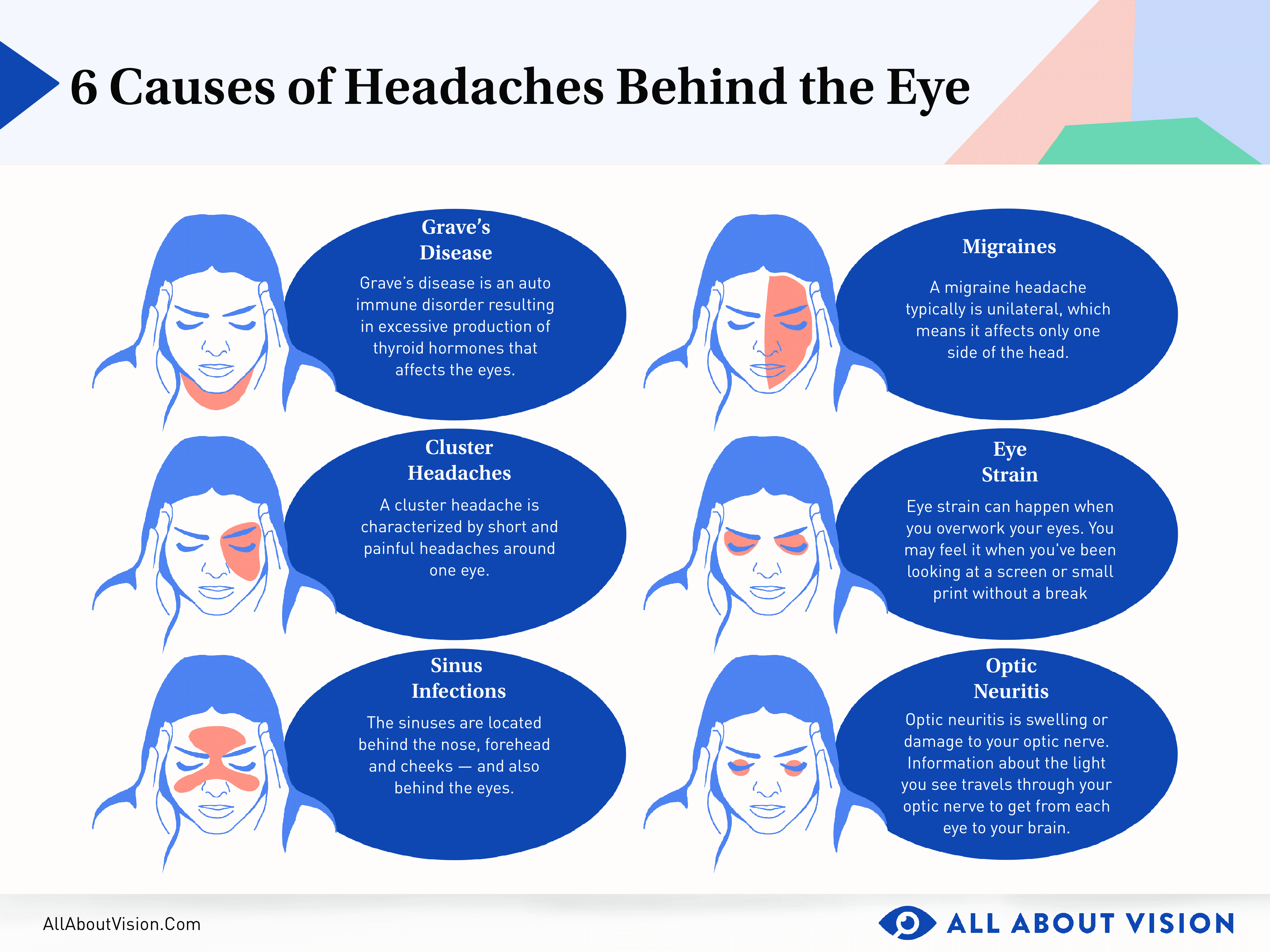
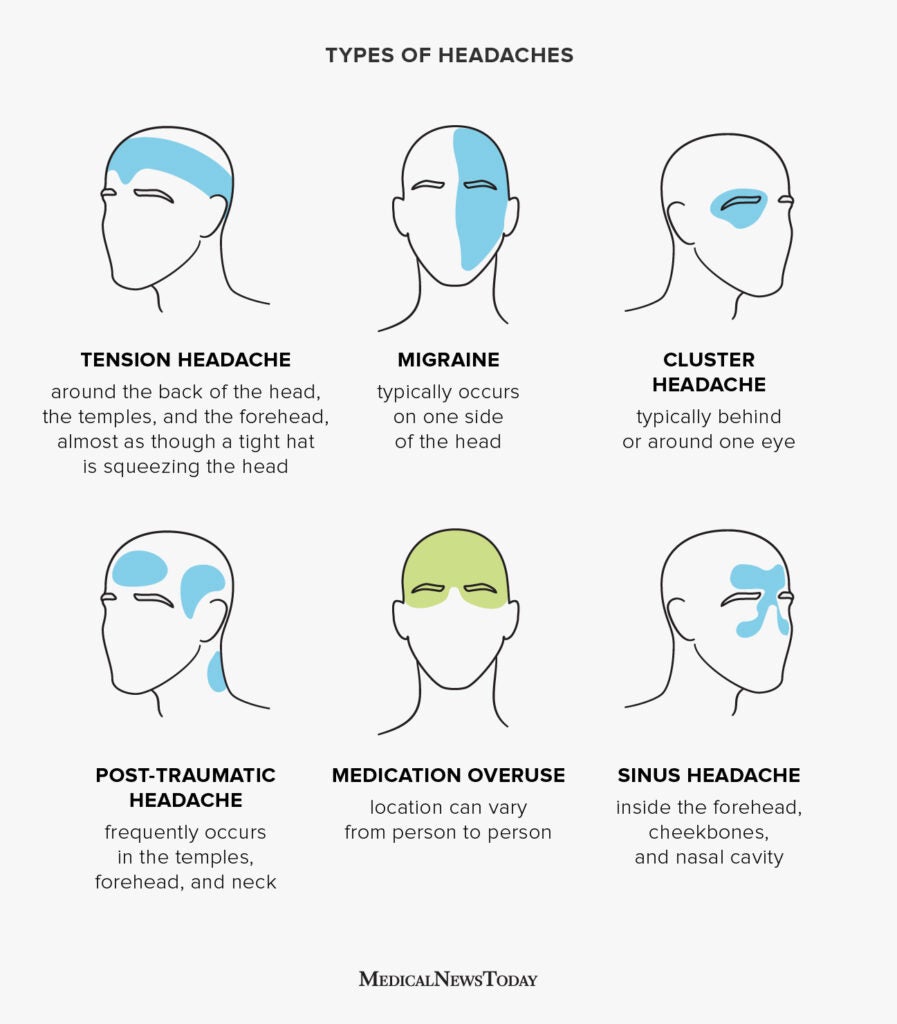
Understanding Different Headache Locations and Their Implications
Headaches can vary greatly in their location, intensity, and underlying causes. Understanding the placement of your headache can offer insights into potential triggers and inform more effective treatment strategies.
- Frontal Headaches: Often linked to tension or sinus issues, frontal headaches manifest across the forehead. They can be caused by stress, poor posture, or sinus infections.
- Temporal Headaches: Located at the sides of the head, these headaches can be associated with temporal arteritis, tension, or migraines.
- Occipital Headaches: Situated at the back of the head, occipital headaches can indicate neck tension or issues related to nerve compression.
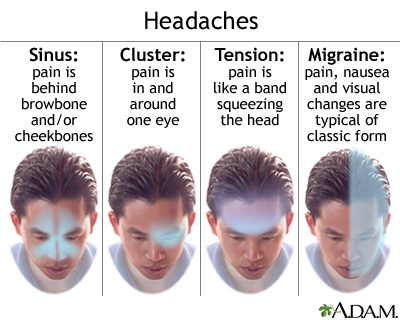
- Cluster Headaches: Known for their excruciating pain around one eye or temple, these are rare and involve a series of short but intense headaches.
- Cervicogenic Headaches: Stemming from the neck, these headaches typically radiate towards the back of the head and are often due to structural issues.
- Hormonal Headaches: Fluctuations in hormones can lead to headaches typically felt on one side of the head, common during menstrual cycles or pregnancy.
Each type of headache has distinct characteristics and may require different approaches for relief. Recognizing the type of headache you"re experiencing is the first step toward finding effective treatment and improving your quality of life.

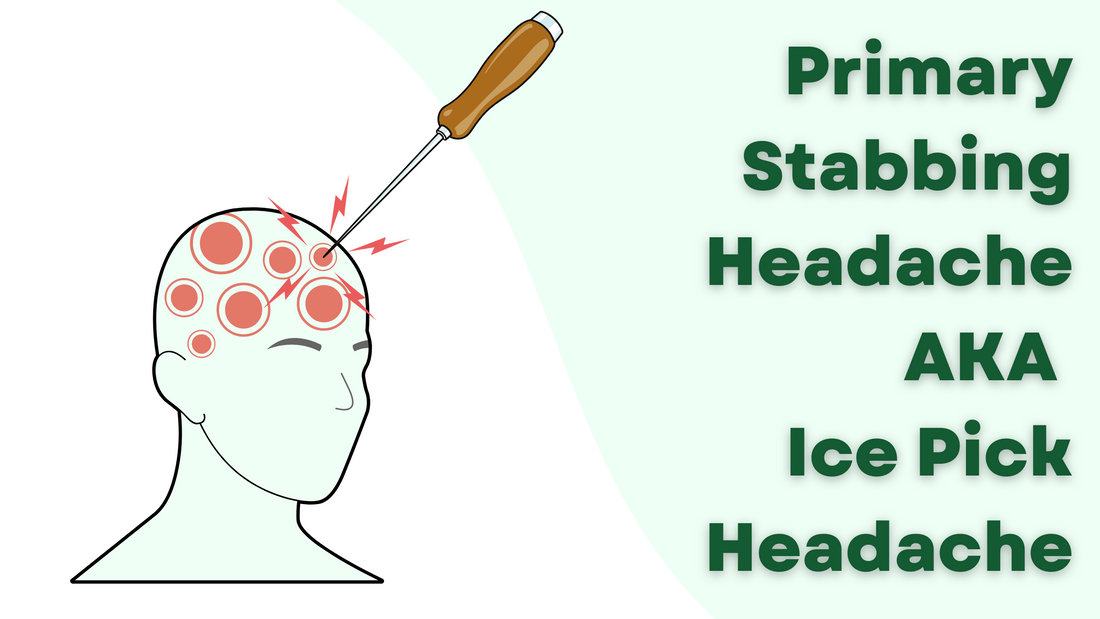
Cluster Headaches: Identification and Treatment Options
Cluster headaches are recognized for their distinctive pattern and severity. These headaches are characterized by intense burning or piercing pain around one eye or temple, often accompanied by tearing, nasal congestion, or eyelid drooping on the affected side.
- Identification: These headaches occur in cyclical patterns or clusters, presenting suddenly and lasting for 15 minutes to 3 hours. The attacks may happen multiple times a day for weeks or months, followed by remission periods.
- Triggers: While the exact cause is unknown, factors like alcohol consumption, smoking, and certain foods have been identified as potential triggers.
- Treatment Options: Treatment aims to reduce the severity and frequency of attacks. Options include:
- Oxygen therapy to alleviate pain quickly.
- Triptans, administered through nasal sprays or injections, can provide rapid relief.
- Preventative medications, such as verapamil, considered the first-line defense.
- Occipital nerve stimulation and deep brain stimulation for chronic cases.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoiding known triggers and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage and reduce the frequency of cluster headache attacks.
Early diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan are crucial for managing cluster headaches effectively, enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
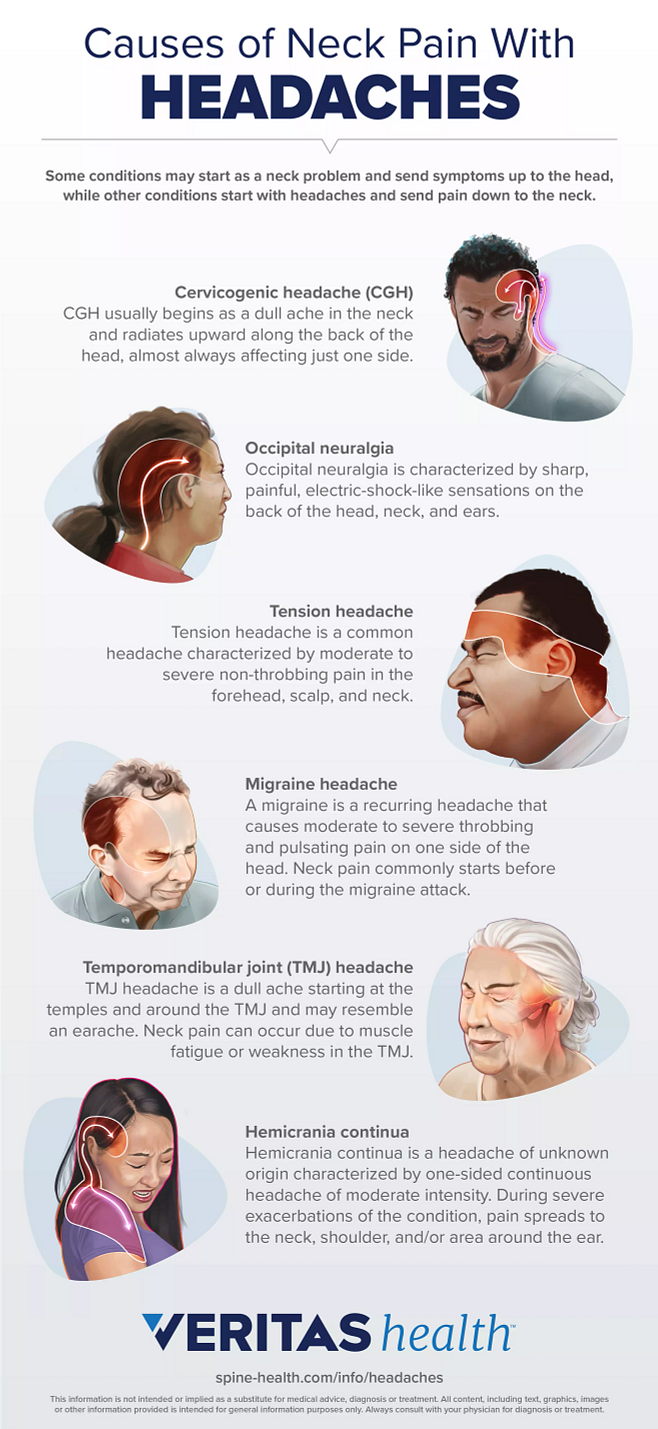
Cervicogenic and Occipital Neuralgia Headaches: Symptoms and Causes
Cervicogenic and occipital neuralgia headaches are distinct types due to their origins and the nature of their symptoms. Understanding these can aid in seeking appropriate treatment and management strategies.
- Cervicogenic Headaches Symptoms: These headaches originate from the cervical spine or the base of the skull. Symptoms can include a steady, non-throbbing pain at the back of the head, neck, and sometimes pain radiating towards the front of the head or behind the eyes. Movement of the neck can exacerbate the pain.
- Cervicogenic Headaches Causes: Causes often include structural issues in the neck, such as arthritis, injuries, or disc problems that affect nerve roots. Poor posture or chronic neck tension can also contribute.
- Occipital Neuralgia Symptoms: This condition is characterized by sharp, jabbing pain in the back of the head, neck, and behind the eyes. It is often described as an electric shock in these areas. The pain might also follow the path of the occipital nerve, leading to sensitivity to light or scalp tenderness.
- Occipital Neuralgia Causes: It can result from irritation or injury to the occipital nerves, possibly due to neck tension, trauma, or as a result of diseases like diabetes or inflammation of blood vessels. Compression of the nerves from tight muscles or osteoarthritis in the neck can also be a factor.
Identifying the specific characteristics of these headaches is crucial for effective treatment, which may include physical therapy, medication, or nerve blocks, depending on the underlying cause.
Hormonal Headaches: Recognizing and Managing Menstrual and Pregnancy-Related Headaches
Hormonal fluctuations are a common trigger for headaches, particularly in women. These fluctuations can cause headaches that are often predictable and sometimes debilitating. Understanding the symptoms and causes can help in managing these effectively.
- Symptoms: Hormonal headaches may manifest as migraines, characterized by a throbbing pain on one side of the head, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound. They often occur in the days leading up to, during, or immediately after menstruation, as well as during pregnancy or menopause.
- Causes: The primary cause is changes in estrogen levels. During menstruation, estrogen levels drop, which can trigger headaches. Similarly, during pregnancy, hormone levels fluctuate significantly, especially in the first trimester, leading to headaches.
- Management Strategies: Managing hormonal headaches involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medication, and sometimes hormonal therapy.
- Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and staying hydrated.
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or aspirin, under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Prescription medications, including triptans, may be recommended for severe cases.
- Hormonal therapy, such as birth control pills, can help stabilize hormone levels and reduce the frequency of headaches.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Stress management techniques, such as yoga and meditation, can also be beneficial. Tracking headache patterns in relation to the menstrual cycle can help anticipate and mitigate them.
Working closely with a healthcare provider is crucial to tailor a treatment plan that addresses individual needs and symptoms, ensuring effective management of hormonal headaches.
Sinus Headaches: Distinguishing Features and Effective Treatments
Sinus headaches are often confused with migraines due to their similar symptoms. However, understanding their unique characteristics can lead to more effective treatments and relief.
- Distinguishing Features: Sinus headaches are characterized by a deep, constant pain in the cheekbones, forehead, or bridge of the nose. The pain typically intensifies with sudden head movements or straining and may be accompanied by other sinus symptoms, such as nasal discharge, feeling of fullness in the ears, fever, and facial swelling.
- Causes: These headaches are caused by sinus infection or inflammation (sinusitis), often due to allergic reactions or infections like the common cold.
- Effective Treatments: Treatment focuses on relieving sinus pressure and inflammation.
- Decongestants and antihistamines can reduce nasal congestion and relieve headache symptoms.
- Nasal corticosteroid sprays reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Steam inhalation and warm compresses can also help alleviate the pain by opening the sinuses.
- Antibiotics are prescribed if a bacterial infection is the cause.
- Preventive Measures: Avoiding known allergens, staying hydrated, and using a humidifier can help prevent sinus headaches.
Understanding the specific symptoms and triggers of your sinus headaches is crucial for effective management and treatment. If you experience frequent sinus headaches, it"s important to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Dehydration Headaches: Symptoms, Prevention, and Relief Strategies
Dehydration headaches occur when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to reduced blood volume and temporarily reduced oxygen supply to the brain. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding how to prevent and relieve these headaches is essential for maintaining optimal health and well-being.
Symptoms of Dehydration Headaches
- Dull or throbbing head pain
- Sensation of tightness or pressure across the forehead or on the sides and back of the head
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Dark yellow urine
- Dry mouth and thirst
- Fatigue
Prevention Strategies
Preventing dehydration headaches involves maintaining adequate hydration and modifying lifestyle factors:
- Drink plenty of fluids daily. The amount depends on your body size, activity level, and the climate, but aiming for 8-10 glasses of water per day is a good rule of thumb.
- Include foods with high water content in your diet, such as fruits and vegetables.
- Avoid or limit diuretics like caffeine and alcohol, which can increase dehydration.
- Pay attention to your body"s hydration cues, such as thirst and the color of your urine.
- Wear protective clothing and seek shade when outdoors in hot weather to reduce sweat-induced fluid loss.
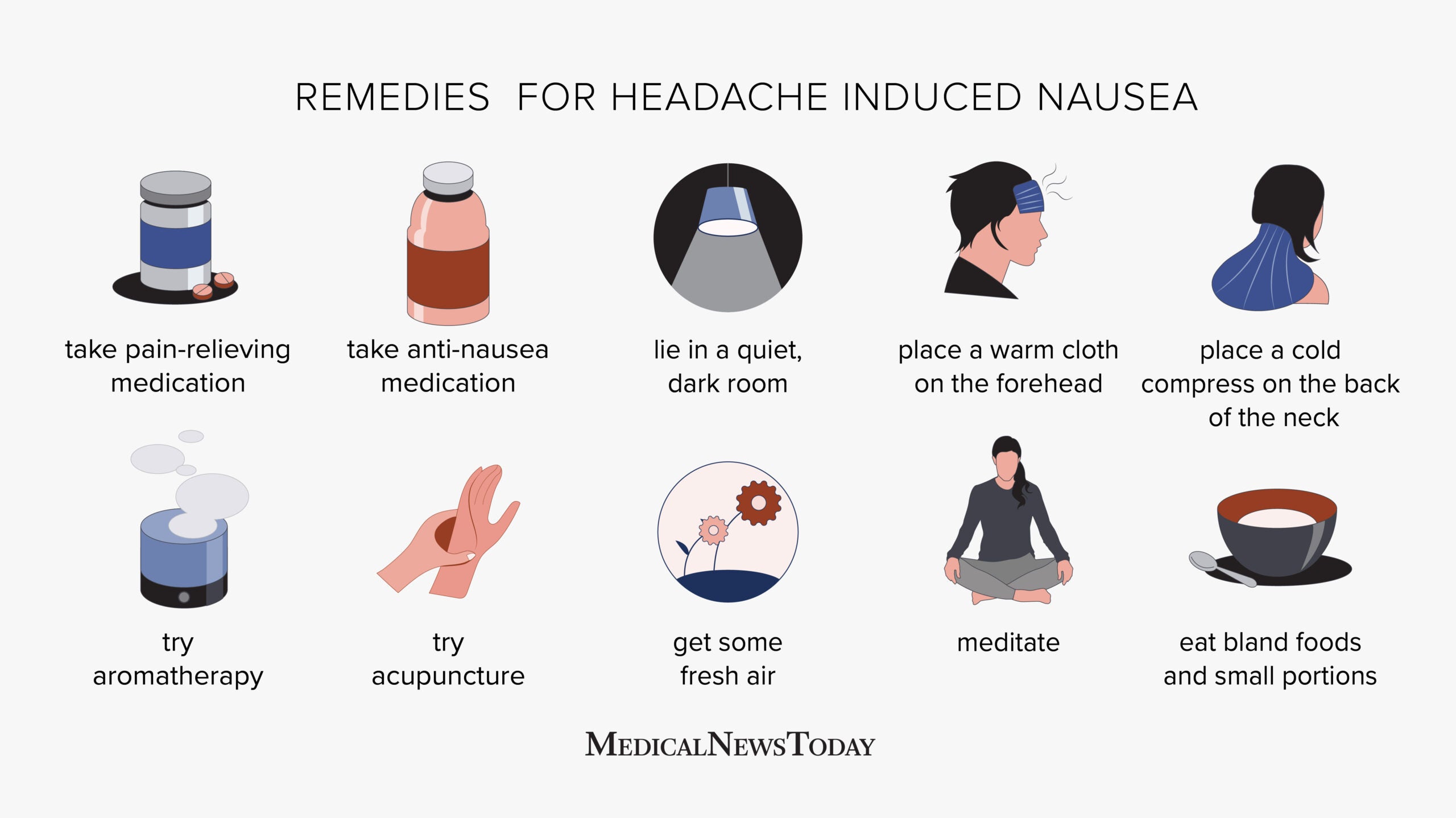
Relief Strategies
If you find yourself suffering from a dehydration headache, consider the following relief strategies:
- Rehydrate by drinking water, oral hydration solutions, or sports drinks that contain electrolytes to quickly restore fluid balance.
- Rest in a cool, quiet place to help alleviate headache symptoms.
- Apply a damp cloth or ice pack to your forehead or the back of your neck to help reduce the pain.
- Gentle stretching exercises can relieve tension in the neck and shoulders, which can exacerbate headache pain.
- If your headache does not improve after rehydrating and resting, consider over-the-counter pain relief medication, following the dosage recommendations.
Understanding the link between dehydration and headaches is crucial for effective prevention and relief. By recognizing the early signs of dehydration and implementing these strategies, you can help prevent dehydration headaches and maintain your health and comfort.
Primary vs Secondary Headache with Red Flags: Tension Type, Migraine, Cluster Headache
\"Learn how to spot common red flags in relationships and protect yourself from potential harm. This video will provide valuable insight into identifying warning signs and maintaining healthy boundaries in any partnership.\"
Upper Neck Pain and Headache
\"Discover effective exercises and techniques to relieve tension and pain in the upper neck area. This informative video offers helpful tips for improving posture and promoting overall neck health. Say goodbye to stiffness!\"
Tension Headaches: Common Causes and Relief Methods
Tension headaches, characterized by a dull, aching pain on both sides of the head, are the most common type of headache among adults. They are often described as feeling like a tight band around the forehead. Understanding the causes and effective relief methods can help manage and reduce the frequency of these headaches.
Common Causes of Tension Headaches
- Stress and anxiety, which can lead to muscle tension
- Poor posture, contributing to neck and scalp muscle strain
- Eye strain, especially from prolonged screen use
- Lack of sleep or changes in sleep patterns
- Dehydration
- Skipping meals, leading to low blood sugar levels
Relief Methods
While tension headaches can be disruptive, there are several effective ways to relieve them:
- Stress Management: Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and other relaxation methods can help reduce stress.
- Improve Posture: Adjusting your workspace to promote good posture can alleviate neck and shoulder strain. Taking frequent breaks to stretch can also help.
- Eye Care: Regular breaks from screens and using proper lighting can reduce eye strain. Consider consulting an eye specialist if eye strain persists.
- Adequate Sleep: Establishing a regular sleep schedule and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can improve sleep quality.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Drinking plenty of water and eating balanced meals at regular intervals can prevent headaches caused by dehydration and low blood sugar.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can reduce tension and improve overall well-being.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications such as ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen can provide quick relief. However, they should be used sparingly to avoid overuse headaches.
- Heat or Cold Therapy: Applying a warm cloth or heating pad to the neck and shoulders, or a cold pack to the forehead, can ease muscle tension.
By understanding the common triggers and implementing these relief methods, you can effectively manage tension headaches and improve your quality of life.
Migraine Management: Understanding Triggers and Treatment
Migraines are a complex neurological condition characterized by intense, throbbing headaches, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Understanding your triggers and the available treatments can significantly improve your quality of life. Here"s a comprehensive guide to help you manage migraines effectively.
Identifying Your Migraine Triggers
Various environmental, dietary, and physiological factors can trigger migraines. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is a crucial step in managing your condition:
- Food and Drinks: Aged cheeses, red wine, processed foods, and foods containing MSG or aspartame are common dietary triggers.
- Stress: High stress levels are a well-known trigger. Learning stress management techniques can help reduce the frequency of migraines.
- Sleep Patterns: Both too much and too little sleep can trigger migraines. Aim for a regular sleep schedule.
- Hormonal Changes: For women, fluctuations in estrogen levels can trigger migraines. Tracking your cycle can help predict migraine occurrence.
- Environmental Factors: Bright lights, loud sounds, strong smells, and changes in weather or barometric pressure can all trigger migraines.
Treatment Options
While there"s no cure for migraines, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and reduce their frequency:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, triptans (which specifically target migraine pain), and anti-nausea medications are commonly used.
- Preventive Medications: Beta-blockers, antidepressants, and anti-seizure drugs may help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, adequate hydration, a balanced diet, and stress reduction can significantly impact your migraine patterns.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and cognitive behavioral therapy have shown promise in managing migraine symptoms.
- Supplements: Magnesium, riboflavin (vitamin B2), and coenzyme Q10 are supplements that may reduce migraine frequency for some individuals.
Creating a migraine diary can help you track your triggers, symptoms, and the effectiveness of your treatment plan. This information is invaluable for you and your healthcare provider to develop a tailored migraine management strategy.
Remember, managing migraines is a personal journey. What works for one person may not work for another. Patience and persistence in trying different management strategies are key to finding what works best for you.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Your Headache
While most headaches are not indicative of a serious medical condition, certain symptoms can signal a need for immediate medical attention. Understanding when to seek help is crucial for your health. Below are guidelines to help you determine when a headache requires a doctor"s care.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
- Sudden, Severe Onset: A headache that comes on suddenly and is severe in intensity, sometimes described as a "thunderclap" headache, can indicate a serious condition such as an aneurysm.
- Change in Pattern: A significant change in the frequency, severity, or pattern of your headaches warrants a medical evaluation.
- Neurological Symptoms: Headaches accompanied by confusion, difficulty speaking, vision loss, or muscle weakness in part of the body should prompt immediate medical attention.
- Worsening Symptoms: Headaches that progressively worsen or do not improve with over-the-counter medication require a doctor"s evaluation.
- Fever and Stiff Neck: A headache accompanied by a fever, stiff neck, nausea, and vomiting can be signs of meningitis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- After Head Injury: Headaches that develop after a head injury, especially if they worsen, may indicate a concussion or other serious injury.
- Age Factor: New onset of headaches in individuals over 50 years old can indicate more serious conditions and should be evaluated.
When to Schedule a Doctor"s Visit
If your headaches are not accompanied by the above warning signs but are frequent, disrupt your daily life, or do not respond to standard treatments, it"s wise to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. They can help diagnose the type of headache you"re experiencing and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Treatment and Evaluation
During your visit, your doctor may perform a physical examination, review your headache history, and possibly recommend further testing such as MRI or CT scans to rule out underlying conditions. Treatment will depend on the diagnosis and may include medication, lifestyle changes, or referral to a specialist.
Remember, regular headaches should not interfere with your quality of life. If you"re experiencing headaches that concern you, seeking medical advice is always a prudent step.
Understanding headache placement and its meanings empowers you to effectively manage and seek treatment for various types of headaches, improving your overall health and well-being. Take control of your comfort and explore these insights for relief.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headaches-as-a-symptom-of-multiple-sclerosis-2440798-01-ac13321fbd2d4dca99f899a63b8ea265.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-dehydration-symptoms-7480908-Horiz-e2500f0828b746ee9d2e2b5257af60cb.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headache-on-the-right-side-5216756_final-b9d0145864d74706b0316a2e9b62dd37.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)
