Topic migraine vs headache: Explore the key differences between migraines and headaches in this comprehensive guide, aimed at shedding light on common misconceptions and offering relief strategies.
Table of Content
- What are the symptoms and differences between migraines and headaches?
- Understanding Migraines and Headaches
- Signs and Symptoms of Migraines vs Headaches
- Causes of Migraines and Headaches
- Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Migraines and Headaches
- YOUTUBE: Migraine vs. Headache: How to Tell Them Apart
- Diagnosing Migraines and Headaches
- Treatment Options for Migraines and Headaches
- Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
- When to See a Doctor for Migraines and Headaches
- Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms and differences between migraines and headaches?
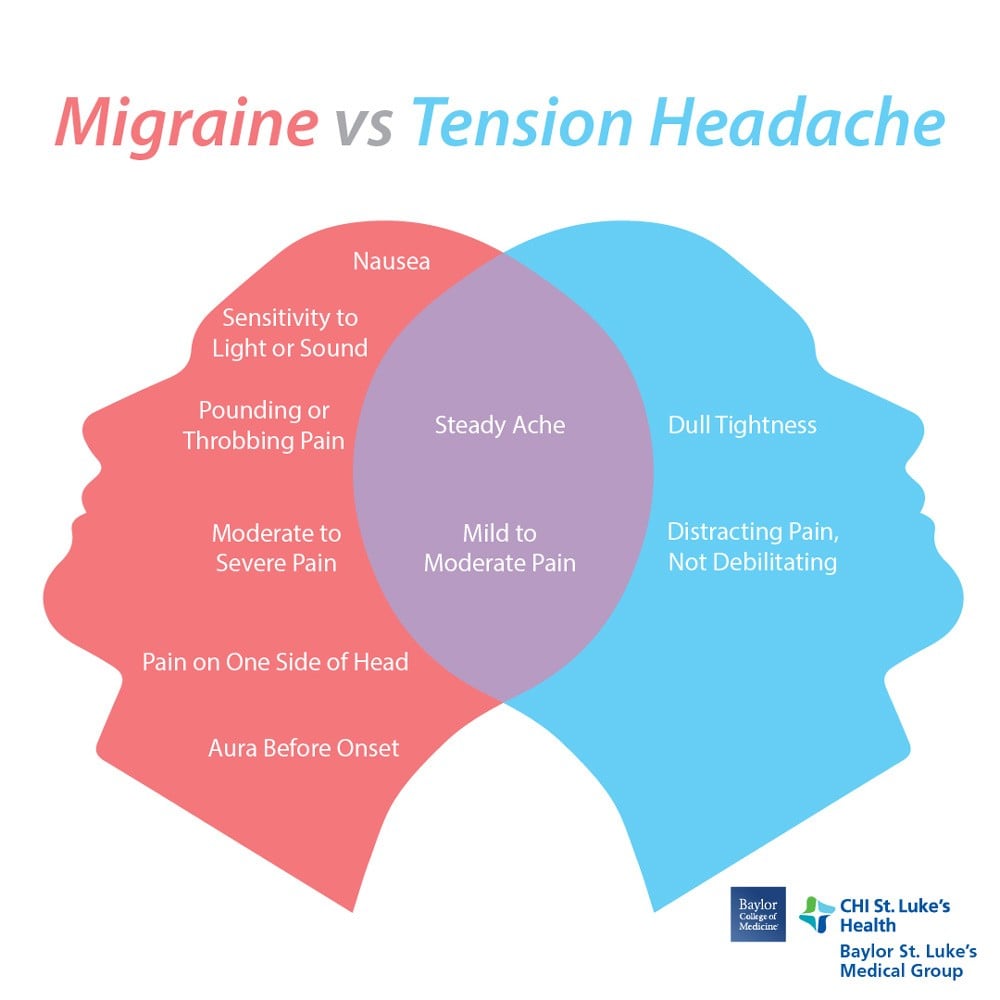
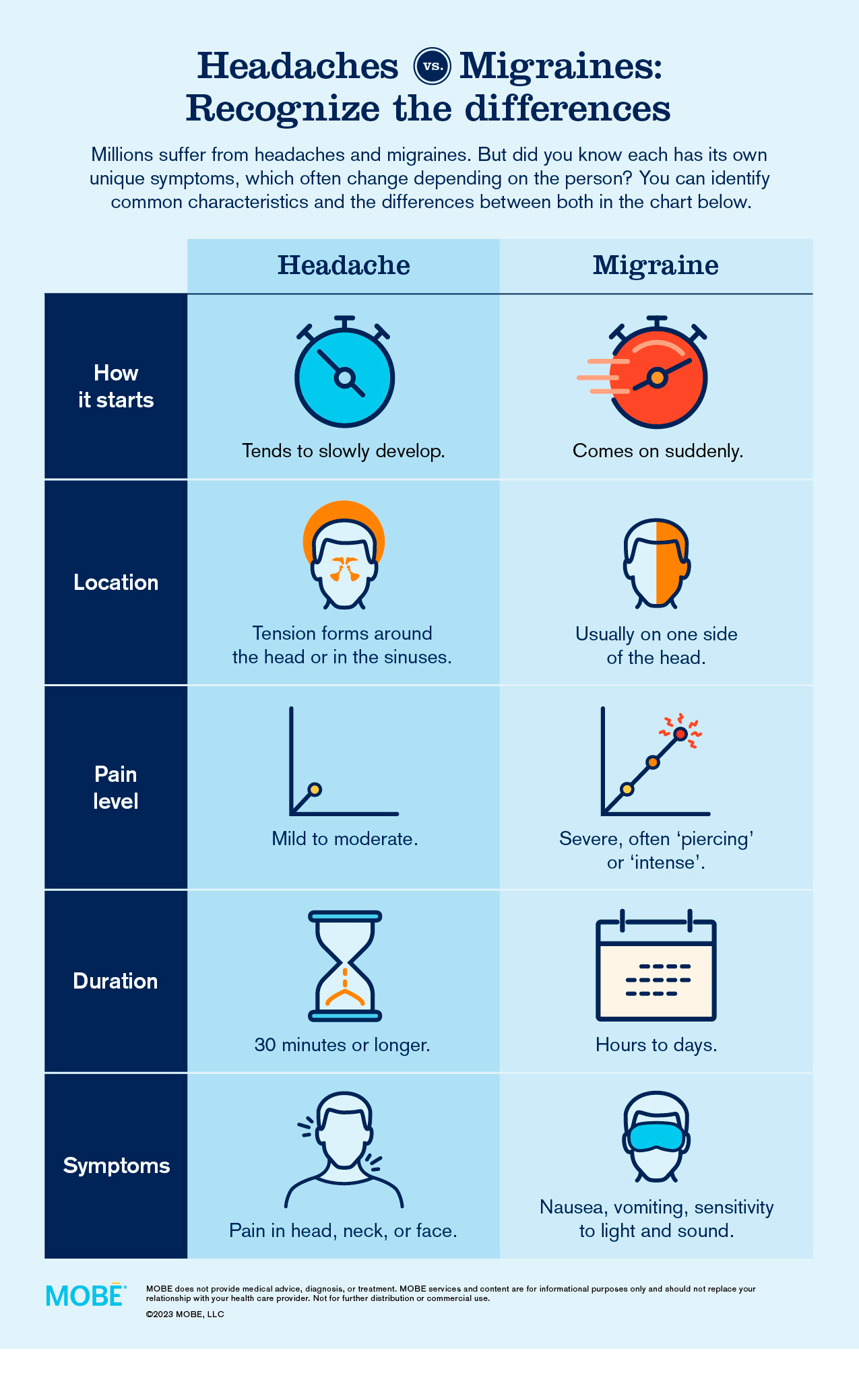
Migraine and headache are two different types of head pain, although they can sometimes have overlapping symptoms. Here are the symptoms and differences between migraines and headaches:
- Symptoms of Migraines:
- Severe, throbbing pain, often on one side of the head
- Sensitivity to light, sound, and smell
- Nausea and vomiting
- Symptoms of Headaches:
- Steady, dull ache or pressure on both sides of the head
- Mild to moderate pain intensity
- No sensitivity to light, sound, or smell
- No visual disturbances or aura
- Differences between Migraines and Headaches:
- Pain intensity: Migraine pain is usually moderate to severe, while headache pain is typically mild to moderate.
- Pain location: Migraines often occur on one side of the head, whereas headaches can be felt on both sides.
- Associated symptoms: Migraines are often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, sound, and smell, as well as visual disturbances and aura. Headaches typically do not have these associated symptoms.
- Duration: Migraines can last for hours to days, while headaches usually resolve within a few hours.
In summary, migraines are more severe and accompanied by additional symptoms compared to regular headaches. It\'s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
READ MORE:
Understanding Migraines and Headaches
Migraines and headaches are common disorders of the nervous system, each presenting with their own set of symptoms, triggers, and treatments. Understanding their differences is crucial for effective management and relief.
- Headaches: Typically characterized by a constant ache or pressure on both sides of the head, headaches can range from mild to severe but usually do not cause additional symptoms beyond pain.
- Migraines: More intense than a regular headache, migraines are often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances known as aura.
Both migraines and headaches can be triggered by a variety of factors including stress, diet, environmental changes, and hormonal fluctuations. However, migraines are often linked to specific genetic factors and changes in brain chemistry.
- Identifying Triggers: Keeping a diary can help identify potential triggers that lead to migraines or headaches.
- Medical Diagnosis: A healthcare provider can diagnose migraines and headaches based on medical history, symptoms, and by ruling out other causes.
- Treatment Approaches: Treatment varies widely and can include over-the-counter or prescription medications, lifestyle adjustments, and alternative therapies.
Understanding the distinctions between migraines and headaches is the first step towards finding relief. While both can significantly impact daily life, recognizing the specific symptoms and triggers of each can guide more effective treatment and management strategies.

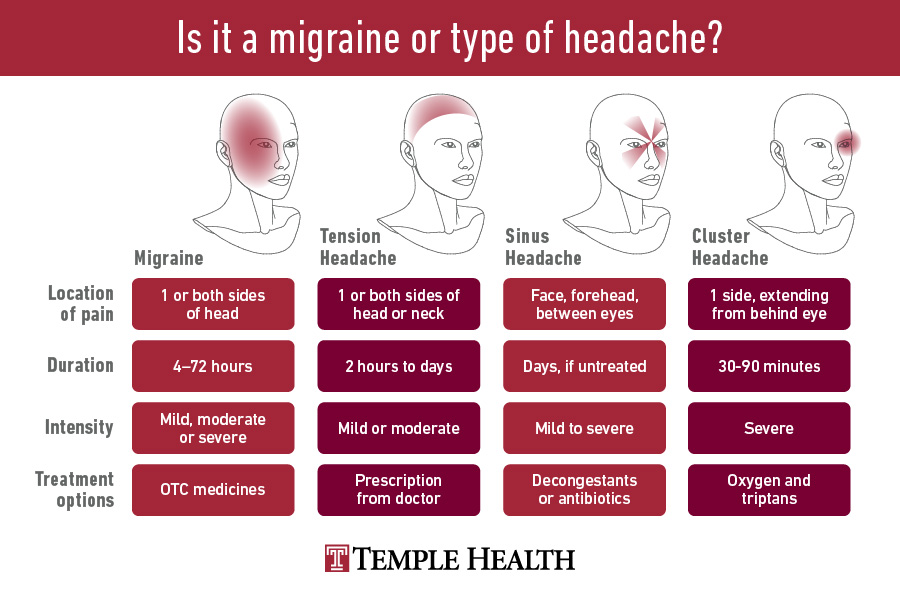
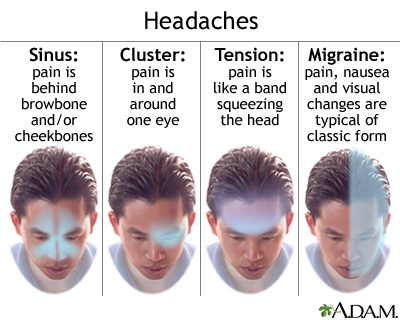
Signs and Symptoms of Migraines vs Headaches
Distinguishing between migraines and headaches is crucial for effective treatment. While both conditions share the primary symptom of head pain, their other characteristics can vary significantly.
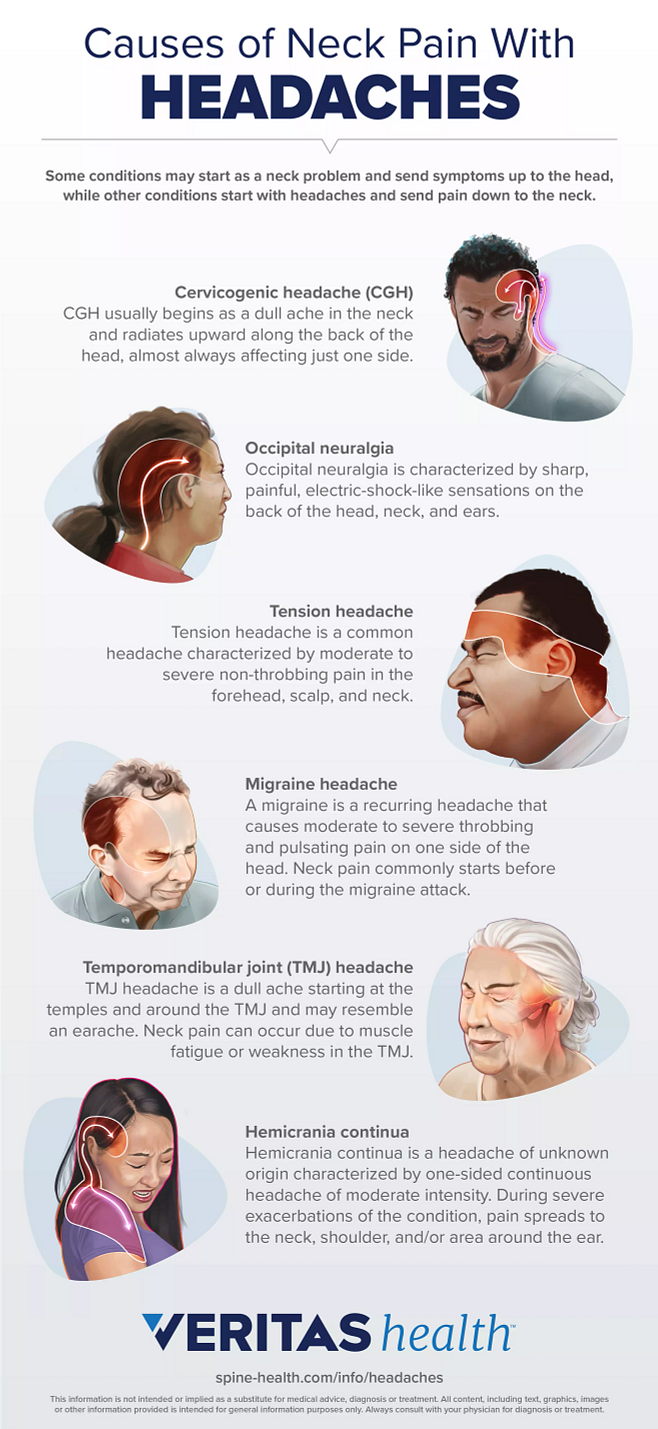
- Headache Symptoms: Headaches generally cause a persistent, dull ache across both sides of the head. Some headaches, like tension headaches, might also involve sensitivity around the neck and shoulders.
- Migraine Symptoms: Migraines are often identified by a pulsating or throbbing pain on one side of the head. They can also include nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound. Some individuals experience aura before a migraine, manifesting as visual disturbances, tingling in the arms or legs, or difficulty speaking.
Other symptoms unique to migraines include:
- Changes in vision, such as seeing flashes of light or blind spots.
- A feeling of weakness or numbness in the face or one side of the body.
- Dizziness or a spinning sensation (vertigo).
- Difficulty speaking clearly.
- Unusual sensitivity to smells, touches, and tastes.
Understanding these signs and symptoms can help differentiate between a migraine and a headache, guiding towards the appropriate treatment path. While headaches can often be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers and rest, migraines may require a more comprehensive approach including prescription medication, lifestyle changes, and preventative strategies.
Causes of Migraines and Headaches
Understanding the causes of migraines and headaches is essential for effective prevention and treatment. While the exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, several factors have been identified that contribute to both conditions.
- Genetic Factors: Migraines often run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition to this condition.
- Environmental Triggers: Both migraines and headaches can be triggered by factors such as stress, weather changes, loud noises, and strong smells.
Specific causes of headaches include:
- Tension from stress, anxiety, or muscle strain.
- Dehydration or caffeine withdrawal.
- Eyestrain from prolonged screen use.
For migraines, additional triggers may include:
- Hormonal changes, particularly in women due to menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause.
- Certain foods and additives, such as aged cheeses, alcohol, and monosodium glutamate (MSG).
- Irregular sleep patterns or changes in routine.
Both migraines and headaches can significantly impact an individual"s quality of life. Identifying and understanding the specific causes and triggers is a crucial step towards managing and reducing the frequency of these conditions.
Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Migraines and Headaches
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in the frequency and severity of migraines and headaches. Making positive changes can help manage and reduce the impact of these conditions.
- Diet: Certain foods and beverages can trigger migraines and headaches, including aged cheeses, alcohol, caffeine, and foods containing MSG. A balanced diet with regular meal times can help.
- Hydration: Dehydration is a common trigger for headaches. Maintaining adequate hydration throughout the day can prevent onset.
- Sleep: Both too little and too much sleep can trigger migraines and headaches. Establishing a regular sleep schedule is beneficial.
- Stress: High levels of stress are linked to both migraines and tension headaches. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or exercise can reduce their frequency.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can reduce the frequency and severity of migraines and headaches by relieving tension and stress.
- Screen Time: Extended periods of screen use can strain the eyes and trigger headaches. Taking regular breaks using the 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds) can help.
Adjusting these lifestyle factors not only contributes to overall well-being but also plays a crucial role in managing migraines and headaches. Individuals may benefit from tracking their habits and symptoms to identify specific triggers and effective strategies for mitigation.
Migraine vs. Headache: How to Tell Them Apart
\"Learn how to differentiate yourself from the competition and stand out in your industry with this informative and practical video. Discover unique strategies that will set you apart and help you achieve success!\"
Is it a Headache or a Migraine?
\"Discover the power of distinguishing between similar concepts and gaining a clear understanding of their nuances. This video will provide you with valuable insights and techniques to enhance your analytical skills and make more informed decisions.\"
Diagnosing Migraines and Headaches
Accurately diagnosing migraines and headaches is essential for effective treatment. The process typically involves a detailed medical history and may include specific tests to rule out other causes.
- Medical History: A thorough discussion of symptoms, frequency, duration, and triggers of headaches or migraines. Family history of migraines is also considered.
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive physical exam to identify any neurological abnormalities and assess overall health.
- Diagnostic Criteria: For migraines, doctors refer to criteria such as the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) for diagnosis.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: Sometimes, additional tests like MRI or CT scans are conducted to exclude other causes of headache symptoms, such as tumors or vascular disease.
Keeping a headache diary can be invaluable in the diagnostic process, helping to identify patterns, triggers, and the effectiveness of any treatments tried. This information is critical for healthcare providers to make an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment strategies.
It"s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience frequent or severe headaches or migraines. Early diagnosis and treatment can lead to better management of symptoms and improve quality of life.

Treatment Options for Migraines and Headaches
Effective management of migraines and headaches involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes alternative therapies. The right approach depends on the frequency, severity, and individual patient circumstances.
- Medications:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are commonly used for headaches.
- Prescription medications, including triptans and ergotamines, are often prescribed for migraines.
- Preventive medications, such as beta-blockers, anticonvulsants, or antidepressants, may reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as stress or certain foods, can help prevent migraines and headaches.
- Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and staying hydrated.
- Regular physical activity.
- Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture, biofeedback, and cognitive behavioral therapy have shown effectiveness for some individuals.
- Supplements, such as magnesium, riboflavin (vitamin B2), and coenzyme Q10, may also help prevent migraines.
It"s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. For some, a combination of treatments may be necessary to effectively manage symptoms.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting certain lifestyle changes and preventive measures can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of migraines and headaches. Here are some strategies that have proven effective for many individuals.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can help reduce stress and prevent migraines.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels and reduce the occurrence of migraines and headaches.
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, ensuring a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime can improve sleep quality and prevent migraines.
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding known dietary triggers, such as alcohol, caffeine, and foods high in histamine or MSG, can help prevent migraines. Eating balanced meals at regular intervals is also beneficial.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for preventing headaches, which are often triggered by dehydration.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding individual triggers, whether environmental, such as strong smells or bright lights, or related to lifestyle, such as certain foods or sleep disruption, is key to prevention.
While these measures may not eliminate migraines or headaches completely, they can significantly reduce their impact on your life. It"s important to work with a healthcare provider to identify the most effective strategies for your situation.
When to See a Doctor for Migraines and Headaches
While occasional headaches may not require medical attention, certain situations warrant consulting a healthcare professional for migraines and headaches.
- Sudden Onset: A headache that appears suddenly and is severe, sometimes described as a "thunderclap" headache, can be a sign of a serious condition and requires immediate medical attention.
- Changes in Pattern: Significant changes in the frequency, severity, or characteristics of your headaches or migraines are reasons to see a doctor.
- Accompanied Symptoms: Headaches or migraines accompanied by symptoms such as confusion, difficulty speaking, vision loss, or weakness in one part of the body should prompt a medical evaluation.
- Impact on Daily Life: If headaches or migraines are impacting your ability to work, sleep, or participate in daily activities, it"s time to seek medical advice.
- Overuse of Medication: Relying on over-the-counter or prescription headache medication more than two days a week can lead to rebound headaches and warrants a doctor"s visit.
- Existing Conditions: People with existing medical conditions or those who are pregnant should consult a doctor if experiencing frequent headaches.
Getting the right diagnosis and treatment plan can significantly improve your quality of life. A healthcare provider can offer tailored advice and treatment options based on your individual health needs.
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between a migraine and a headache?
- Migraines are a type of headache characterized by intense pain, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Headaches can vary in intensity but do not typically include these additional symptoms.
- Can certain foods trigger migraines or headaches?
- Yes, certain foods and additives, such as aged cheeses, red wine, caffeine, and MSG, can trigger migraines and headaches in some individuals.
- Are migraines hereditary?
- Yes, migraines have a genetic component, and it"s common for them to run in families.
- How can I prevent migraines and headaches?
- Preventing migraines and headaches involves identifying and avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, ensuring regular sleep patterns, and staying hydrated.
- When should I seek medical attention for migraines or headaches?
- If your headaches are severe, frequent, or accompanied by other symptoms like vision changes or weakness, seek medical attention. Also, consult a doctor if your headache pattern changes or your headaches worsen.
- Are there any treatments available for migraines and headaches?
- Yes, treatment options include over-the-counter and prescription medications, lifestyle changes, stress management techniques, and, for some, preventive medications to reduce the frequency of attacks.
Understanding the nuances between migraines and headaches empowers you to seek appropriate care and improve your quality of life. Embrace the journey toward relief and wellness with informed choices and proactive management.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-dehydration-symptoms-7480908-Horiz-e2500f0828b746ee9d2e2b5257af60cb.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headache-on-the-right-side-5216756_final-b9d0145864d74706b0316a2e9b62dd37.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)
