Topic constant headache: Experiencing constant headaches can be debilitating, but understanding their causes and exploring effective solutions can significantly improve your quality of life.
Table of Content
- What are the causes and treatments for constant headaches?
- Common Causes of Constant Headaches
- When to See a Doctor: Warning Signs
- Different Types of Constant Headaches
- Potential Treatments and Management Strategies
- Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Remedies
- Understanding Medication Overuse Headaches
- YOUTUBE: Constant Headache
- Role of Diet and Hydration in Managing Headaches
- Stress Management Techniques for Headache Relief
- Importance of Regular Sleep Patterns
- Seeking Professional Help: Therapies and Specialist Consultations
What are the causes and treatments for constant headaches?
Constant headaches, also known as chronic daily headaches, can have various causes. Some common causes include:
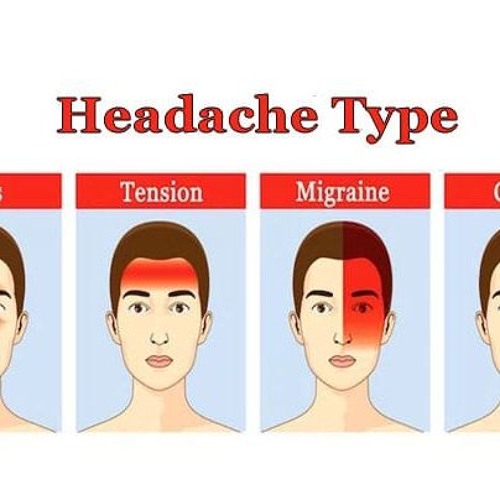
- Tension headaches: These are the most common type of headache and can occur due to stress, anxiety, or muscle tension.
- Migraines: Migraines are characterized by severe, throbbing pain on one side of the head and can be accompanied by other symptoms like nausea, light sensitivity, and aura.
- Sinus headaches: Inflammation and congestion in the sinuses can lead to headaches, usually felt in the forehead and around the eyes.
- Cluster headaches: These are intense headaches that occur in clusters or cycles, often causing severe pain around one eye.
- Medication overuse: Overuse of pain relievers or other medications can lead to rebound headaches, where regular use of medication actually causes headaches.
- Other potential causes: Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, brain tumors, or infections, can also cause chronic headaches.
The treatment for constant headaches depends on the underlying cause, and it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management. However, some general treatment options include:
- Identifying triggers: Keeping a headache diary can help identify specific triggers or patterns that contribute to headaches, such as certain foods, stress, or lack of sleep.
- Lifestyle modifications: Making healthy lifestyle changes like managing stress, getting regular exercise, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and practicing relaxation techniques can help reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can provide temporary relief for mild headaches. For more severe or frequent headaches, prescription medications may be necessary, such as triptans for migraines or preventive medications to reduce the frequency of headaches.
- Alternative therapies: Some people find relief from constant headaches through alternative therapies like acupuncture, massage, biofeedback, or relaxation exercises.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan based on the specific cause and severity of constant headaches. They can provide proper diagnosis, recommend appropriate medications or therapies, and offer guidance on managing and preventing headaches.
READ MORE:
Common Causes of Constant Headaches
Understanding the root causes of constant headaches is crucial in finding the right treatment. Here are some of the most common factors:
- Stress: High stress levels can lead to tension headaches, presenting as constant pressure around the head.
- Lack of Sleep: Inadequate or irregular sleep patterns can trigger chronic headaches.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can lead to dehydration headaches, often felt as a dull, constant ache.
- Eyestrain: Long hours in front of screens without breaks can cause headaches due to eyestrain.
- Dietary Triggers: Certain foods and beverages, such as those containing caffeine or alcohol, can trigger headaches in sensitive individuals.
- Medication Overuse: Overuse of headache medication can lead to rebound headaches, becoming more frequent and severe over time.
- Environmental Factors: Changes in weather, altitude, or exposure to certain chemicals can trigger headaches.
- Medical Conditions: Sinus infections, dental issues, or neurological disorders can also be underlying causes of constant headaches.

When to See a Doctor: Warning Signs
It"s crucial to recognize when a constant headache requires medical attention. Here are key warning signs indicating it"s time to consult a doctor:
- Headaches that suddenly become severe or are described as the "worst ever."
- Changes in headache patterns or headaches that progressively worsen.
- Headaches accompanied by fever, stiff neck, confusion, double vision, weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking.
- Headaches following a head injury, especially if they worsen.
- Chronic headaches that impact your daily life or are not relieved by over-the-counter medications.
- New headache pain if you"re over 50 years old.
Seeking timely medical advice can help diagnose any underlying conditions and provide relief through appropriate treatment strategies.
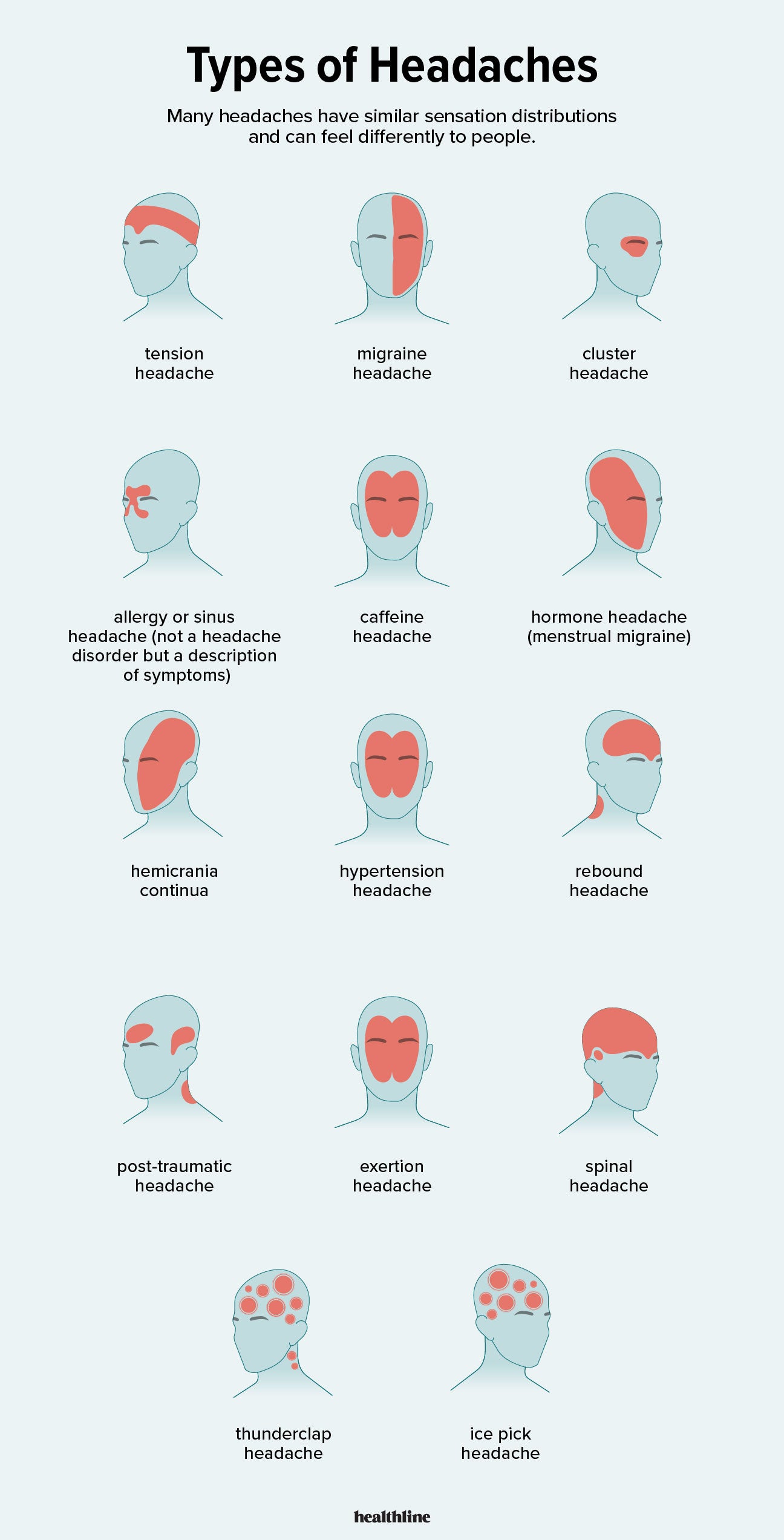
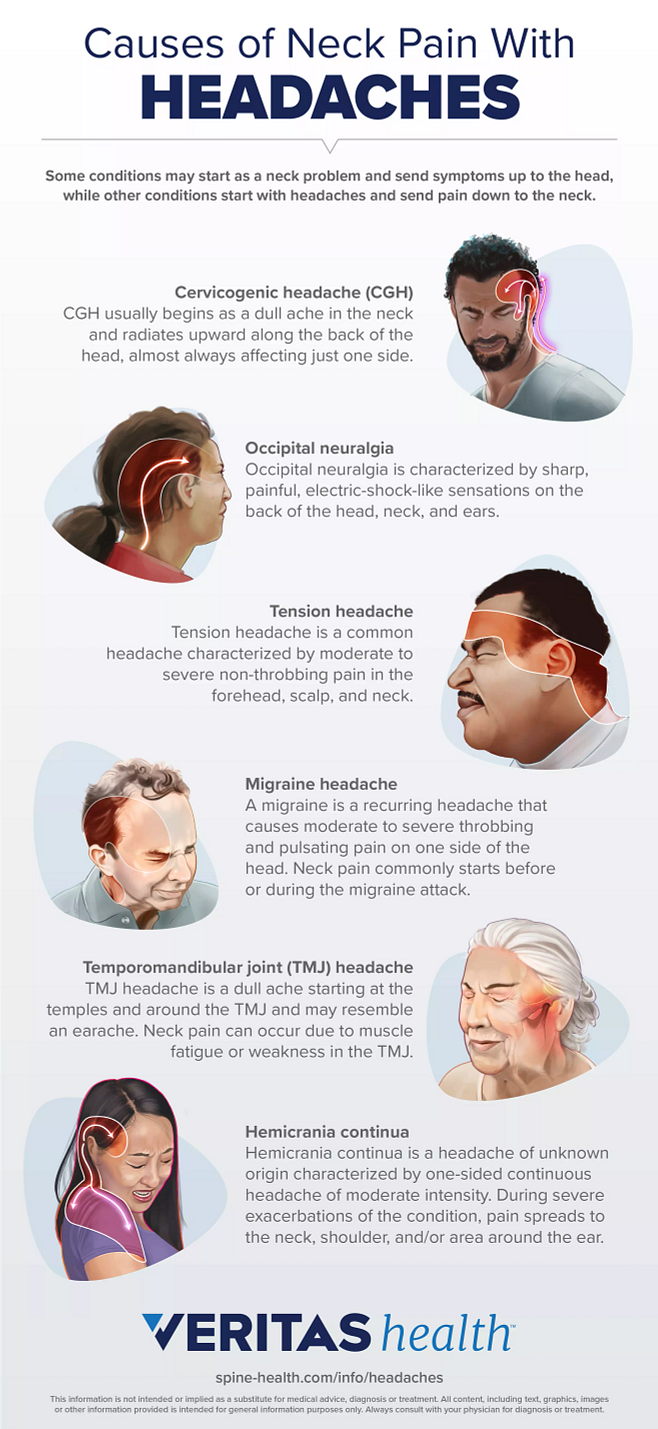
Different Types of Constant Headaches
Understanding the variety of constant headaches can guide you towards the right treatment. Here are the main types:
- Tension Headaches: Often described as a tight band around the head, these are the most common type of headache, characterized by mild to moderate pain.
- Migraines: Intense, throbbing pain typically affecting one side of the head, accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and sometimes visual disturbances.
- Cluster Headaches: Excruciating pain around one eye or temple, occurring in groups or "clusters" over a period. These are less common but significantly painful.
- Chronic Daily Headaches: Named for their frequency, occurring 15 or more days a month. They can be short or long in duration, often affecting quality of life.
- Medication Overuse Headaches: Caused by the regular, long-term use of medication to treat headaches, leading to a cycle of rebound headaches.
- Secondary Headaches: Resulting from underlying health conditions, such as sinusitis, dehydration, or more serious conditions like a tumor or aneurysm.
Identifying the type of headache you"re experiencing is a crucial step towards finding effective treatment and relief.
Potential Treatments and Management Strategies
Managing constant headaches often requires a combination of treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some effective strategies:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can be effective for mild headaches. Prescription medications, including triptans for migraines and preventative medications, may be recommended for more severe cases.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, adequate hydration, sufficient sleep, and a healthy diet can significantly reduce headache frequency and intensity.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and reduce headache occurrence.
- Physical Therapy: For tension headaches, physical therapy can help relieve pain through posture improvement, neck stretching, and strengthening exercises.
- Acupuncture: Some find acupuncture helpful in reducing headache frequency and severity.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can be effective in managing chronic headaches by changing pain management behaviors and reducing stress.
- Avoiding Trigger Foods: Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger headaches can be a crucial step in management.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help monitor the effectiveness of treatment plans and adjust as necessary.
It"s essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and headache type.
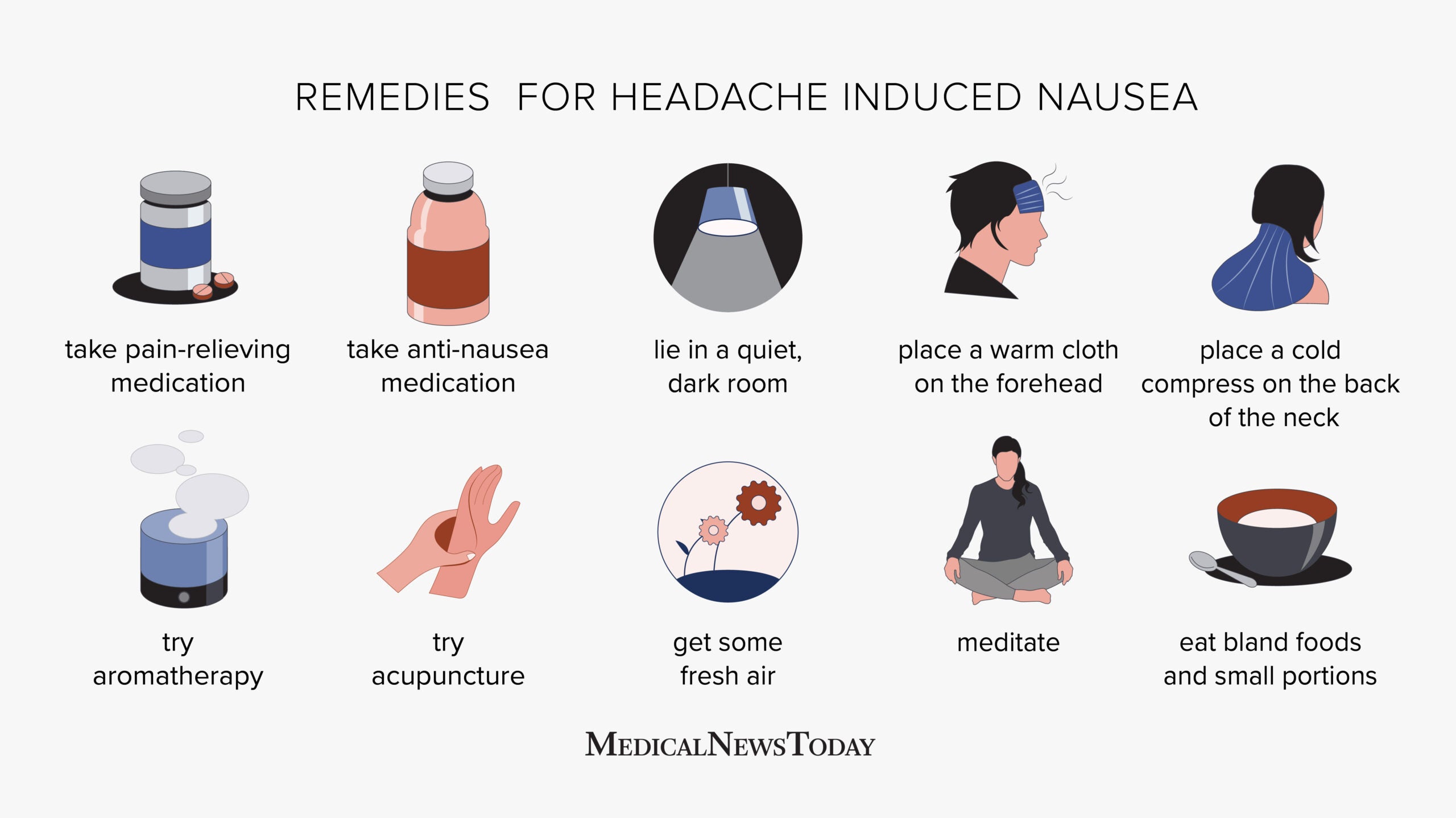
Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Remedies
Making certain lifestyle adjustments and trying home remedies can significantly alleviate the frequency and severity of constant headaches. Here are some effective strategies:
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can trigger headaches. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water daily to prevent dehydration.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Avoid foods known to trigger headaches, such as processed meats, aged cheeses, chocolate, and foods high in MSG. Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can reduce stress and prevent headaches.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol can trigger headaches in some individuals. Moderation is key.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to manage stress levels.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Poor sleep can trigger headaches. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and try to go to bed and wake up at the same times every day.
- Limit Screen Time: Prolonged use of screens can lead to eye strain and headaches. Take regular breaks and use the 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds).
- Use Essential Oils: Applying peppermint or lavender oil to the temples can help reduce headache symptoms for some people.
- Apply Heat or Cold: Using a hot or cold compress on your head or neck can provide relief. Cold packs can reduce inflammation, while a warm pack can relax tense muscles.
- Avoid Chewing Gum: Chewing gum can lead to jaw strain and headaches in some individuals.
- Consider Supplements: Magnesium, riboflavin (vitamin B2), and coenzyme Q10 have been shown to help prevent migraines in some people.
- Practice Good Posture: Poor posture can contribute to tension headaches. Work on strengthening and stretching your back and neck muscles.
Remember, while these lifestyle adjustments and home remedies can be effective, they may not work for everyone. It"s important to consult with a healthcare professional to tailor a plan that"s right for you.

Understanding Medication Overuse Headaches
Medication Overuse Headaches (MOH), often referred to as rebound headaches, occur when headache medications are used too frequently. Understanding the dynamics of MOH is crucial for both prevention and treatment. Here"s what you need to know:
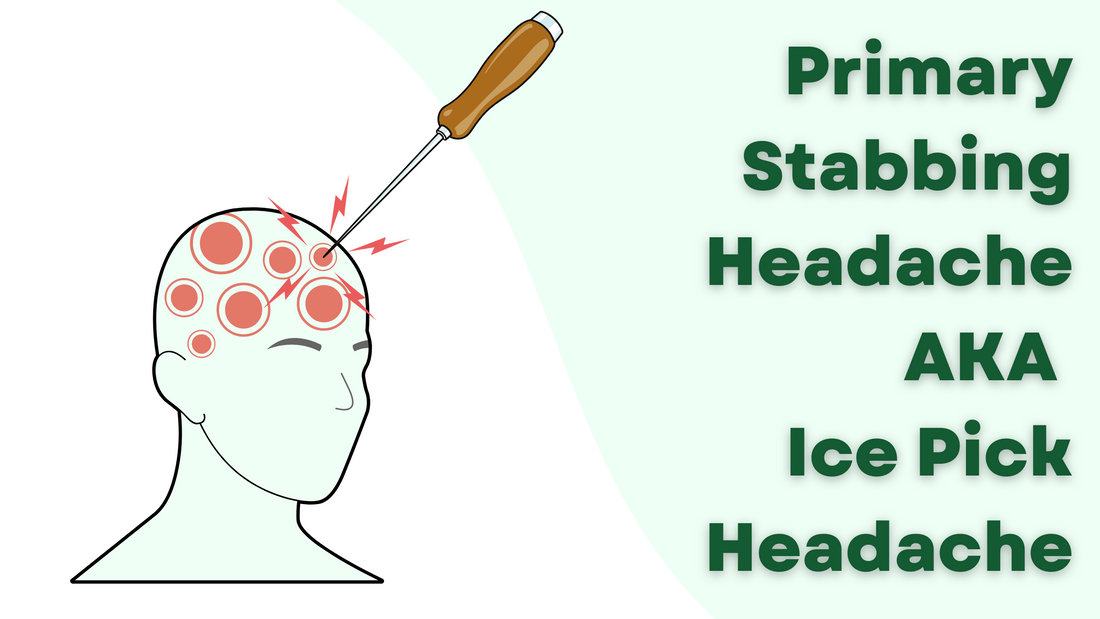
- Definition: MOH are headaches that occur on 15 or more days per month in a patient with a pre-existing primary headache disorder due to regular overuse of medication for acute or symptomatic headache relief for more than three months.
- Causes: The condition is triggered by the chronic use of headache medications, including over-the-counter (OTC) drugs like aspirin, acetaminophen, NSAIDs, as well as prescription medications such as triptans, ergotamines, and opioids.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include daily or near-daily headaches, a decrease in medication effectiveness, and an increase in headache frequency over time.
- Risk Factors: Individuals with a history of chronic headaches, particularly migraines or tension-type headaches, are at higher risk. The risk increases with the frequency of medication use, particularly when used more than two or three days per week.
- Prevention: Limit the use of headache medications to no more than two days per week. Consider non-pharmacological treatments for headache management to reduce dependency on medications.
- Treatment: The first step in treating MOH is to discontinue or significantly reduce the overused medication. This process should ideally be supervised by a healthcare professional due to potential withdrawal symptoms. Transition to preventive headache medications may also be recommended.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Patients may experience withdrawal symptoms such as increased headache frequency and intensity, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, restlessness, and nervousness, which typically improve within a few weeks.
- Support and Management: Cognitive-behavioral therapy, hydration, regular exercise, stress management, and establishing a regular sleep schedule can support recovery and prevent recurrence.
Understanding and addressing MOH is a critical component of headache management. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Constant Headache
\"Discover effective ways to manage and alleviate migraine pain in this informative video. Learn about holistic treatments and natural remedies that can provide much-needed relief and enable you to regain control of your life.\"
Causes of Everyday Headaches - Dr. Advait Kulkarni
\"Uncover the root causes of common health issues and gain a deeper understanding of how they can impact your well-being. This enlightening video explores various causes of ailments and empowers you with knowledge to make positive changes for a healthier future.\"
Role of Diet and Hydration in Managing Headaches
The impact of diet and hydration on headaches is profound, offering both preventative and therapeutic benefits. Adhering to specific dietary guidelines and ensuring adequate hydration can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Here"s a comprehensive overview:
- Hydration: Dehydration is a common trigger for headaches. Drinking sufficient water, typically 8-10 glasses a day, can prevent dehydration-related headaches. Additionally, reducing beverages that can lead to dehydration, such as alcohol and caffeine, is advisable.
- Regular Meals: Skipping meals or fasting can trigger headaches in some individuals due to low blood sugar levels. Eating regular, balanced meals helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and can prevent these types of headaches.
- Food Triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal food triggers is crucial. Common culprits include aged cheeses, processed meats, chocolate, and foods containing MSG or artificial sweeteners. Keeping a food diary can help identify specific triggers.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and may reduce headache occurrences. Certain diets, such as those high in omega-3 fatty acids and low in omega-6 fatty acids, have been shown to be beneficial.
- Limit Certain Substances: Excessive caffeine and alcohol intake can trigger headaches in some people. Moderation or elimination of these substances can be helpful in managing headache frequency and intensity.
- Supplements: Some evidence suggests that certain dietary supplements, including magnesium, riboflavin (vitamin B2), and coenzyme Q10, may reduce migraine frequency. However, it"s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet, such as turmeric, ginger, and berries, may help reduce the frequency of headaches by reducing inflammation in the body.
It"s important to note that individual responses to dietary changes and hydration levels can vary. A personalized approach, possibly guided by a healthcare professional or a dietitian, can help determine the most effective strategies for managing headaches.
Stress Management Techniques for Headache Relief
Stress can be a significant trigger for headaches, making stress management an essential part of headache relief. Implementing effective stress management techniques can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Meditation: Regular meditation can help calm the mind, reduce stress, and decrease the occurrence of headaches. It involves focusing your attention and eliminating the stream of jumbled thoughts that may be crowding your mind and causing stress.
- Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to improve mental and physical health. The relaxation and exercise components of yoga can help reduce stress and prevent headaches.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing is a simple yet effective way to reduce stress and relax. Try breathing deeply from your diaphragm, allowing your chest and stomach to rise as you fill your lungs with air, then exhale slowly.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): PMR involves tensing each muscle group in the body tightly, but not to the point of strain, and then slowly relaxing them. This practice can help reduce stress and ease headaches.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce stress and tension that may lead to headaches. Even a daily walk or other moderate exercise can make a difference.
- Sufficient Sleep: Lack of sleep can exacerbate stress and lead to headaches. Ensuring you get enough quality sleep can help manage stress and reduce headaches.
- Healthy Eating Habits: A well-balanced diet can improve your overall health and help manage stress. Avoiding foods and drinks that may trigger headaches is also crucial.
- Time Management: Effective time management can help reduce stress by preventing last-minute rushes and the feeling of being overwhelmed. Plan ahead and prioritize your tasks.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Set achievable goals to avoid the stress of trying to accomplish too much in too little time. Breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable steps can also help.
- Seeking Social Support: Talking to friends, family, or a professional can help you manage stress by sharing your feelings and seeking advice or assistance.
Implementing these techniques into your daily routine can help manage stress levels and reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches. Remember, if your headaches persist or worsen, it"s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
Importance of Regular Sleep Patterns
Regular sleep patterns play a crucial role in managing headaches and migraines. Sleep and headache share a bidirectional relationship, where sleep problems can trigger headaches, and headaches can disrupt sleep. Maintaining consistent sleep and wake times and ensuring you get the recommended 7 to 8 hours of sleep per night can significantly reduce headache frequency. This is because both too little and too much sleep can serve as headache triggers.
To promote restful sleep, engaging in good sleep hygiene practices is essential. These include:
- Setting a consistent bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends, to regulate your body"s clock.
- Creating a restful sleeping environment, free from noise and light, and minimizing electronic device use before bedtime.
- Incorporating relaxation techniques into your evening routine, such as paced breathing, mindfulness meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation.
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime, as they can disrupt sleep patterns.
- Ensuring your bedroom is for sleep and intimacy only, avoiding activities like watching TV or working.
- Exercising regularly but not too close to bedtime, as physical activity can promote better sleep.
Understanding the link between sleep and migraines can also help in managing symptoms effectively. Migraine attacks are more likely during early morning hours, possibly due to sleep or circadian rhythm disruptions. Strategies that align your sleep patterns with your natural circadian rhythms can help in preventing migraines and improving overall sleep quality.
By focusing on regular sleep patterns and good sleep hygiene, individuals suffering from constant headaches can find relief and improve their quality of life.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Coping-with-New-Daily-Persistent-Headache_Illustrator_Julie-Bang_Final-17370e7368a94bbbb08e9e42e425e942.jpg)
READ MORE:
Seeking Professional Help: Therapies and Specialist Consultations
If constant headaches disrupt your daily life, seeking professional help can be a crucial step towards finding relief. Various therapies and specialist consultations can offer targeted treatments based on the type of headaches you experience. Understanding when and how to seek help can empower you to manage your condition effectively.
Start with a visit to your primary care physician, who can evaluate your symptoms and provide initial treatment recommendations. If your headaches persist or if a more specialized approach is needed, your doctor may refer you to a neurologist or a headache specialist. These professionals can offer more advanced diagnostic tests and treatments.
- Neurologist Consultations: A neurologist can assess neurological causes of your headaches and suggest treatments such as prescription medications, lifestyle adjustments, or further testing.
- Headache Specialists: These are doctors with specialized training in headache management, offering tailored therapies that may include medication, behavioral strategies, and preventive measures.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): For those whose headaches may be linked to stress, anxiety, or depression, CBT can be effective in teaching coping strategies to manage headache triggers.
- Physical Therapy: If your headaches are related to muscle tension or posture issues, physical therapy can help relieve symptoms through specific exercises and manual therapy.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and relaxation techniques can complement traditional treatments by reducing headache frequency and severity.
In addition to these options, your healthcare provider may also suggest dietary changes, supplements, or lifestyle modifications to help manage your headaches. Regular follow-ups and open communication with your healthcare team are key to adjusting treatments and finding what works best for you.
Remember, while seeking professional help, it"s important to keep a detailed headache diary that tracks the frequency, duration, intensity, and triggers of your headaches. This information can be invaluable in diagnosing your condition and tailoring your treatment plan.
Overcoming constant headaches starts with understanding their causes and exploring a range of treatments. Empower yourself with knowledge, seek professional guidance, and discover effective strategies to manage your condition and improve your quality of life.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headaches-as-a-symptom-of-multiple-sclerosis-2440798-01-ac13321fbd2d4dca99f899a63b8ea265.png)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-dehydration-symptoms-7480908-Horiz-e2500f0828b746ee9d2e2b5257af60cb.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headache-on-the-right-side-5216756_final-b9d0145864d74706b0316a2e9b62dd37.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/migraine-relief-pressure-points-5205811-FINAL-cdc9e0d051cb460bac8baa98bc01954f.jpg)