Topic eye pain and headache: Experiencing eye pain and headache can be alarming, but understanding their causes and exploring effective solutions can lead to relief and improved well-being.
Table of Content
- What are the causes of eye pain and headache?
- Common Causes of Eye Pain and Headache
- Symptoms to Watch For
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Diagnosis Techniques and Tests
- Treatment Options for Relief
- Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
- YOUTUBE: Eye Pain and Headache: Potential Causes - Dr. Sunita Rana Agarwal
- Preventing Eye Strain and Headaches
- Understanding Migraines with Ocular Symptoms
- The Impact of Digital Screen Use
- Eye Conditions Linked to Headaches
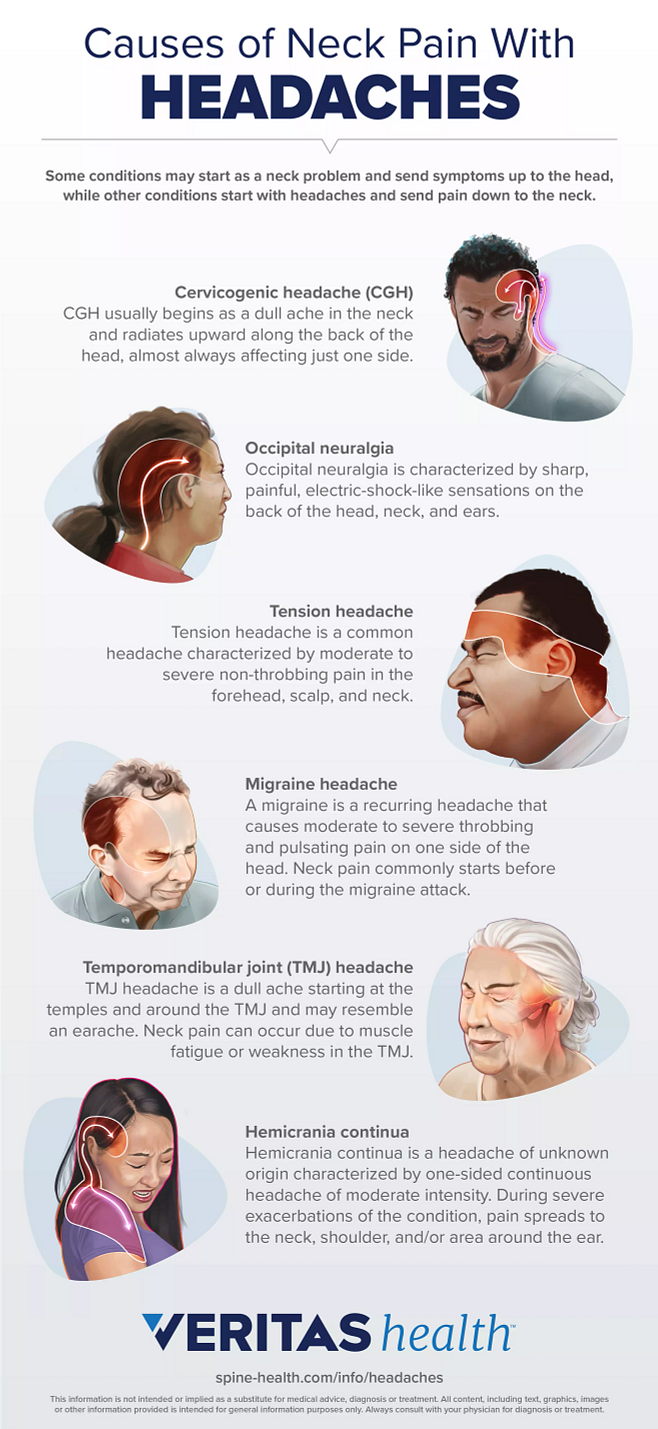
What are the causes of eye pain and headache?
Eye pain and headache can be caused by various factors. Some of the possible causes include:
- Migraine headaches: Migraines are a common cause of both eye pain and headaches. They are often accompanied by other symptoms such as sensitivity to light, nausea, and vomiting.
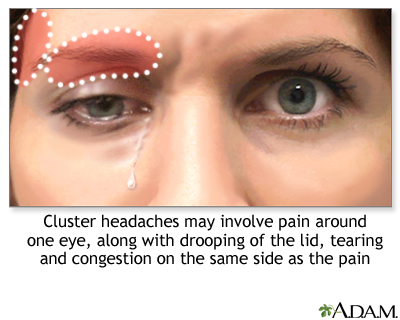
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses can cause referred pain around the eyes and forehead. This may be accompanied by congestion and a runny nose.
- Eyestrain: Prolonged use of digital screens, reading in poor lighting conditions, or focusing on close objects for extended periods can strain the eye muscles, leading to eye pain and headaches.
- Eye infections: Conditions like conjunctivitis (pink eye) or uveitis (inflammation of the middle layer of the eye) can cause eye pain along with redness, discharge, and blurred vision.
- Glaucoma: Increased pressure within the eye can cause eye pain and headaches, often accompanied by reduced peripheral vision and halos around lights.
- Tension headaches: These are typically caused by muscle tension in the head, neck, and scalp. They can cause aching pain in the temples or the back of the head, which may radiate to the eyes.
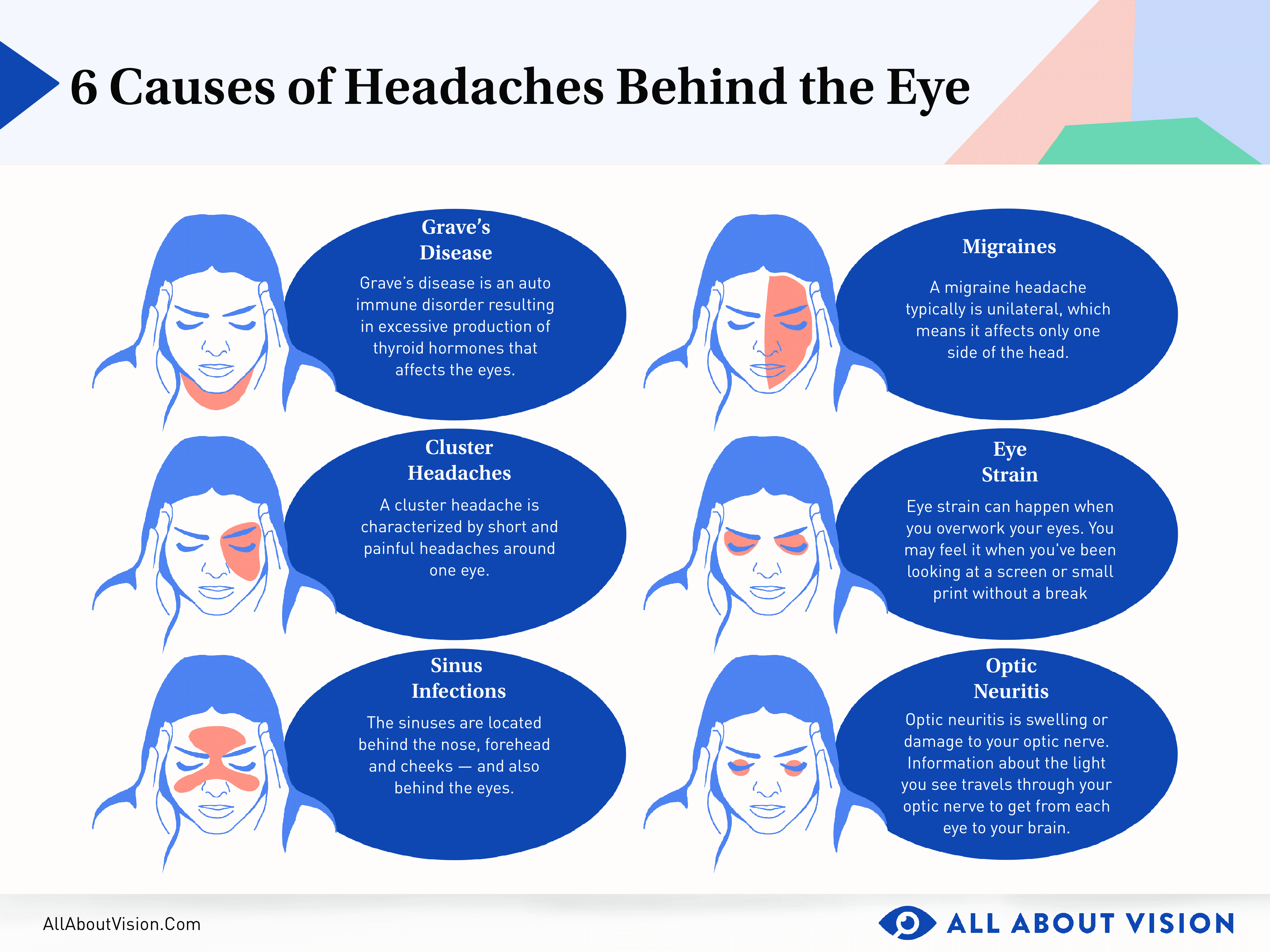
- Cluster headaches: Cluster headaches are rare but extremely painful headaches that occur in clusters over weeks or months. They often cause severe pain on one side of the head, including around the eye.
If you are experiencing persistent or severe eye pain and headaches, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
READ MORE:
Common Causes of Eye Pain and Headache
Eye pain and headache can stem from various conditions, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding these causes is the first step towards effective management and relief.
- Migraines: Often characterized by severe, throbbing pain on one side of the head, migraines can also cause sensitivity to light and sound, nausea, and visual disturbances known as auras.
- Tension Headaches: The most common type of headache, causing mild to moderate pain like a tight band around the head, often associated with stress, lack of sleep, and muscle strain.
- Cluster Headaches: Intensely painful headaches occurring in clusters, typically around one eye. They are rare and can cause eye redness, swelling, and tearing on the affected side.
- Eye Strain: Caused by prolonged activities that require intense eye use, such as computer work, reading, or driving. Symptoms include sore, tired, burning, or itching eyes, and headache.
- Sinus Infections: Inflammation of the sinuses can cause pressure around the eyes and cheeks, leading to a headache.
- Glaucoma: A group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often associated with high eye pressure. Acute angle-closure glaucoma can cause severe eye pain and headache.
- Optic Neuritis: Inflammation of the optic nerve, causing painful eye movements and potential vision loss.
- Dry Eyes: Dry eye syndrome can cause discomfort, including eye pain and associated headache.
- Corneal Abrasions: Scratches on the surface of the eye can cause significant pain and discomfort, along with a headache.
- Eye Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause eye pain, redness, discharge, and potentially headache.
Addressing the underlying cause of eye pain and headache is crucial for effective treatment and relief. Regular eye exams and consultations with healthcare professionals can help identify and manage these conditions.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vision-and-headache-3422017_final-f90b31917b244236a7424b143a537fd3.jpg)
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of eye pain and headache is crucial for early detection and treatment. Here are symptoms that should prompt further evaluation:
- Severe, sudden eye pain: Especially if accompanied by blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting, indicating a possible acute glaucoma attack.
- Recurrent headaches: Particularly if they are localized around one eye or are accompanied by visual disturbances, suggesting migraines.
- Visual disturbances: Such as flashes of light, floating spots, or temporary vision loss, often associated with migraine or ocular migraines.
- Eye redness and tearing: Which could indicate a cluster headache, especially when these symptoms are localized to one eye.
- Sensitivity to light and sound: Commonly experienced during migraine episodes.
- Eye strain: Manifesting as discomfort when using digital devices, reading, or other activities that require focused vision.
- Dry or itchy eyes: Which may suggest dry eye syndrome or allergies, potentially leading to discomfort and headache.
- Pain with eye movement: A symptom of optic neuritis, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Swelling around the eyes: This could be a sign of an infection or inflammation such as sinusitis, which can cause headache.
- Changes in pupil size: Or appearance, which could indicate a serious condition requiring prompt medical evaluation.
These symptoms, particularly if they are new, worsening, or associated with other health concerns, warrant a consultation with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of eye pain and headache can be managed with home remedies and over-the-counter medications, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention:
- Sudden onset of severe pain: If you experience a sharp, intense eye pain or headache, especially if it comes on suddenly, it may indicate a serious condition such as acute glaucoma or a migraine with aura.
- Visual disturbances: Sudden vision changes, including loss of vision, seeing flashes of light, or floaters, warrant immediate evaluation to rule out retinal detachment, glaucoma, or migraine.
- Accompanied by other symptoms: If eye pain or headache is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, or neurological symptoms like weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking, seek medical care promptly.
- After an injury: If your symptoms follow an injury to the eye or head, immediate medical attention is necessary to assess for potential trauma to the eye or brain.
- Non-responsive to usual treatment: Pain that does not improve with rest, over-the-counter pain relievers, or other usual treatments should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
- Pain with eye movement: This could indicate optic neuritis, an inflammation of the optic nerve, which requires prompt medical intervention.
- Redness and discharge from the eye: These symptoms can indicate an infection or inflammation that may need treatment with prescription medication.
- Changes in pupil size or reactivity: Any noticeable changes in the appearance or function of your pupils should be examined by a medical professional immediately.
Early detection and treatment of the underlying cause of eye pain and headache can prevent more serious complications. If in doubt, it is always better to consult with a healthcare provider.
Diagnosis Techniques and Tests
To accurately diagnose the cause of eye pain and headache, healthcare providers may use a variety of techniques and tests. Identifying the right condition is essential for effective treatment.
- Medical History: A detailed patient history helps to identify potential causes based on symptoms, lifestyle, and previous health issues.
- Eye Examination: Comprehensive examination including visual acuity, pupil response, eye pressure, and examination of the eye"s interior structures.
- Visual Field Test: To check for any vision loss or blind spots which could indicate glaucoma or neurological conditions.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: A microscope used to examine the eye"s front part, helping to identify conditions like dry eyes, corneal abrasions, or infections.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans to detect abnormalities in the brain, sinuses, or eye structure that may cause headache and eye pain.
- Blood Tests: To look for underlying systemic conditions, such as infections or autoimmune diseases that might contribute to symptoms.
- Glaucoma Testing: Measuring the pressure inside the eye to check for glaucoma, a common cause of eye pain.
- Corneal Topography: Mapping the curve of the cornea can help diagnose conditions that affect the cornea"s shape, leading to pain and vision issues.
- Fluorescein Angiography: For examining blood vessels in the retina and choroid which can highlight issues related to diabetes, retinal detachment, or macular degeneration.
- Lumbar Puncture: In cases where infection or inflammation of the brain is suspected, to check the cerebrospinal fluid for signs of meningitis or encephalitis.
These diagnostic steps are crucial for determining the specific cause of eye pain and headache, leading to targeted and effective treatment plans.
Treatment Options for Relief
Effective treatment for eye pain and headache varies, depending on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can alleviate mild headaches. Prescription medications, including triptans for migraines and topical or oral antibiotics for eye infections, may also be prescribed.
- Eye Drops: For conditions like dry eye or glaucoma, lubricating eye drops or pressure-lowering drops can provide relief.
- Rest and Hydration: Often, rest in a dark, quiet room and staying well-hydrated can help relieve headache symptoms.
- Warm or Cold Compresses: Applying a warm or cold compress to the eyes or forehead can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: For tension headaches, physical therapy can help relieve muscle tightness and correct posture issues.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and biofeedback can help manage stress, a common trigger for headaches and eye strain.
- Vision Correction: For headaches caused by eye strain, an updated prescription for glasses or contact lenses may be necessary.
- Minimize Screen Time: Reducing the time spent on digital devices can alleviate symptoms of digital eye strain.
- Surgical Options: In certain cases, such as for severe glaucoma or cataracts, surgery may be required to address the underlying cause of eye pain and headache.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep can improve overall health and reduce the frequency of headaches.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the appropriate treatment based on the specific diagnosis. Tailored approaches offer the best chance for relief and recovery.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-PaigeMcLaughlin-WhatisaClusterHeadache-Standard-87c962b6a28d4b1ab0359ed3ae5b696f.jpg)
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Alleviating eye pain and headache can often begin at home with simple remedies and lifestyle adjustments. Here are practical tips to help manage and prevent discomfort:
- Proper Hydration: Drinking enough water can help prevent headaches, especially those caused by dehydration.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring sufficient sleep helps reduce the risk of headaches and eye strain.
- Eye Rest: Follow the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds to reduce eye strain from screen use.
- Screen Brightness: Adjust the brightness of your digital screens to match the lighting of your environment to minimize eye strain.
- Corrective Eyewear: Wear glasses or contact lenses with the correct prescription to prevent strain.
- Ergonomic Workspace: Ensure your work environment is ergonomically set up to prevent neck and eye strain.
- Cold Compress: Apply a cold pack to your forehead or eyes to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to manage stress-induced headaches.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive consumption can contribute to dehydration and trigger headaches.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce the frequency and severity of headaches by improving overall health.
While these remedies can offer relief, it"s important to pay attention to your body"s signals. Persistent or severe symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out more serious conditions.
Eye Pain and Headache: Potential Causes - Dr. Sunita Rana Agarwal
\"Tired of persistent headaches ruining your day? Look no further! This video is your ultimate guide to understanding and treating headaches. Learn practical techniques and natural remedies that will alleviate your discomfort and empower you to take control of your head health!\"
Eye Pain and Headache: Potential Causes - Dr. Sunita Rana Agarwal
\"Tired of persistent headaches ruining your day? Look no further! This video is your ultimate guide to understanding and treating headaches. Learn practical techniques and natural remedies that will alleviate your discomfort and empower you to take control of your head health!\"
Preventing Eye Strain and Headaches
Preventing eye strain and headaches is key to maintaining eye health, especially in our digital-heavy world. Here are effective strategies to minimize discomfort:
- Follow the 20-20-20 Rule: Every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break to look at something 20 feet away. This practice helps reduce eye strain from prolonged screen use.
- Adjust Screen Settings: Lower the brightness of your screens to match the lighting in your room. Increase text size for easier reading to avoid straining your eyes.
- Use Proper Lighting: Ensure your work area is well-lit to reduce glare and harsh reflections that can cause eye strain.
- Maintain Screen Distance: Keep digital screens at an arm"s length away from your eyes and slightly below eye level to reduce strain.
- Blink Regularly: Blinking moistens your eyes to prevent dryness and irritation. People tend to blink less while using computers, which can lead to eye strain.
- Optimize Workspace Ergonomics: Adjust your chair and desk so that your eyes are level with the top of your monitor. This reduces strain on your eyes and neck.
- Limit Screen Time: Take regular breaks from screens to give your eyes a rest. Consider limiting leisure screen time as well.
- Use Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops can help alleviate dryness and discomfort associated with eye strain.
- Practice Eye Exercises: Simple exercises, like focusing on distant objects periodically, can strengthen eye muscles and reduce strain.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is important for maintaining eye moisture and overall health.
Implementing these tips can significantly reduce your risk of developing eye strain and headaches, leading to a more comfortable and productive work environment.

Understanding Migraines with Ocular Symptoms
Migraines with ocular symptoms, often referred to as ocular migraines, can include visual disturbances that significantly impact one"s quality of life. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for managing and treating this condition effectively.
- Visual Aura: Many experiencing ocular migraines report visual phenomena such as flashing lights, zigzag patterns, or blind spots before or during the headache.
- Temporary Vision Loss: In some cases, ocular migraines can lead to partial or complete temporary vision loss in one eye, typically lasting less than an hour.
- Other Visual Disturbances: Symptoms may also include seeing shimmering spots or stars and blurred vision, which are usually temporary.
- Headache: While ocular symptoms can occur without a headache, many people experience moderate to severe headaches, often on one side of the head, during an episode.
- Sensitivity to Light and Sound: Like typical migraines, those with ocular symptoms may also be sensitive to light and sound, seeking relief in dark, quiet environments.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These are common accompanying symptoms, further complicating the discomfort during an attack.
Diagnosis involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional, often including a review of the patient"s medical history and possibly imaging tests to rule out other causes of the symptoms. Treatment may include medication to manage pain and prevent future migraines, as well as lifestyle adjustments to avoid known triggers. Recognizing and understanding the unique aspects of migraines with ocular symptoms are vital steps toward effective management and relief.
The Impact of Digital Screen Use
The widespread use of digital screens in our daily lives has led to increased reports of eye pain and headaches, a condition often referred to as digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome. Understanding the impact of screen use is crucial for mitigating these effects.
- Increased Risk of Eye Strain: Long hours in front of screens can lead to symptoms such as dry eyes, irritation, blurred vision, and eye fatigue.
- Headaches and Migraines: The strain on the eyes from prolonged screen use can also contribute to headaches and trigger migraines, particularly in individuals susceptible to them.
- Blue Light Exposure: Screens emit blue light, which can disrupt sleep patterns and further contribute to eye strain and discomfort.
- Negative Effects on Vision: Continuous focus on screens at close distance can lead to focusing issues, temporary blurred vision, and adjustments in blink rate, leading to dry eyes.
- Postural Problems: Poor posture during screen use can exacerbate neck and shoulder pain, contributing to tension headaches.
- Preventive Measures: Implementing strategies such as taking regular breaks, using blue light filters, adjusting screen settings, and maintaining proper posture can help minimize the impact of screen use on the eyes and head.
- Professional Consultation: Regular eye exams and consulting with eye care professionals can provide personalized advice and solutions to combat the effects of prolonged digital screen use.
Adopting healthy screen habits and making adjustments to our digital device use are essential steps toward preventing eye pain and headaches associated with digital eye strain.
READ MORE:
Eye Conditions Linked to Headaches
Various eye conditions can lead to headaches, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain. Recognizing these conditions is key to seeking appropriate treatment and relief.
- Glaucoma: This group of eye conditions increases pressure inside the eye, potentially causing severe headaches, eye pain, blurred vision, and seeing halos around lights.
- Refractive Errors: Nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism can strain the eyes, leading to headaches from the effort of trying to focus.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: Dry eyes can cause discomfort, including headaches, due to inadequate lubrication and moisture on the eye"s surface.
- Binocular Vision Dysfunction: When the eyes struggle to work together, it can result in eyestrain and headaches.
- Eye Strain: Prolonged use of digital devices or reading without proper lighting can cause eye strain and associated headaches.
- Cataracts: The clouding of the eye"s lens can lead to vision impairment and strain, resulting in headaches.
- Optic Neuritis: Inflammation of the optic nerve can cause painful eye movements and is often accompanied by headaches.
- Uveitis: Inflammation inside the eye can lead to pain, blurred vision, light sensitivity, and headaches.
Addressing these eye conditions with appropriate treatment can significantly reduce or eliminate associated headaches, improving overall quality of life. Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and management of these conditions.
Understanding the causes and effective management of eye pain and headache can greatly enhance your quality of life. Remember, regular eye care and timely medical intervention are key to maintaining your vision and well-being.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headaches-as-a-symptom-of-multiple-sclerosis-2440798-01-ac13321fbd2d4dca99f899a63b8ea265.png)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-dehydration-symptoms-7480908-Horiz-e2500f0828b746ee9d2e2b5257af60cb.jpg)